
What is a Dyes: Explained completely

What is a Natural Dyes: Explained Completely
,

Classification of Dyestuff

FEATURES & APPLICATON OF DYES
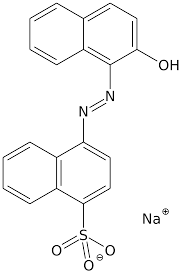
Definition and Chemical Structure of Acid Dyes
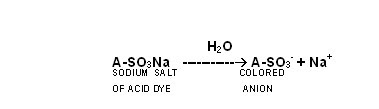
Properties and Mechanism of Acid Dyes

Classification of Acid Dyes According to Dyeing Ch
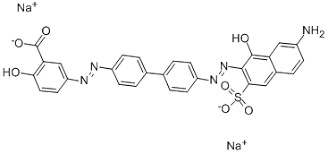
Chemical Nature of Direct Dyes

Application Of Direct Dyes

Dying Method: Explained in brief

Properties Of Direct Dyes

Modified Basic Dyes: Explained in brief

Definition of Reactive Dyes
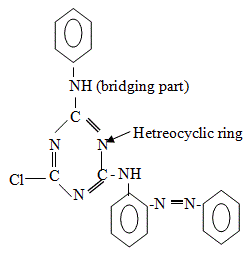
Structure of Reactive Dyes

Classification of Reactive Dyes

Properties of Reactive Dyes

Advantages Of Reactive Dyes

Disadvantages Of Reactive Dyes
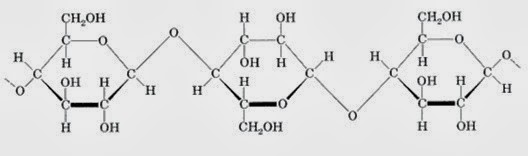
Explanation of Cellulosic Fibers in brief
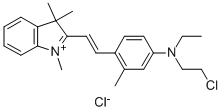
Definition of Cationic Dyes

Application Of Cationic Dyes

Definition and History of Disperse Dye

Properties Of Disperse Dyes

Meaning Of Polyester Microfibers: Explained in bri

Application Of Microfiber
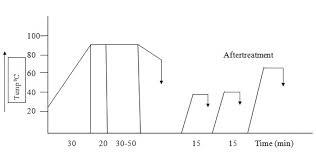
Dyeing Mechanism Of Direct Dyes

Meaning Textile Auxiliaries

Different Types of Auxiliaries and Ingredients Use

Classification of Dyeing Auxiliaries: Explained Co

Vat Dyes: Explained in brief

Properties Of vat Dyes: Explained Completely
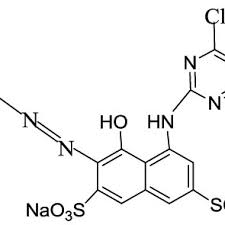
Stages or Chemistry or Mechanism of dyeing with va

General Nature Of Vat Dyes: Explained Completely

Advantages Of Pigment Dyeing: Explained Completely

Limitation Of Printing Dyeing

Meaning and Recipe of Pigment Printing; Explained

Advantages of Pigment Printing

Limitation Of Pigment Printing: Explained Complete
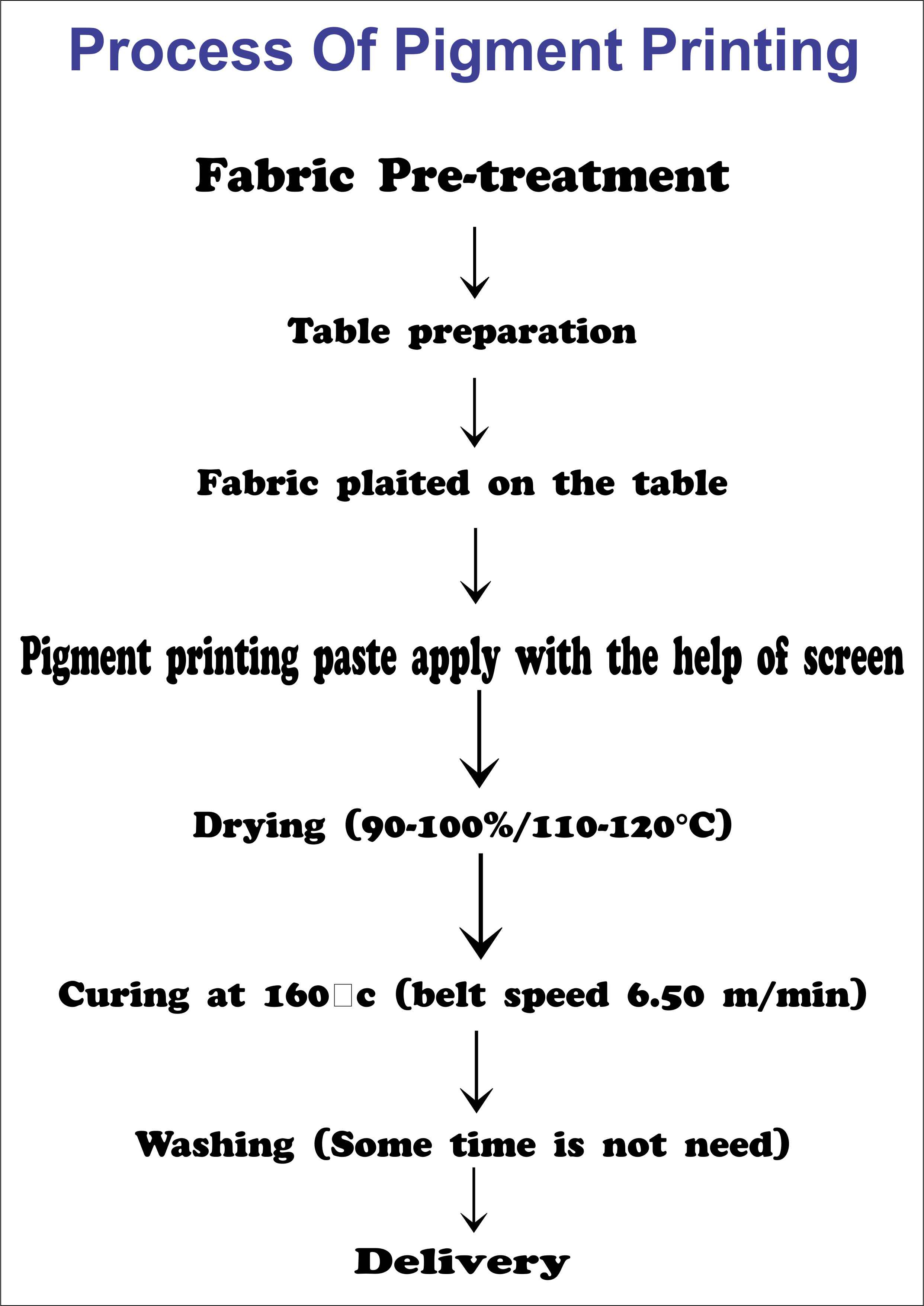
Basic Process Of pigment Printing

Meaning Of Acetate Fibers

Properties Of Acetate Fibers

Physical Properties Of Acetate Fibers

Chemical Properties Of Acetate Fibers

Meaning Of Polyester Fibers

Flow Chart Of Synthetic Fiber Production

Characteristics Of Polyester Fiber: Explained Comp

Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyester: Explain

Definition Of Leather Dyes:

Types/Classification Of Leather Dyes:

Leather Of Coating: Explained in brief

Process Of Leather Printing

Leather Printing's Steps: Explained In Brief

Definition Of Construction Chemicals

Types Of Construction Chemicals

Areas in which Construction Chemicals are used: Ex

Common Properties Of Mineral admixtures

Fly Ash : Explained In Short

Micro Silica: Explained In Short

Advantages Of Micro Silica

Disadvantages Of Micro Silica

Definition and Types Of Chemical Admixtures

Classification Of Concrete Admixtures

Inorganic Acid: Explained Completely

Bases Of Chemistry: Explained in brief
Organic Bases: Explained Completely

Organic Acid: Explained Completely

SALTS: Explained in brief

SODIUM CHLORIDE: Explained Completely

SODIUM SULPHATE: Explained Completely
Oxidising Agents: Explained Completely

Hydrogen peroxide: Explained Completely

Sodium Hypochlorite: Explained Completely

Sodium perborate: Explained Completely

Reducing Agents: Explained Completely
Type Of Reducing Agents: Explained Completely
Miscellaneous Chemical: Explained in brief

Miscellaneous Chemical: Explained Completely

Explanation of Fluorescent whitening agents
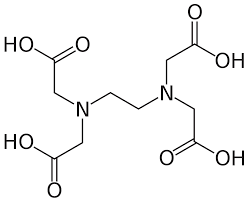
Explanation Of Ethylenediamine tetraacetate:

Definition Of Sulfur Dyes
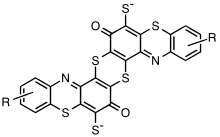
Chemical Structure Of Sulfur Dyes

Types of Textiles: Explained in brief
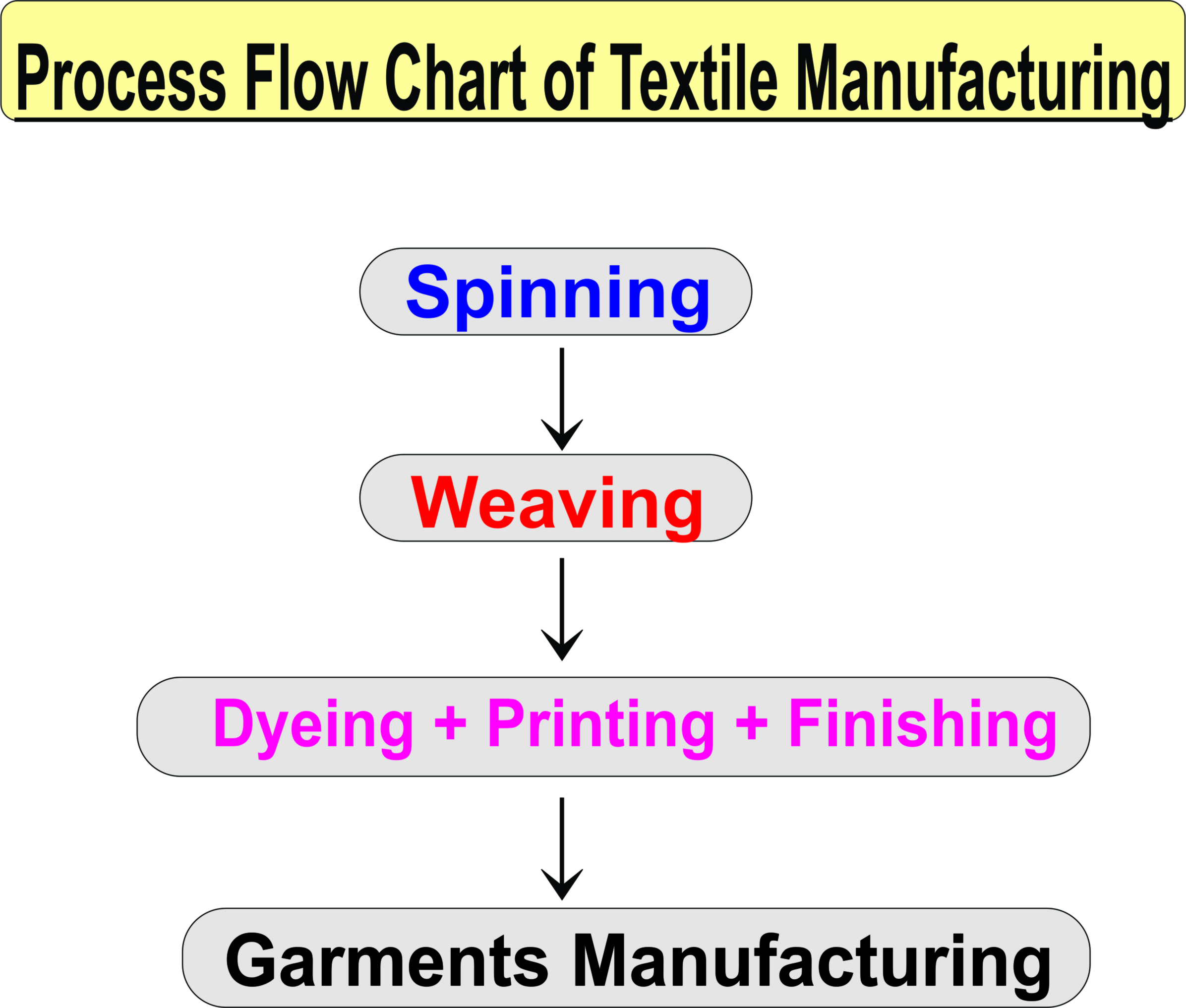
Flow Chart of Textile Manufacturing

Sequestrant function of dyeing auxiliaries

Lubricating: Explained in brief

Dispersing Agent: Explained in brief

Fundamental Mechanisms to contribute a dyeing

Sequestering, Dispersing and Levelling Agent for R

Antifoam: Explained in brief

Flow Chart of Textile Finishing

Anthraquinonoid vat dyes: Explained in brief

Indigoid vat dyes: Explained in brief
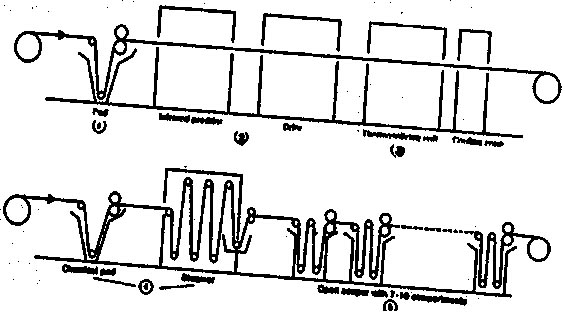
Dyeing of Polyester Fabric in Thermasol Dyeing Met

Component needs for Tie dye

IMPORTANT SYNTHESIS OF DYES

Special Chemical Used in Garments Dyeing

Chemical Used in Garment Dyeing

Wetting Agent: Explained in brief

Scouring and Bleaching agent: Explained in brief.

