Fixation of bifunhctional reactive dyes
by : ---
Fixation of bifunhctional reactive dyes:-
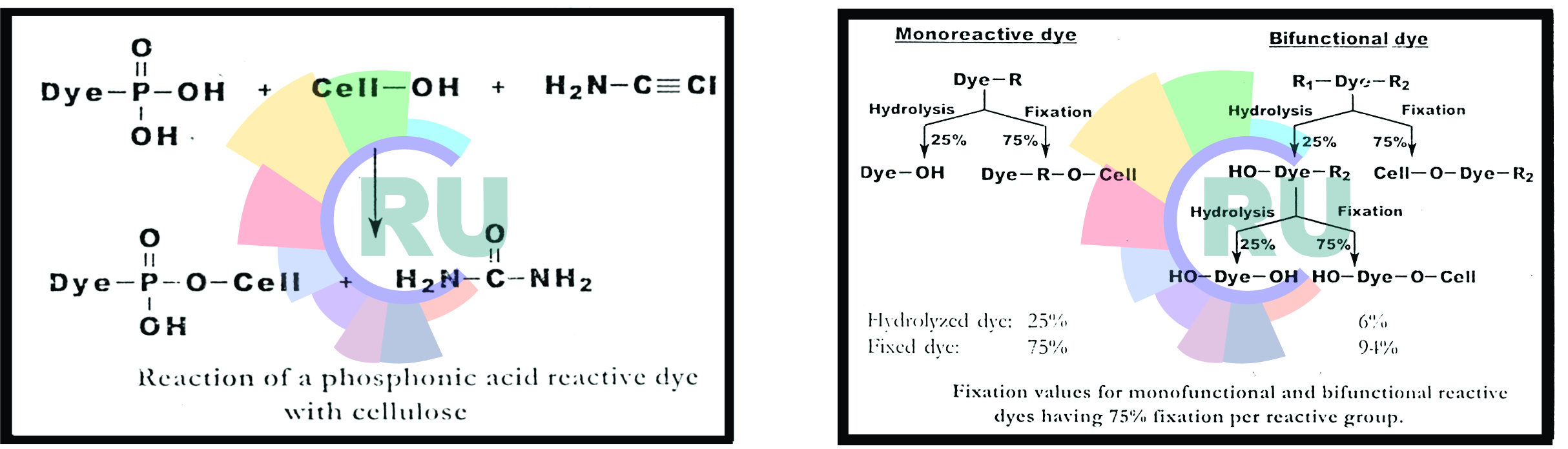
One of the important characteristics of bifunctional reactive dyes is their ability to provide a high percent fixation. figure demonstrates why a typical bifunctional reactive dye gives a higher percent fixation than conventionla monofunctional reactive ydes. In the pad batch method, monofunctional reactive dyes. In the pad batch method, monofunctionla reactive dye achieve an average of 75% fixation. The remaining 25% of the dye is hydrolyzed and finds its way into the wastewater. In the case of a bifunctional reactive dye, one reactive group (R1) could react with the fiber to the same degree (75%) as a monofunctional reactive dye, with 25% unreacted. However, the partially hydrolyzed but still reactive dye can react further, via the second reactive group (R2). Therefore, about 4% of the amount of dye applied bonds to the fiber and only 6% is wasted. The same principle can apply in exhaust dyeing is lower than that of pad dyeing because the dye does not entirely exhaust onto the fiber. When a bifunctional reactive dye exhausts to 85%, a fixation level of 80% can be reached. At the same exhaustion levelo, the fixation of a monofunctional dye averages only 60-65% and much more dye has to be removeed during the wash off process. The reaction of a heterobifunctional reactive dye with cellulose under alkaline conditions [25] proceeds by the pathways shown in Figure