For Saving Al (Used in Garments Dyeing)

Blended fabric: Explained in brief

Formation of Crease: Explained in brief

SULFAMIC ACID: Explained in brief

Properties of Sulfamic Acid

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (1.SPINNING)

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (2. WINDING)

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (3. Warping)

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (4.SIZING)

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (5.GREY CALEND

The Role of Auxiliaries in Textiles (6.WET PROCESS

WET PROCESSING: EXPLAINED COMPLETELY (PART 1)

WET PROCESSING: EXPLAINED COMPLETELY (PART 2)
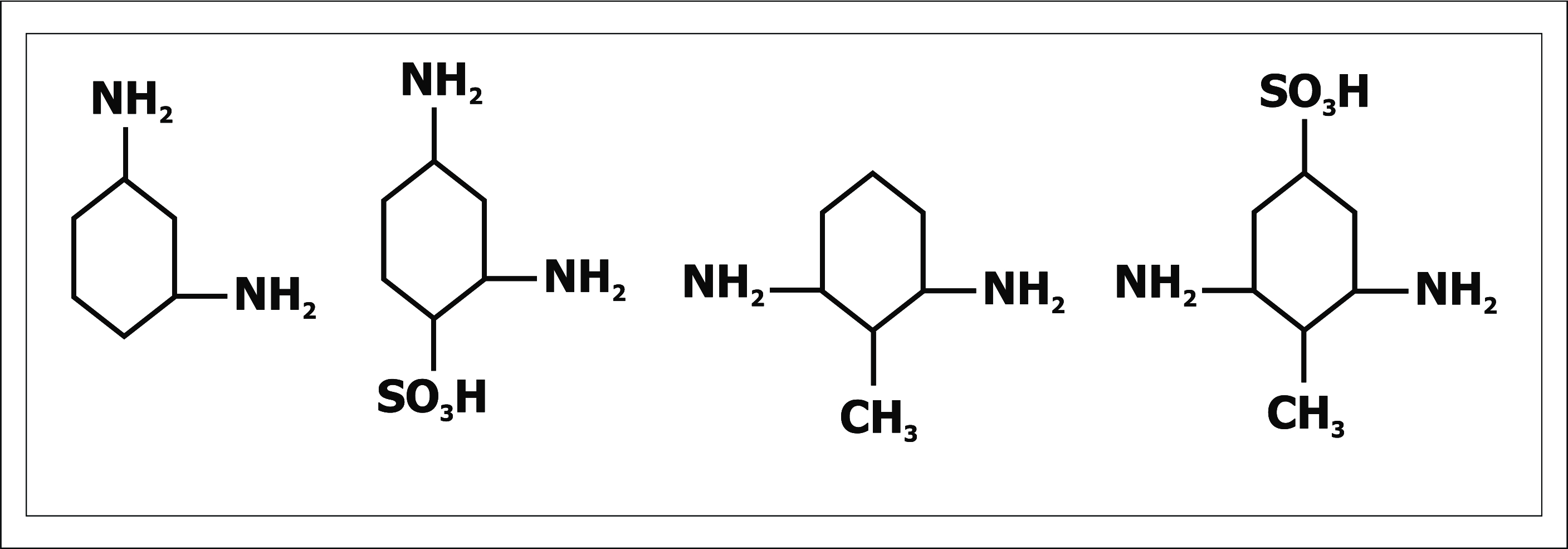
MPD & disubstituted diamines: Explained in brief
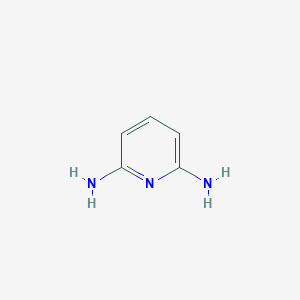
Diamino Pyridines:- Explanation in brief
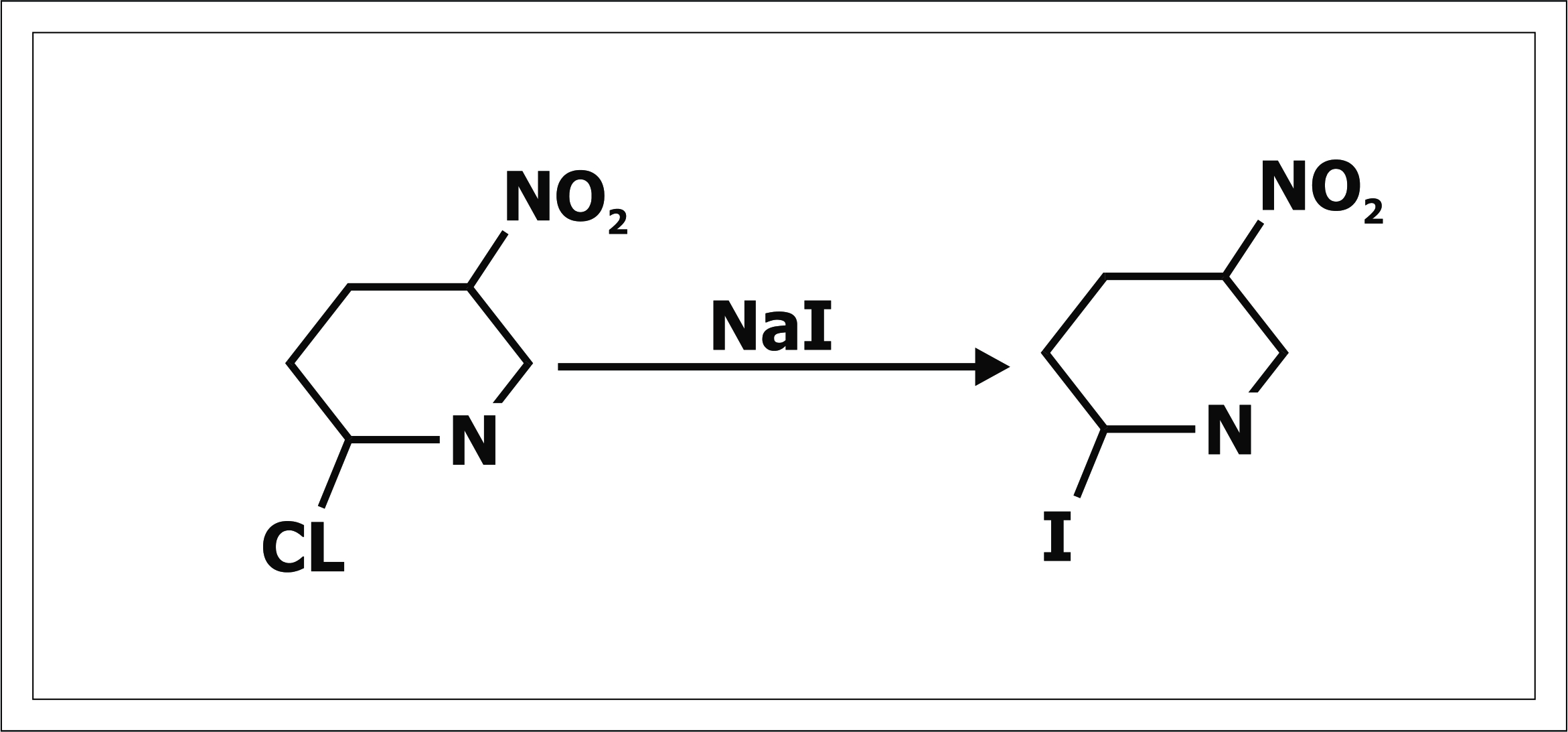
Halogen exchange reaction
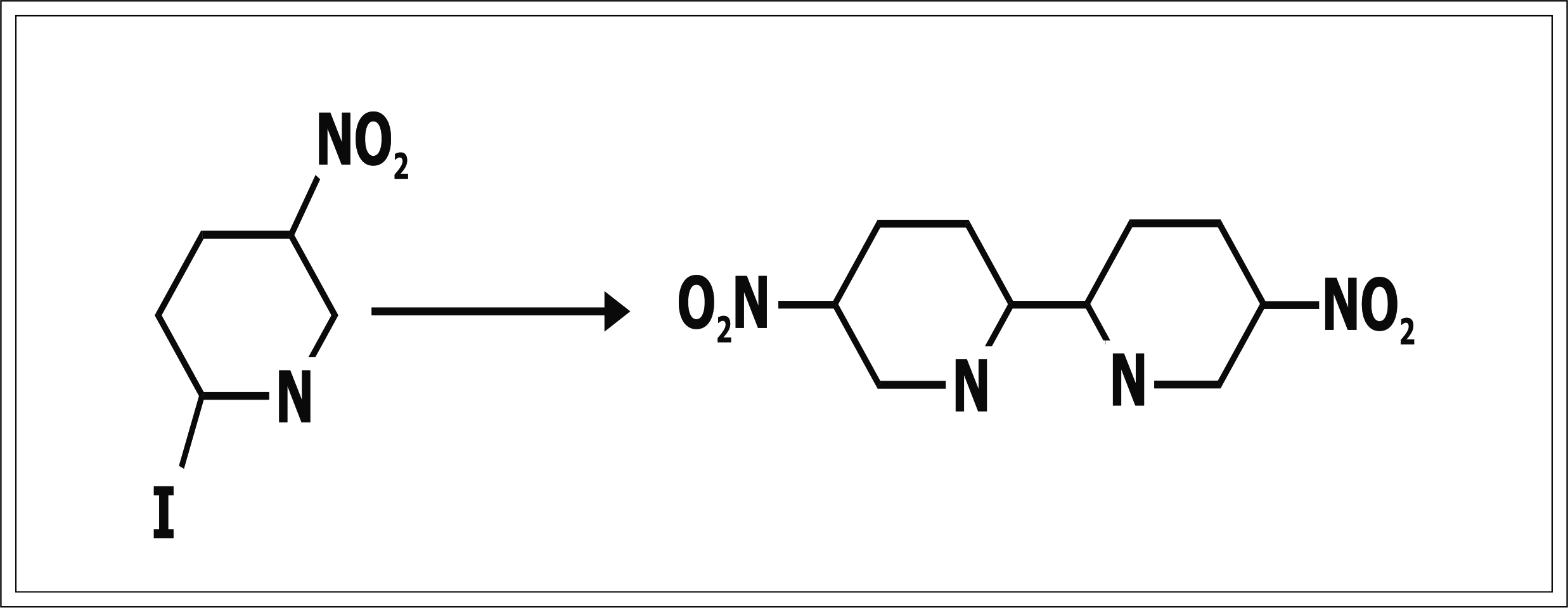
Ullmann Condensation: Explained in brief
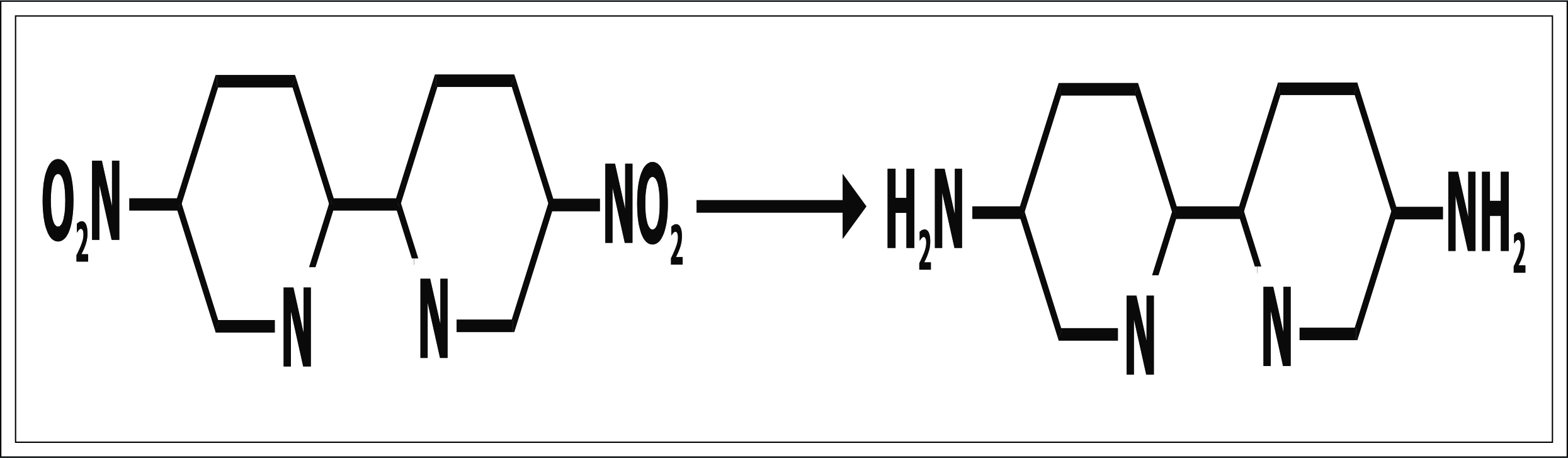
Reduction:- Explained in brief
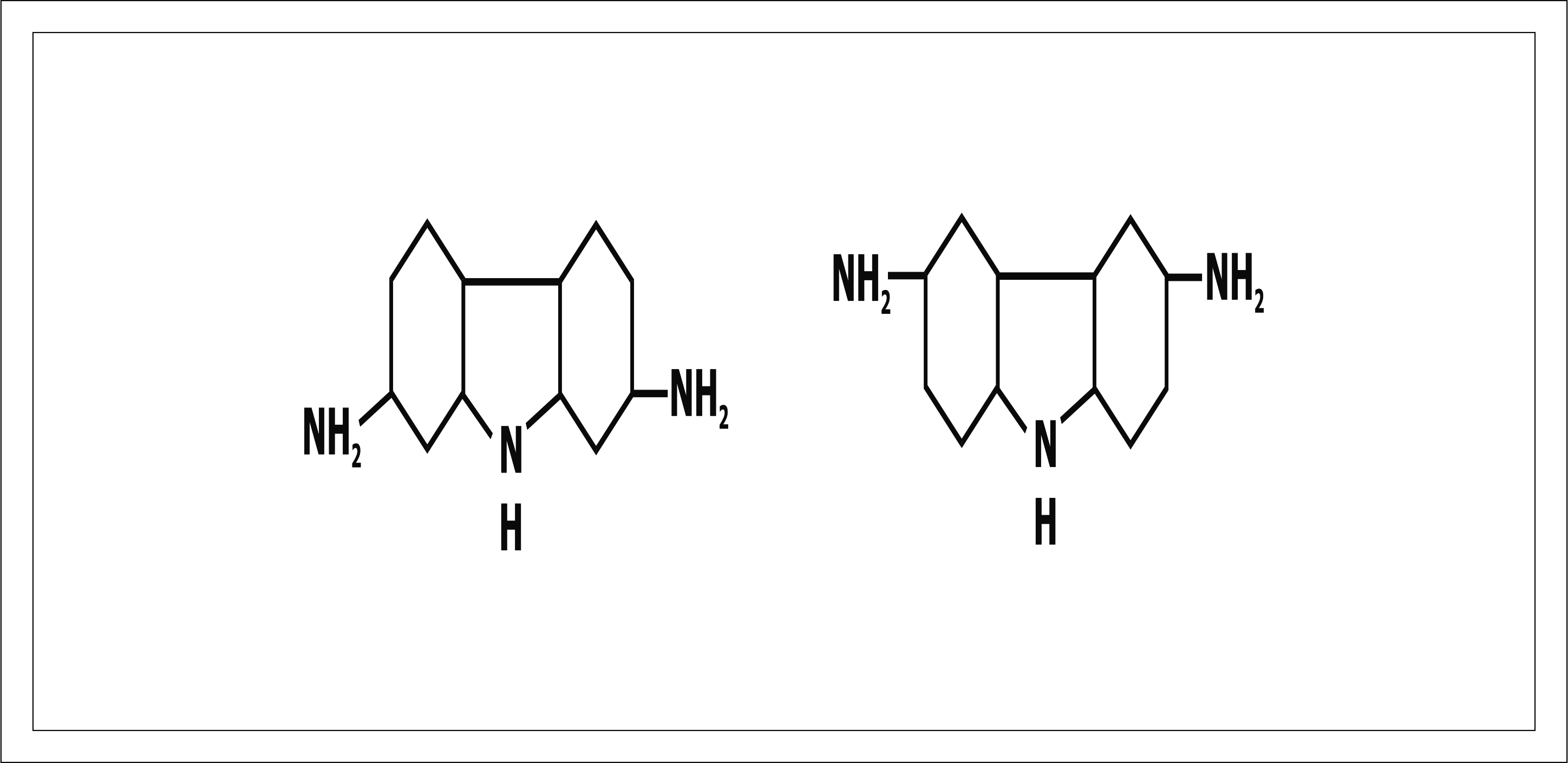
Diamino carbozoles: Explained in brief
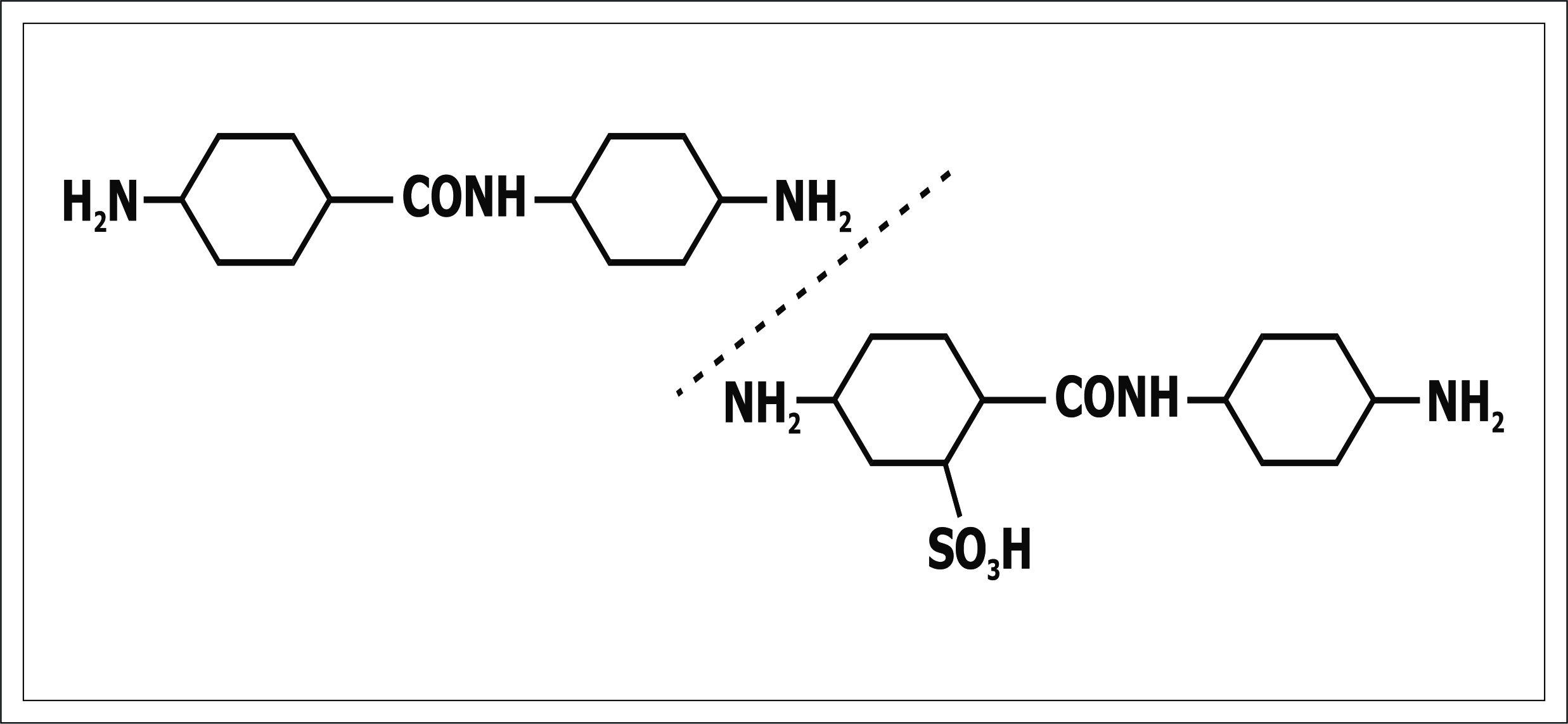
![Diamino Diphenyl Ureas. [-NHCONH-] : Explained in](https://rangudhyog.com/assets_front/blog_images/151.jpg)
Diamino Diphenyl Ureas. [-NHCONH-] : Explained in
Diamino Anilides: Explained in brief
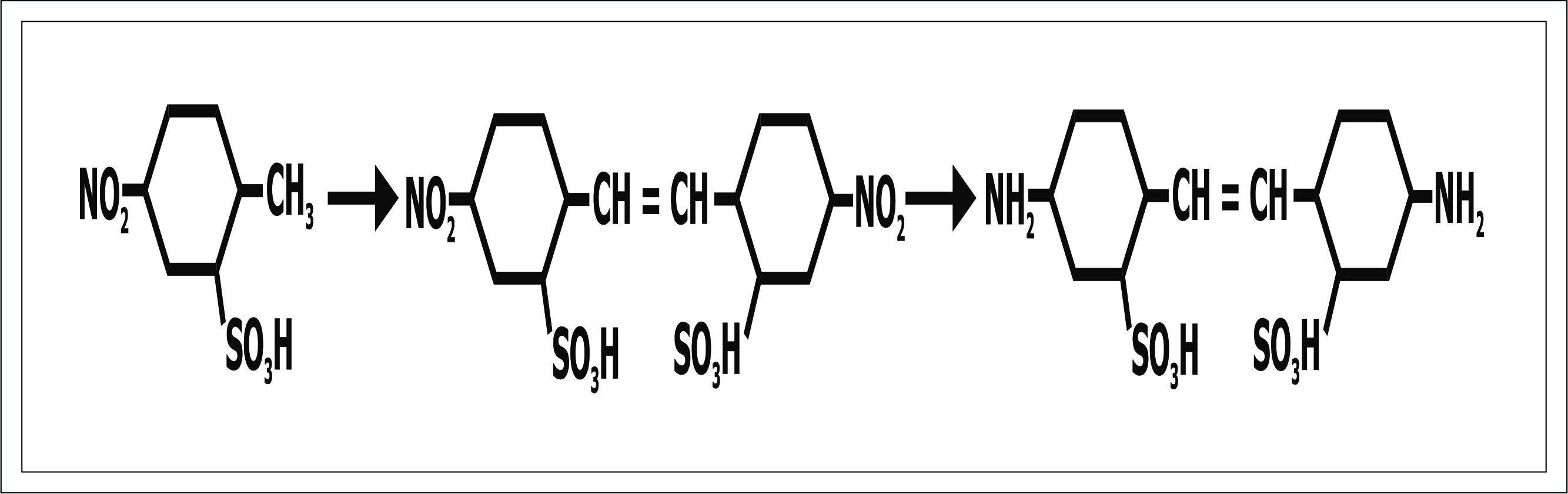
Diamino Stilbenes:- As a Non Benzidine
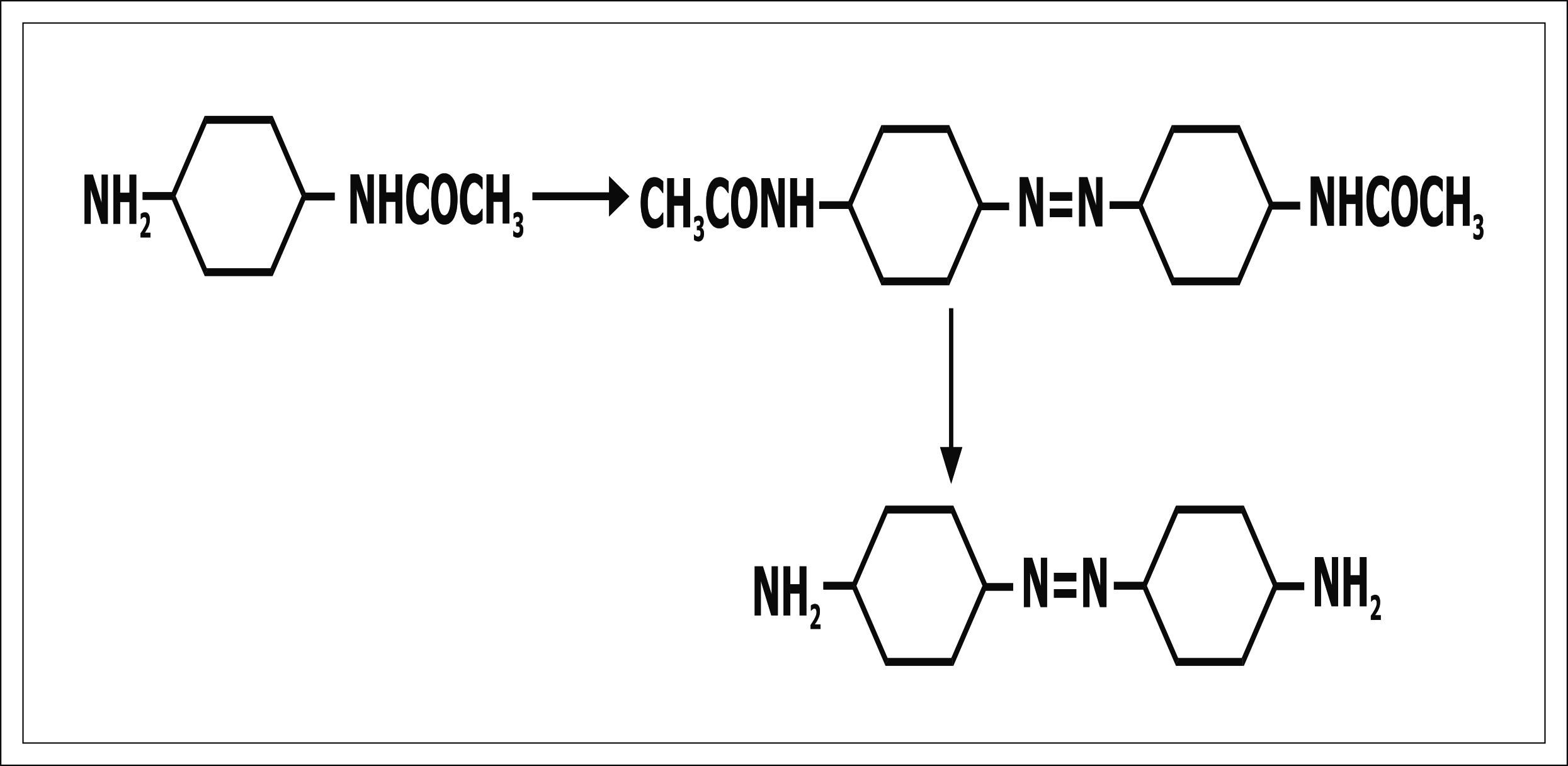
4,4' - diamino crobenzene:- Explained in brief
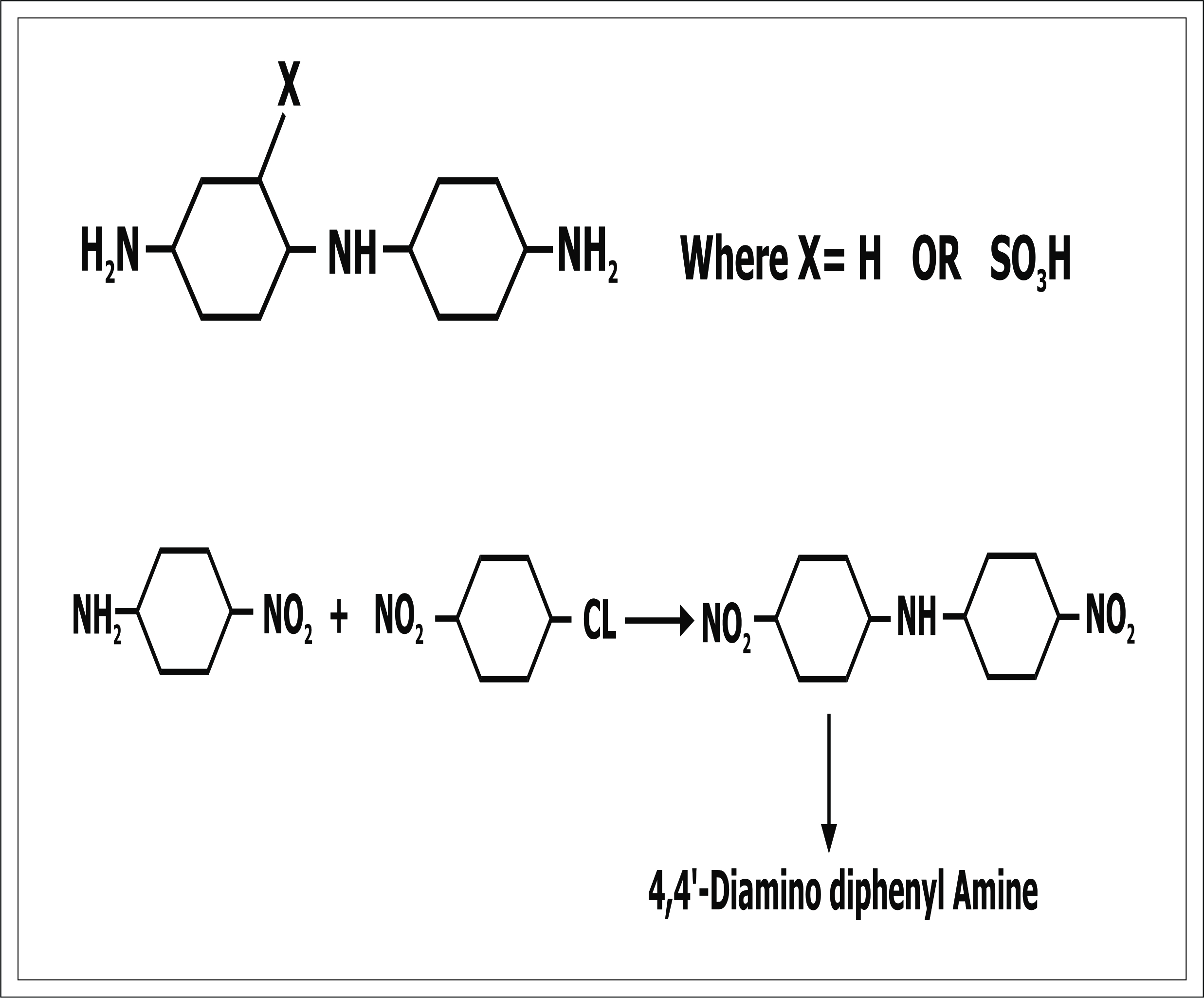
4,4'- diamino diphenyl amines: Explained in brief
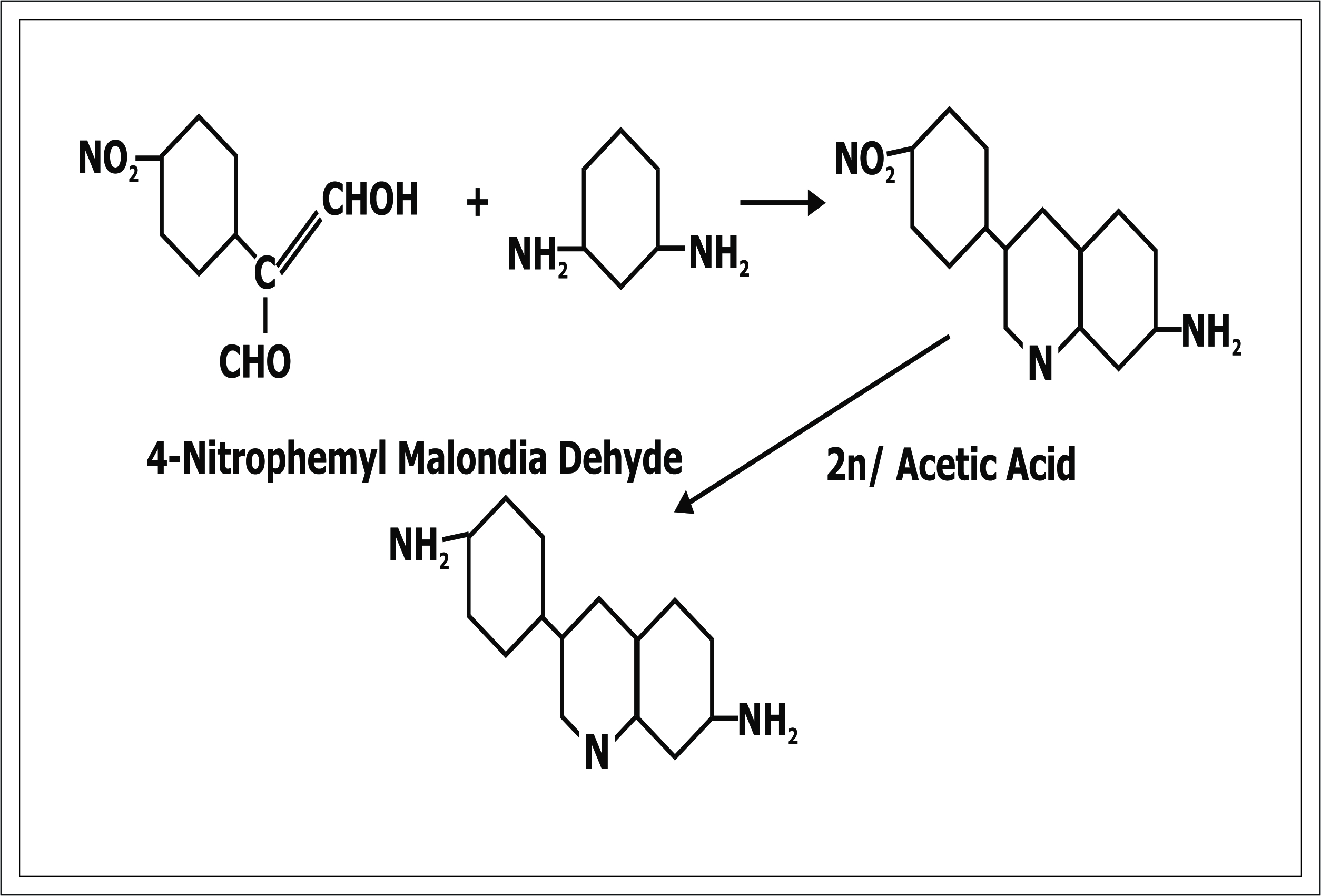
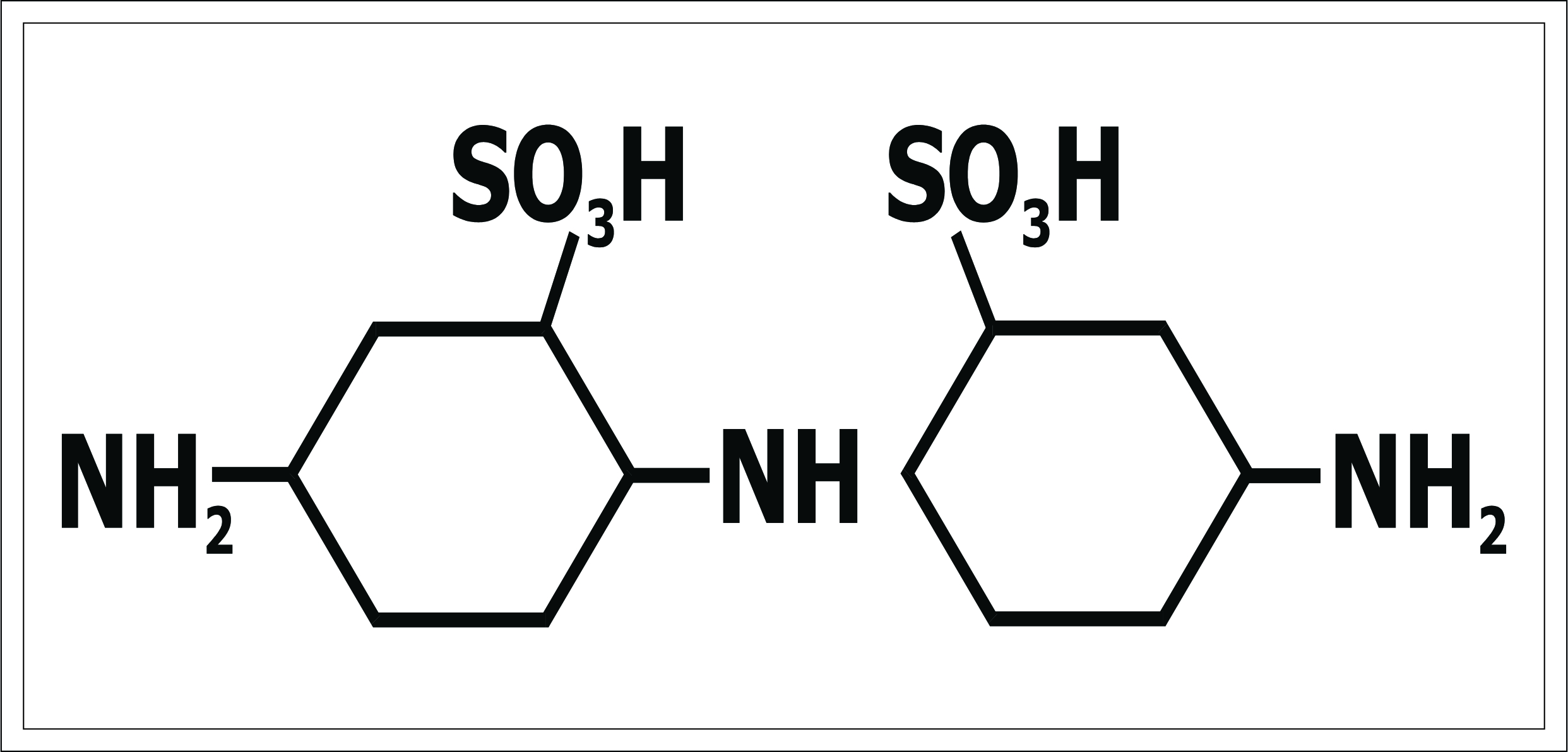
Some other dicmines which can be used as Benzidine
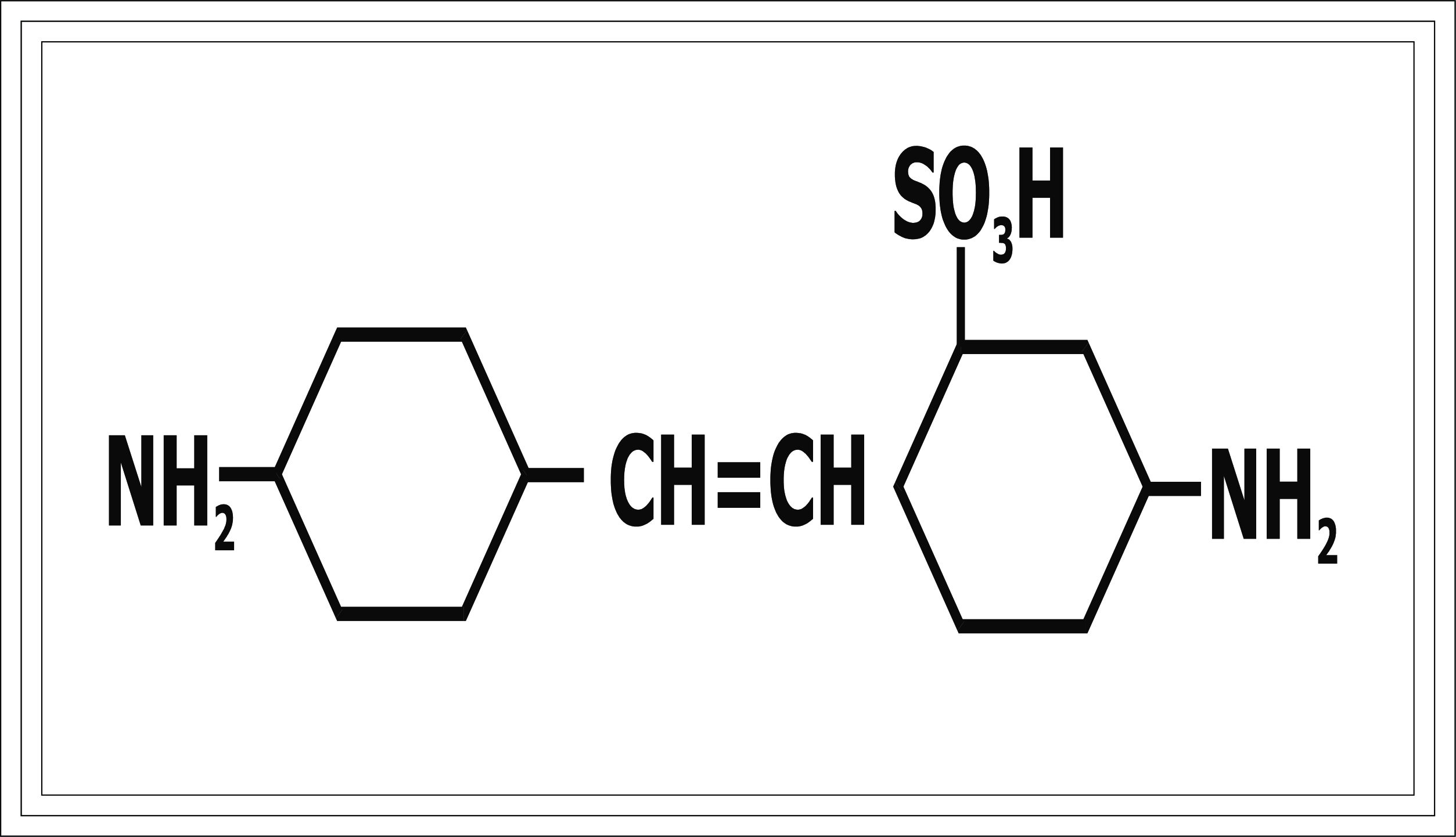
2) 4,-4' diamino stilbene - 2,-2' - disulfonic aci
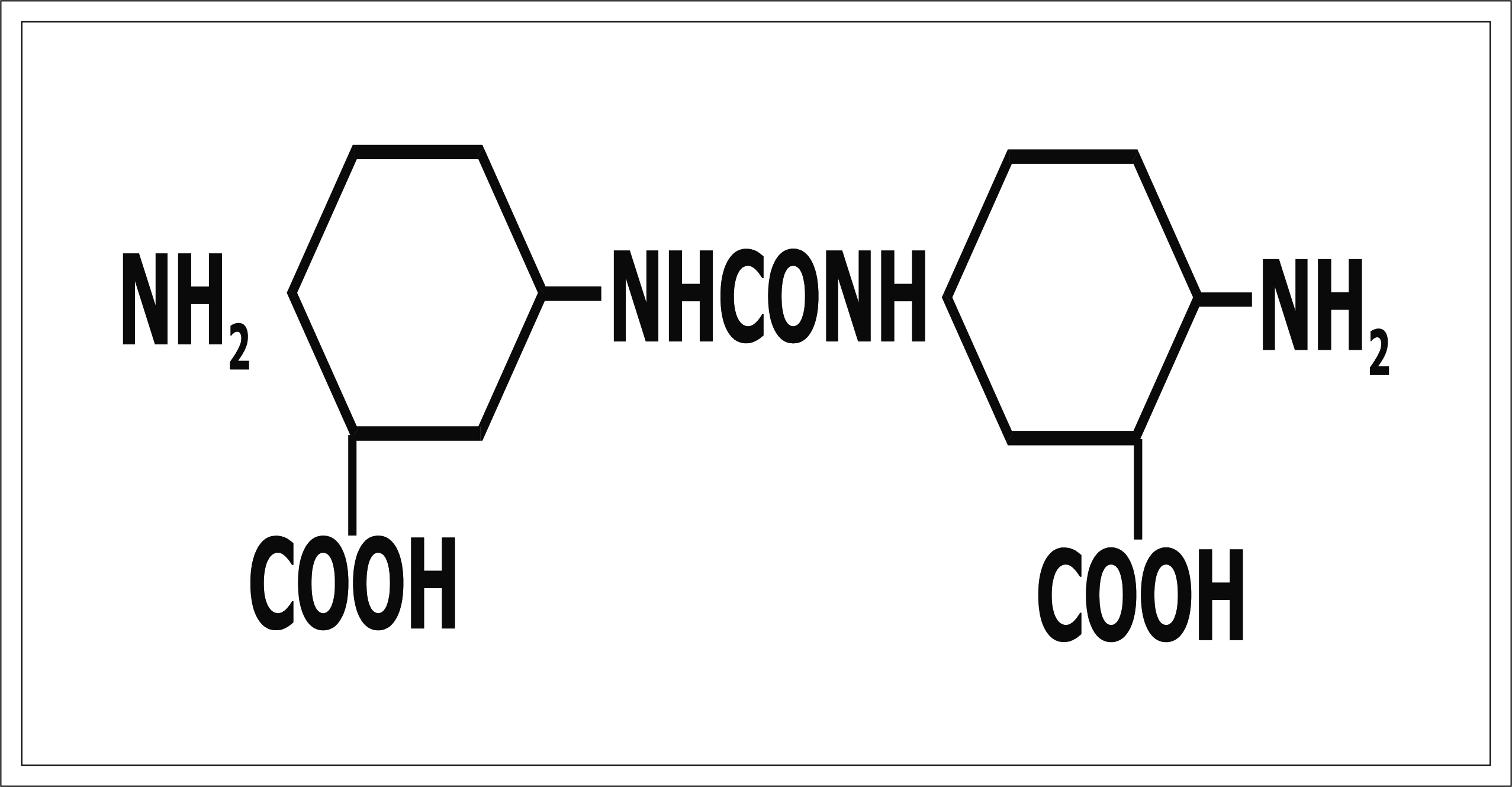
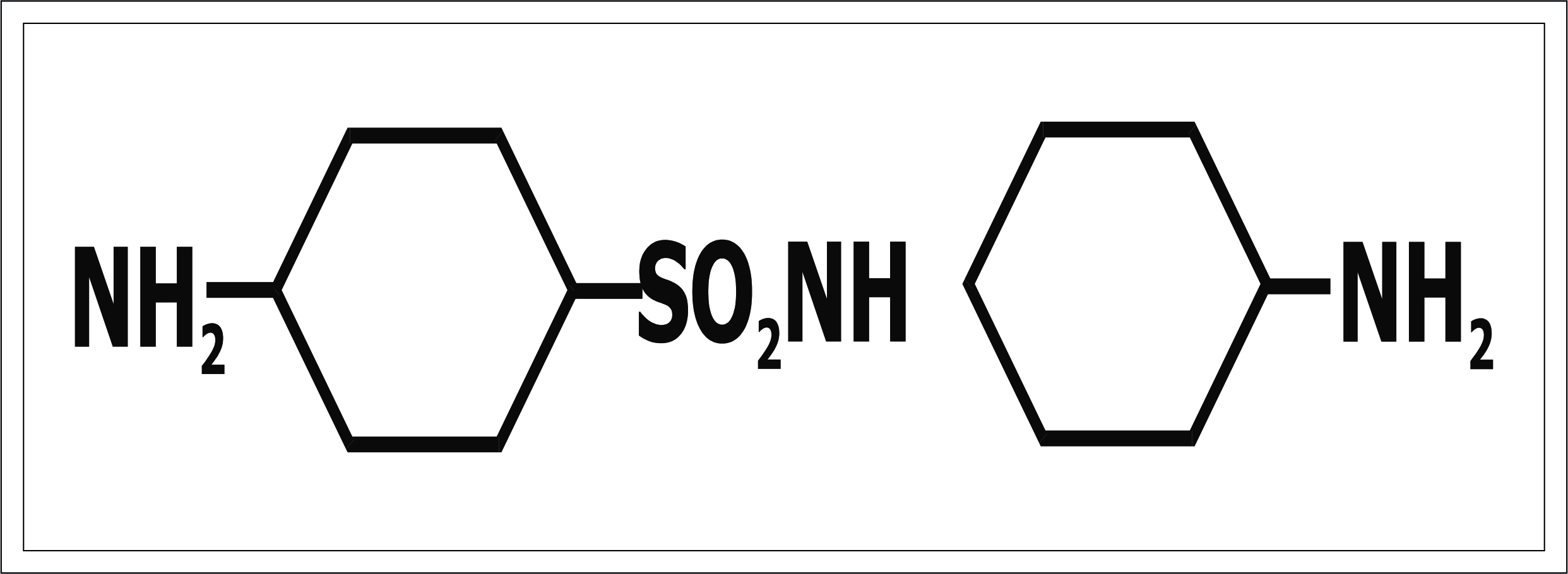
3). 4,4'- diamino diphenyl urea - 3,3'- diceroxyli
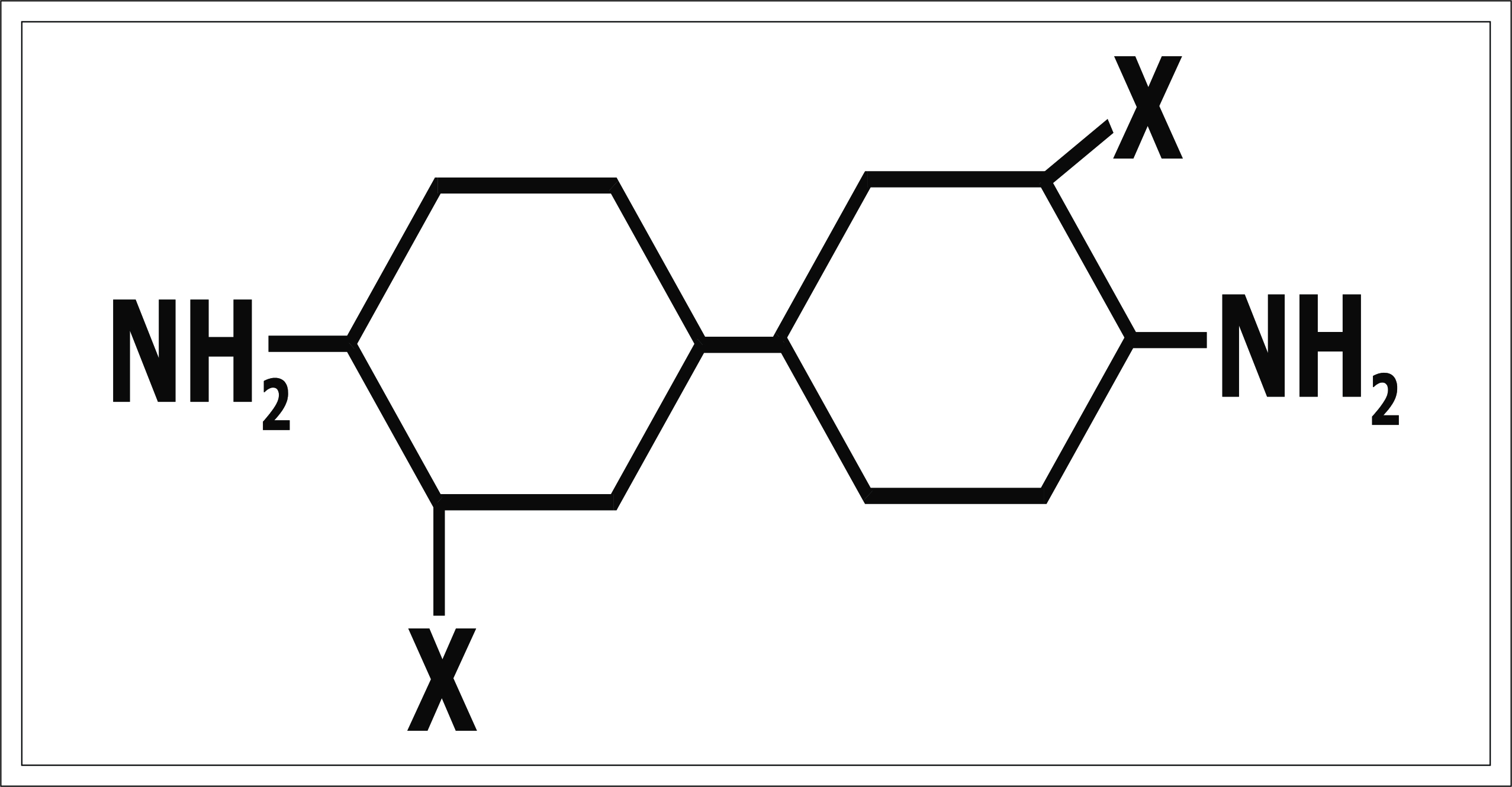
4) 3,3'- disubstituted - 4,4' diamino diphenyl de
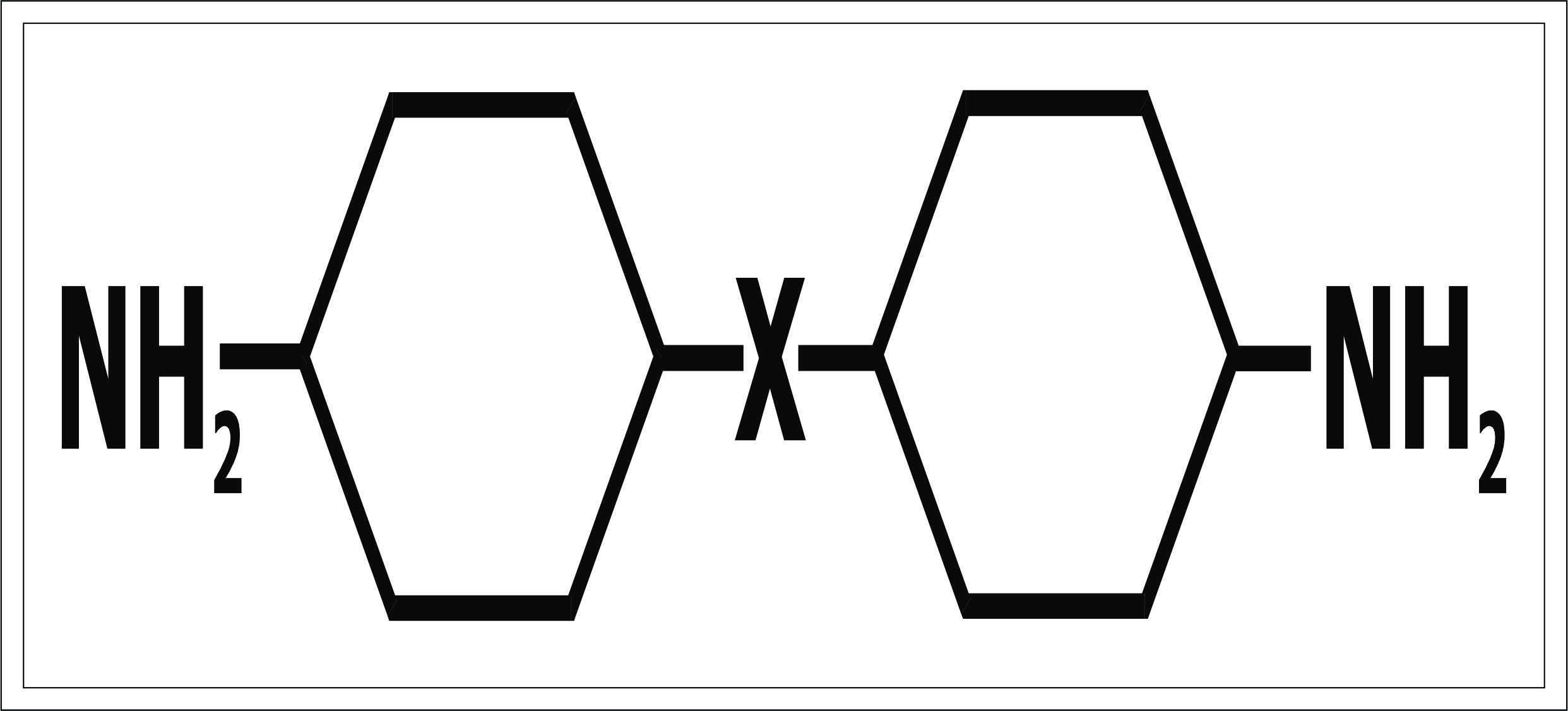
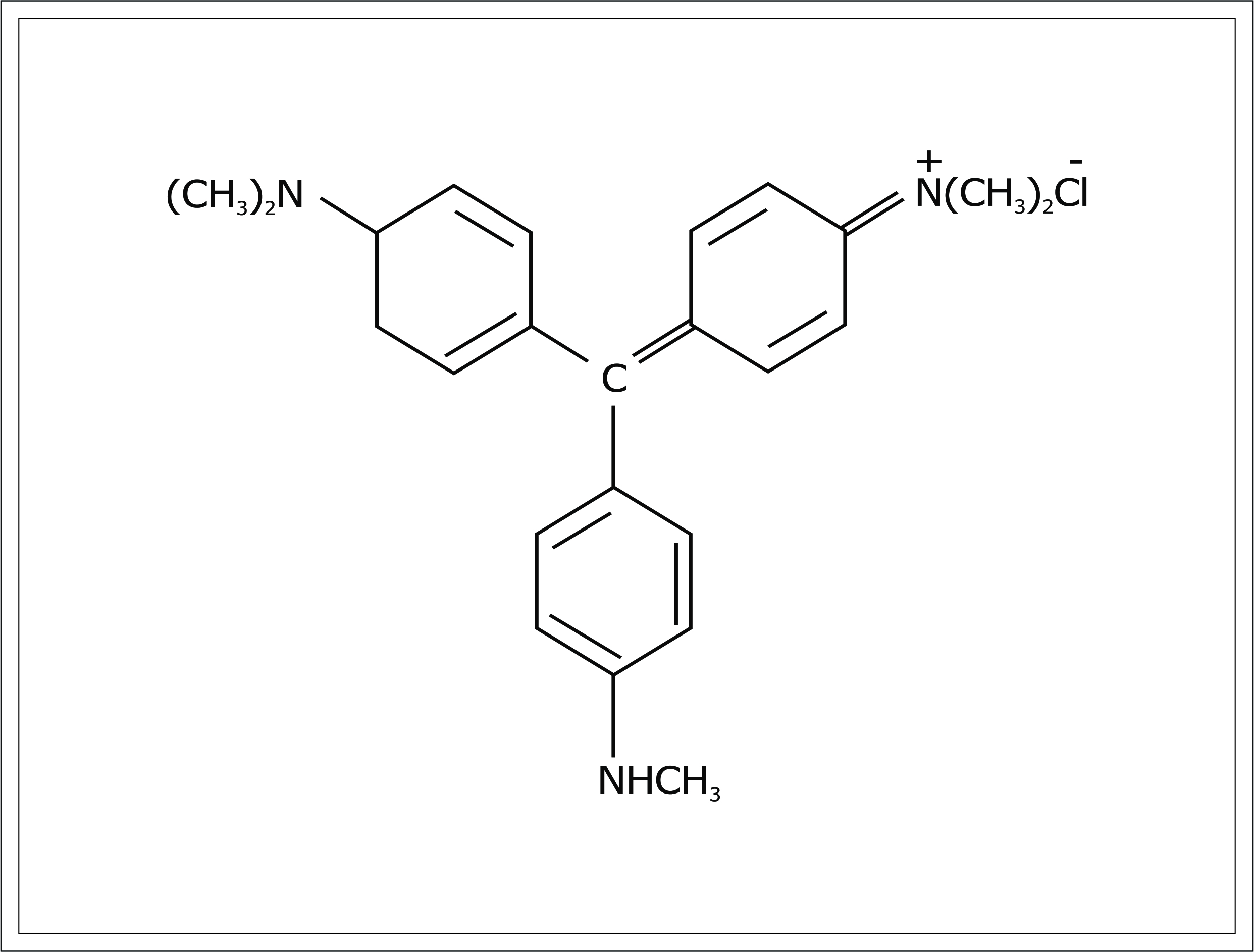
5). Compounds of the type:- Explained by figure
FC Acid :- Explained in brief
DASA: Explained with diagram
Carbon papers: Explained in brief

Food Colours: Explained in brief
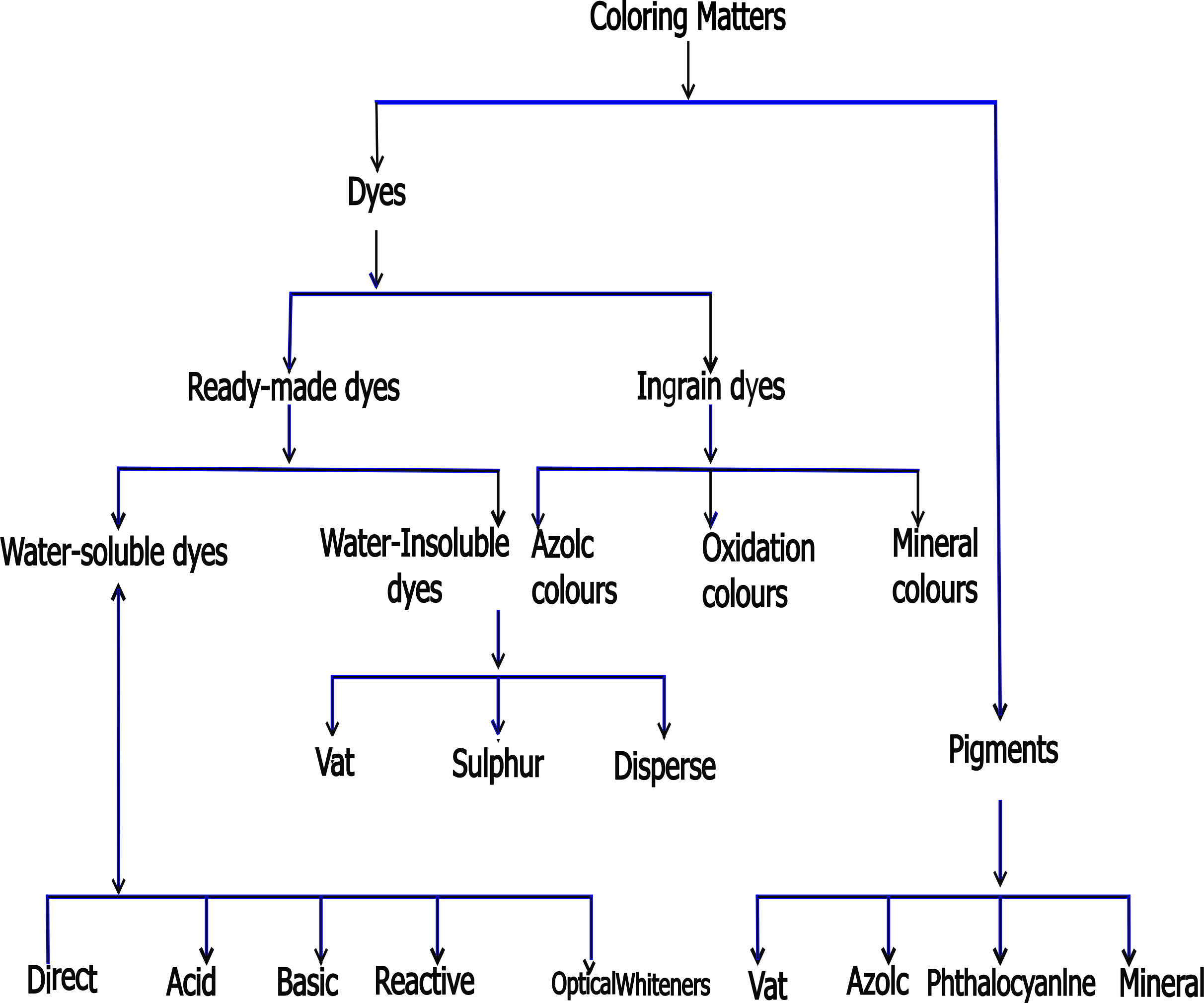
Classification of Dyes: Explained by structure

NON-TEXTILE USES OF DYESTUFFS:-

Polyester Filament:- Explained in brief

Polyester Staple Fiber:- Explained in brief

Quality of Dyestuff : Explained in brief

Dyestuff from Safer and non-pollution processes :

Weight of Fabric, Thickness and Bending Test:-

Color Change Assessment:-

Anti-static Properties of the fabric

Conductivity Properties:- Explained in brief

Anti-bacteria Measurement:- Explained in brief

Surface Observation: Explained in brief

Ultraviolet Radiation Penetration

Preparation for Dyeing: Explained in brief

Acrylics:- Explained in brief

Cotton fibres:- Explained Completely
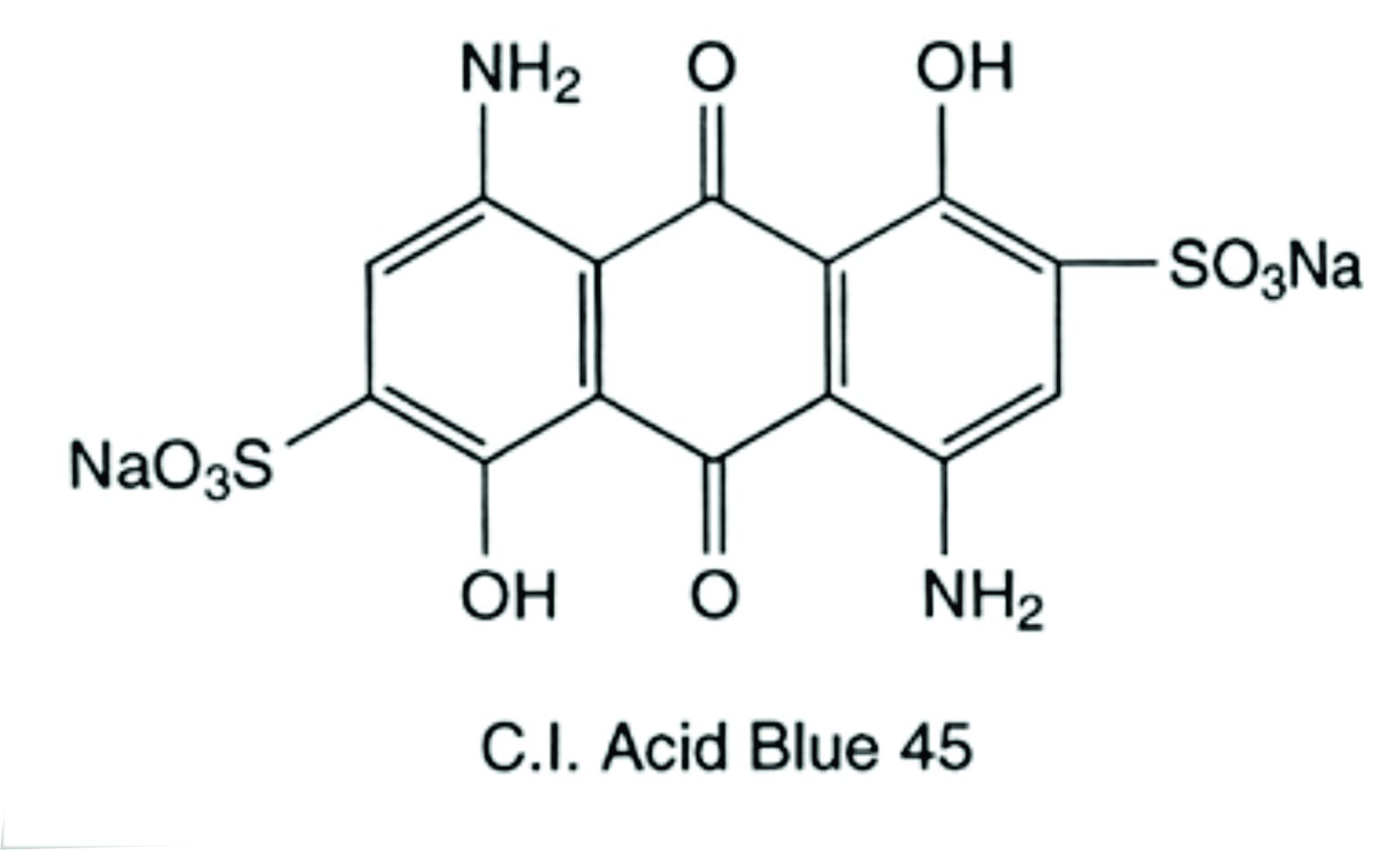
Anthraquinone:- Explained in brief
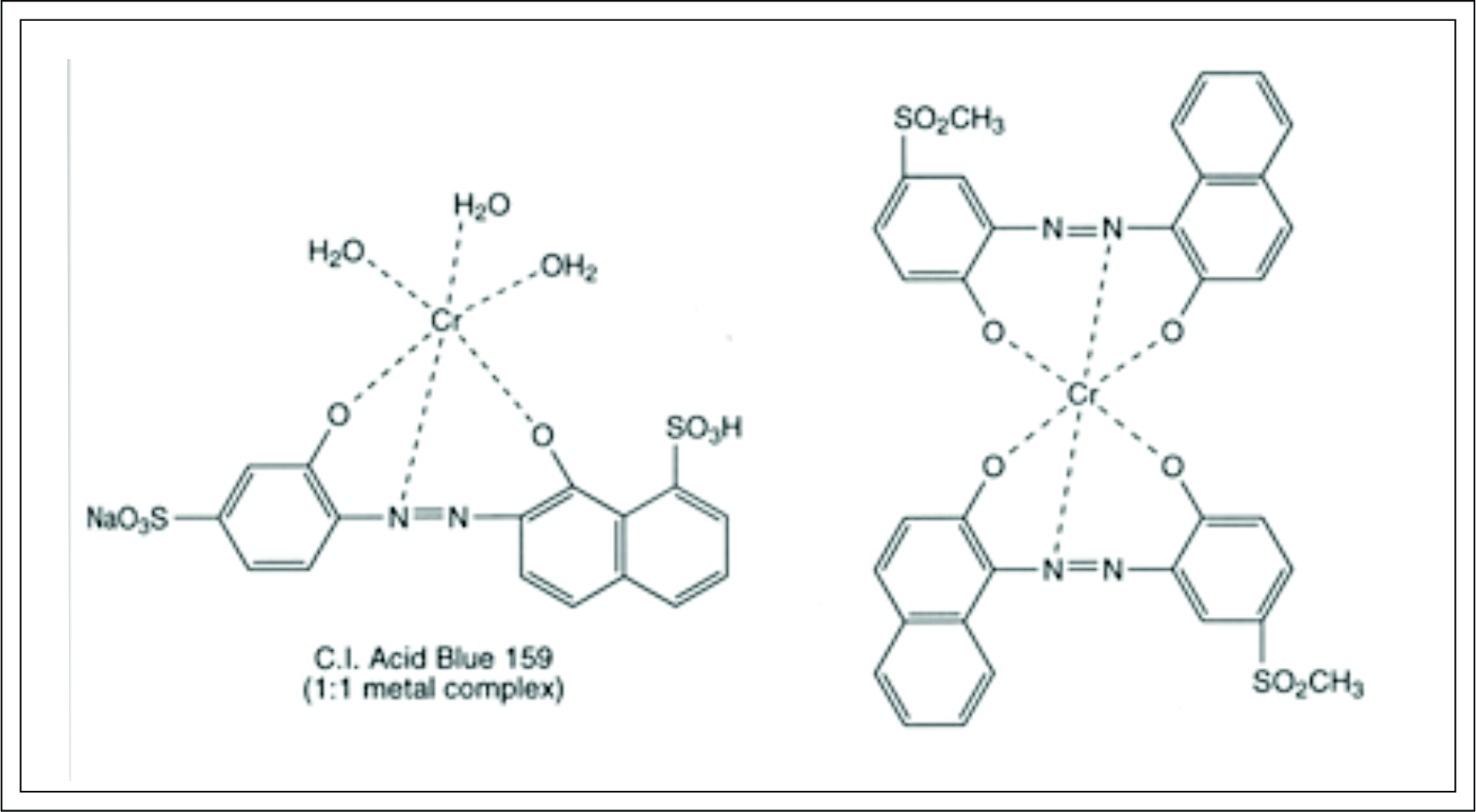
Premetallized acid:- Explained in brief

Silk:- Explained in brief
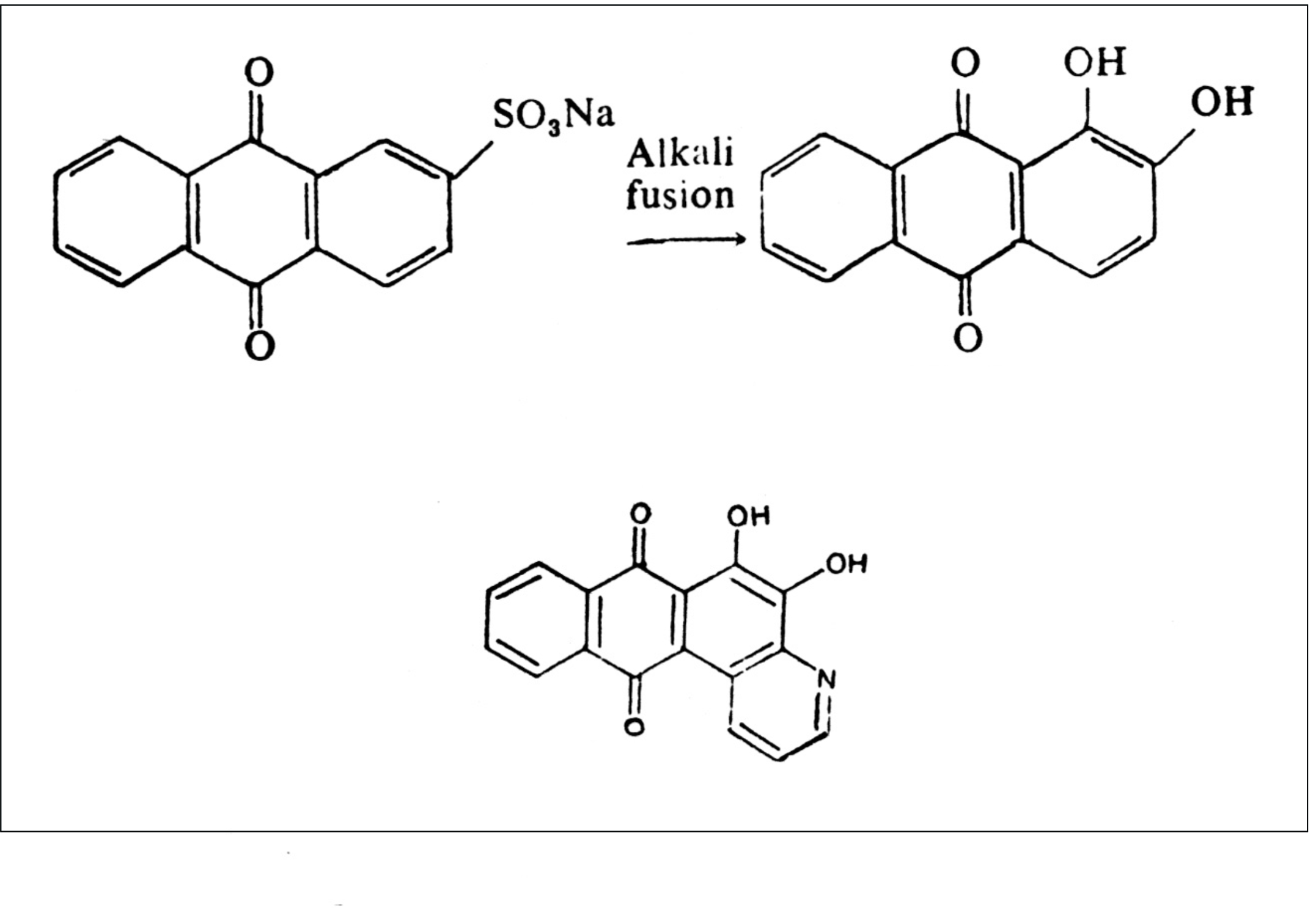
Mordant anthraquinone dyes : Explained in brief
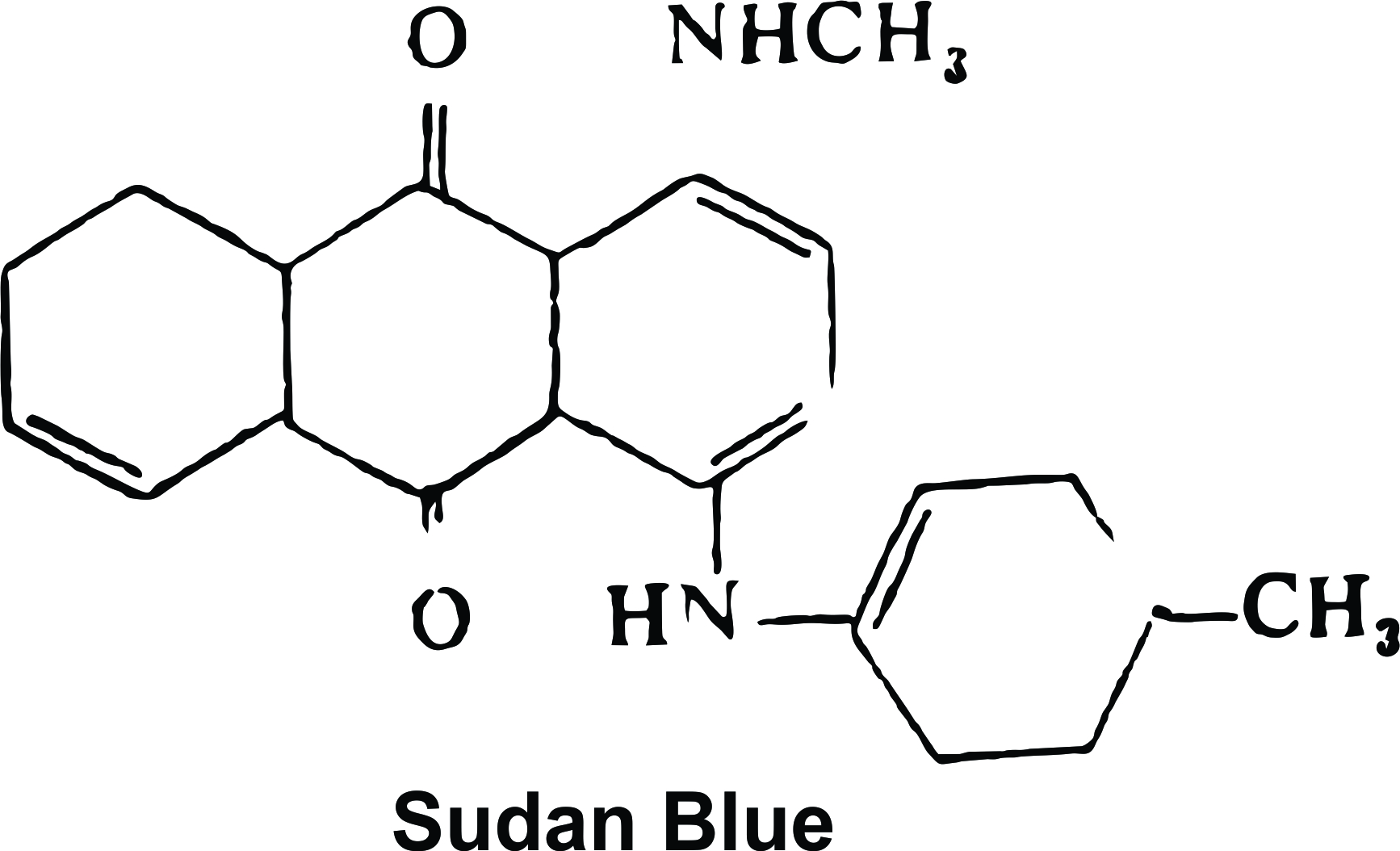
Solvent anthraquinone dyes :

Monofunctional reactive systems:-

Bifunctional reactive systems
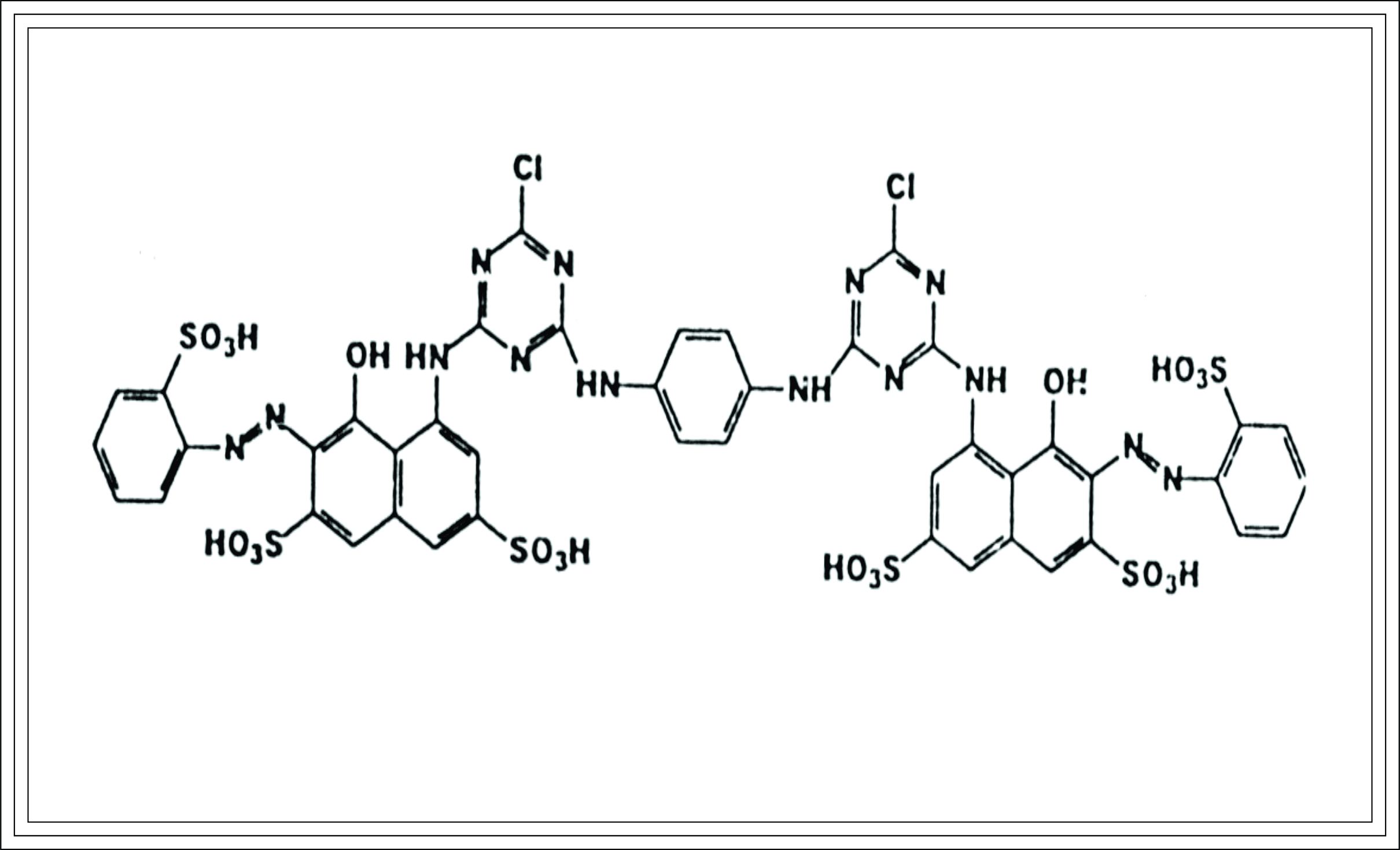
Bis-monochlorotriazine dyes:- Explained in brief
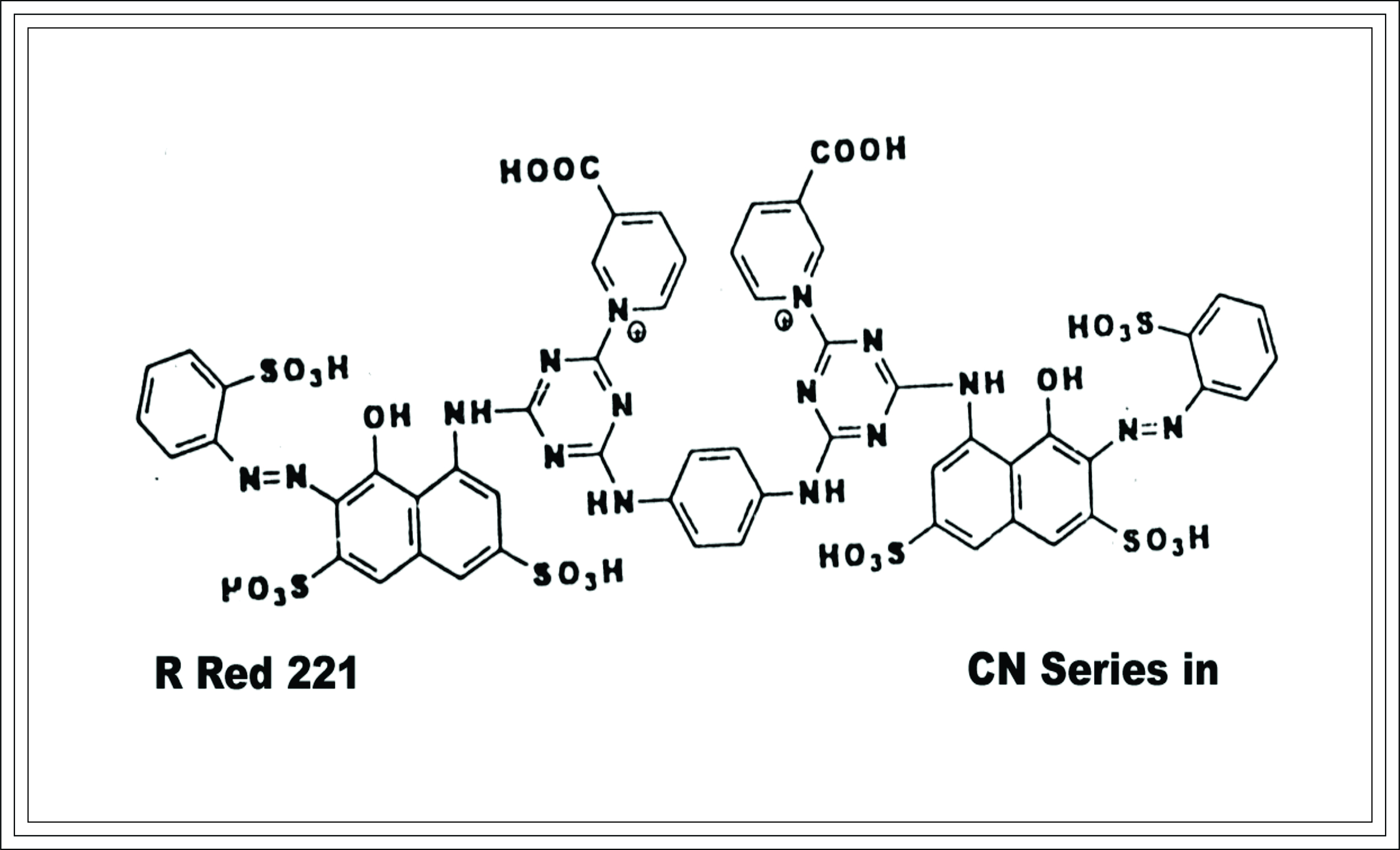
Bis-mononicotinotrazine dyes:
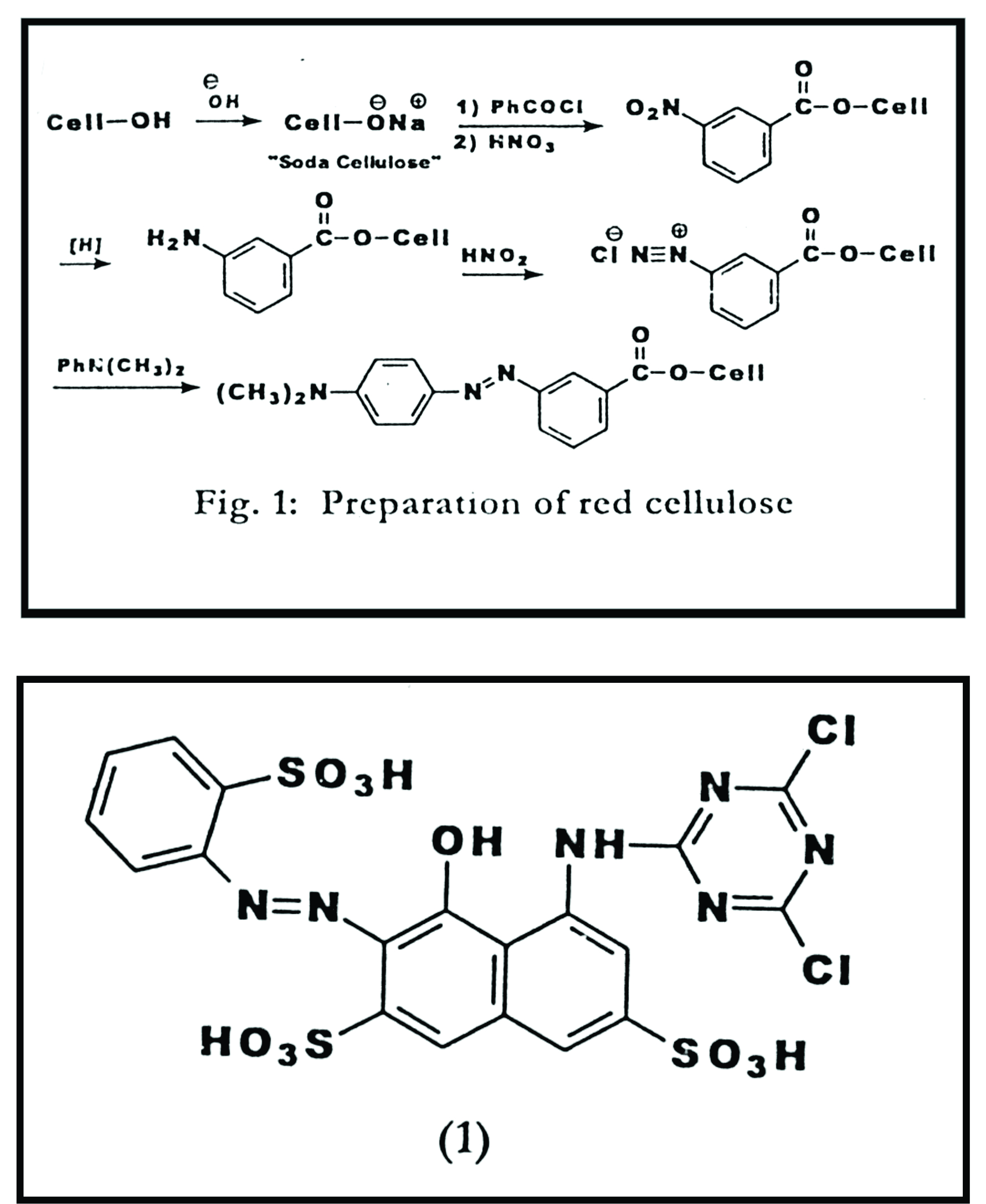
Historical developments:- Explained Completely
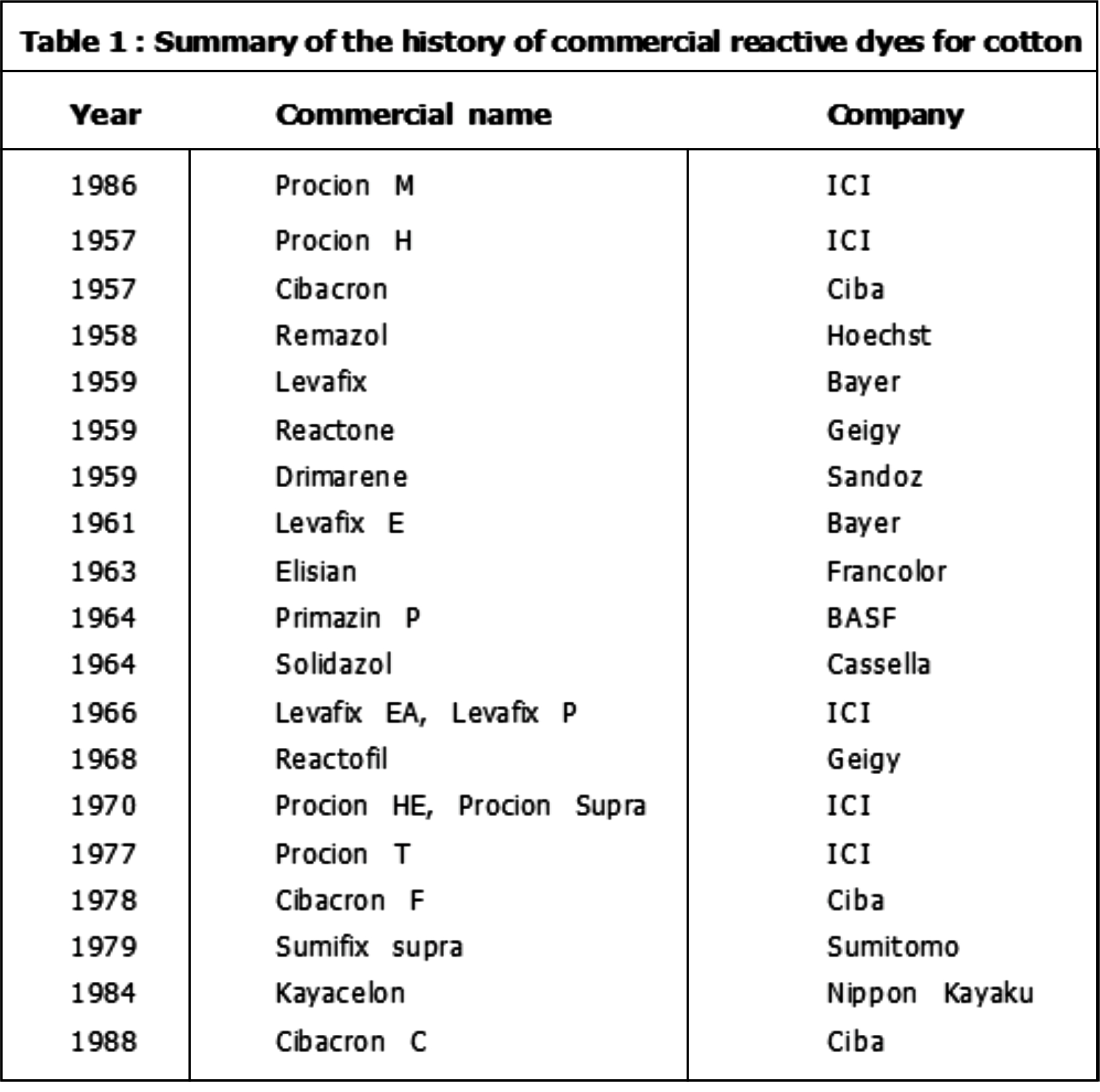
Historical developments:- Explained Completely (Pa

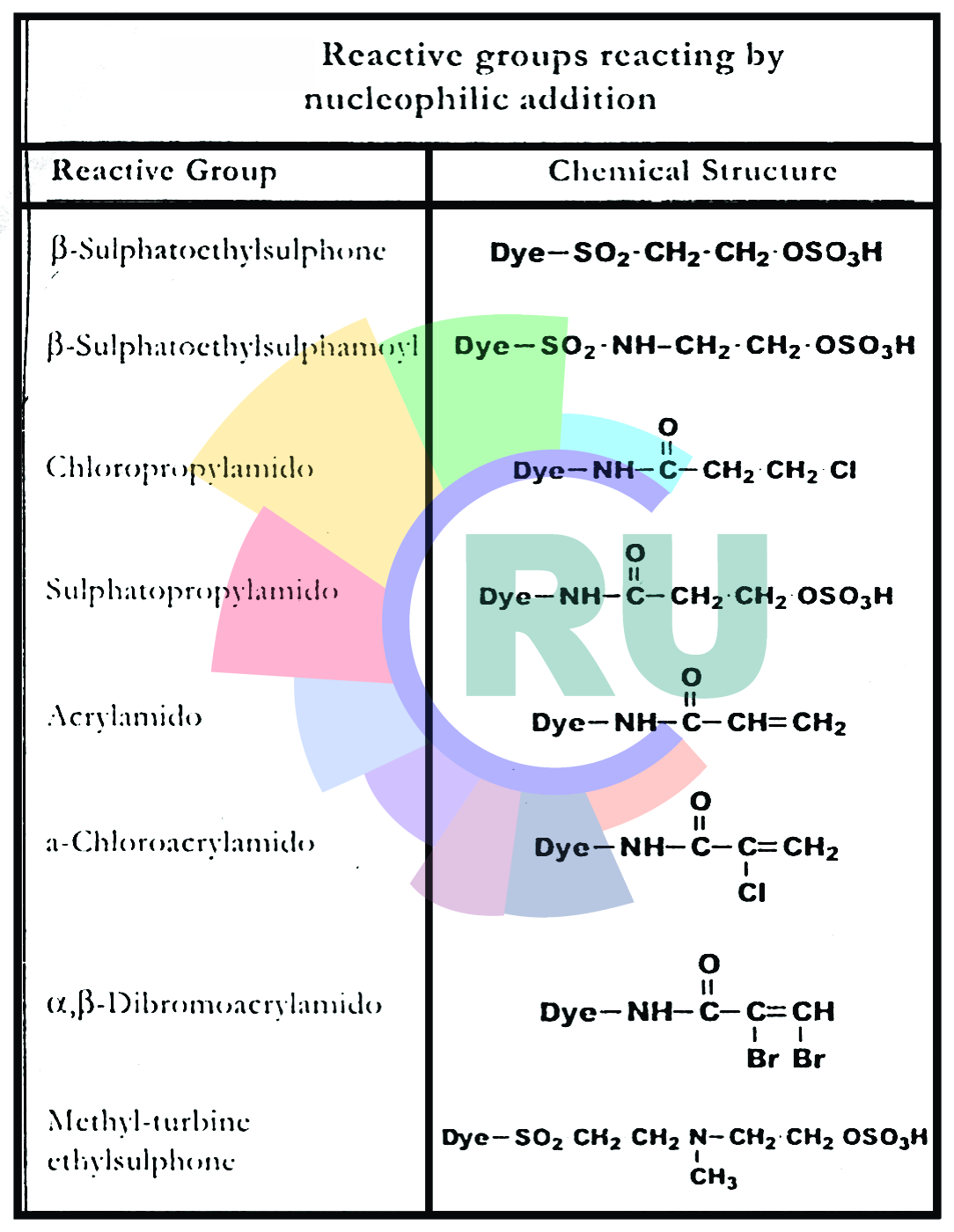
Types of Heterobifunctional reactive dyes:-
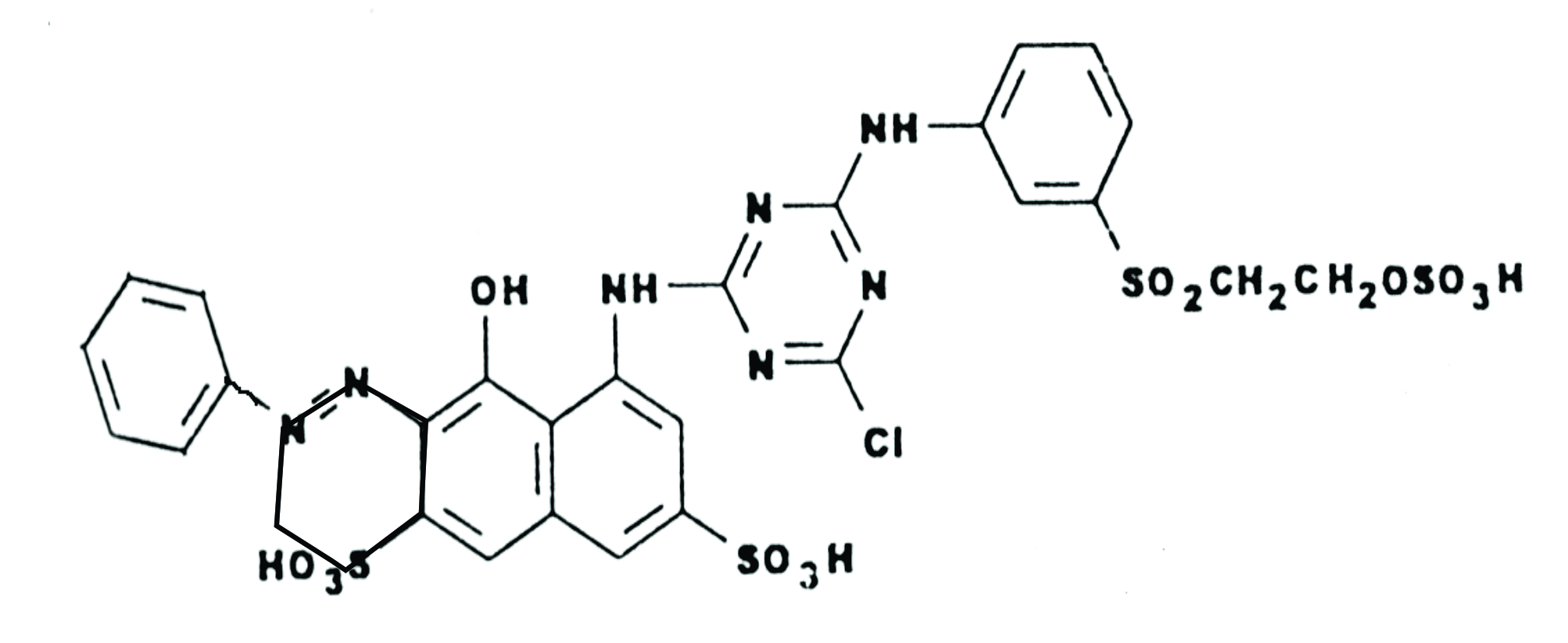
Monochlorotriazine / sulphatoethylsulphone dyes:-
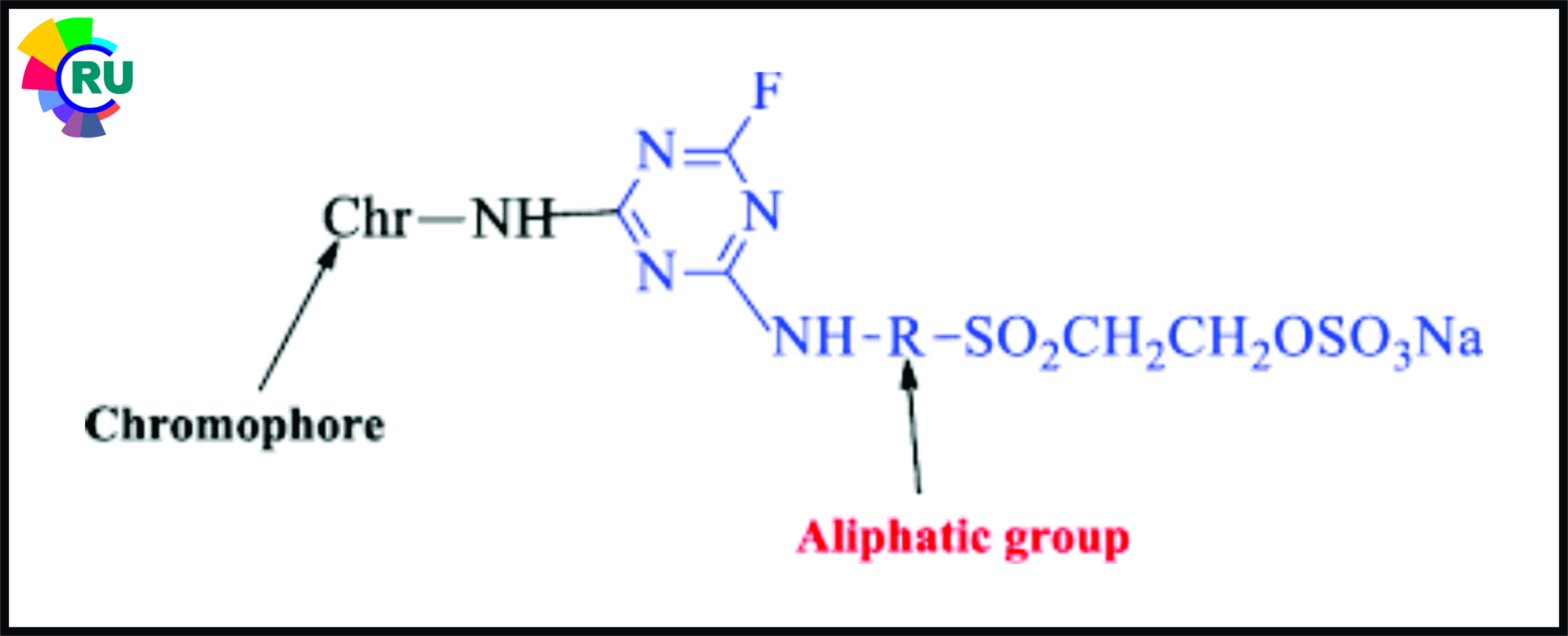
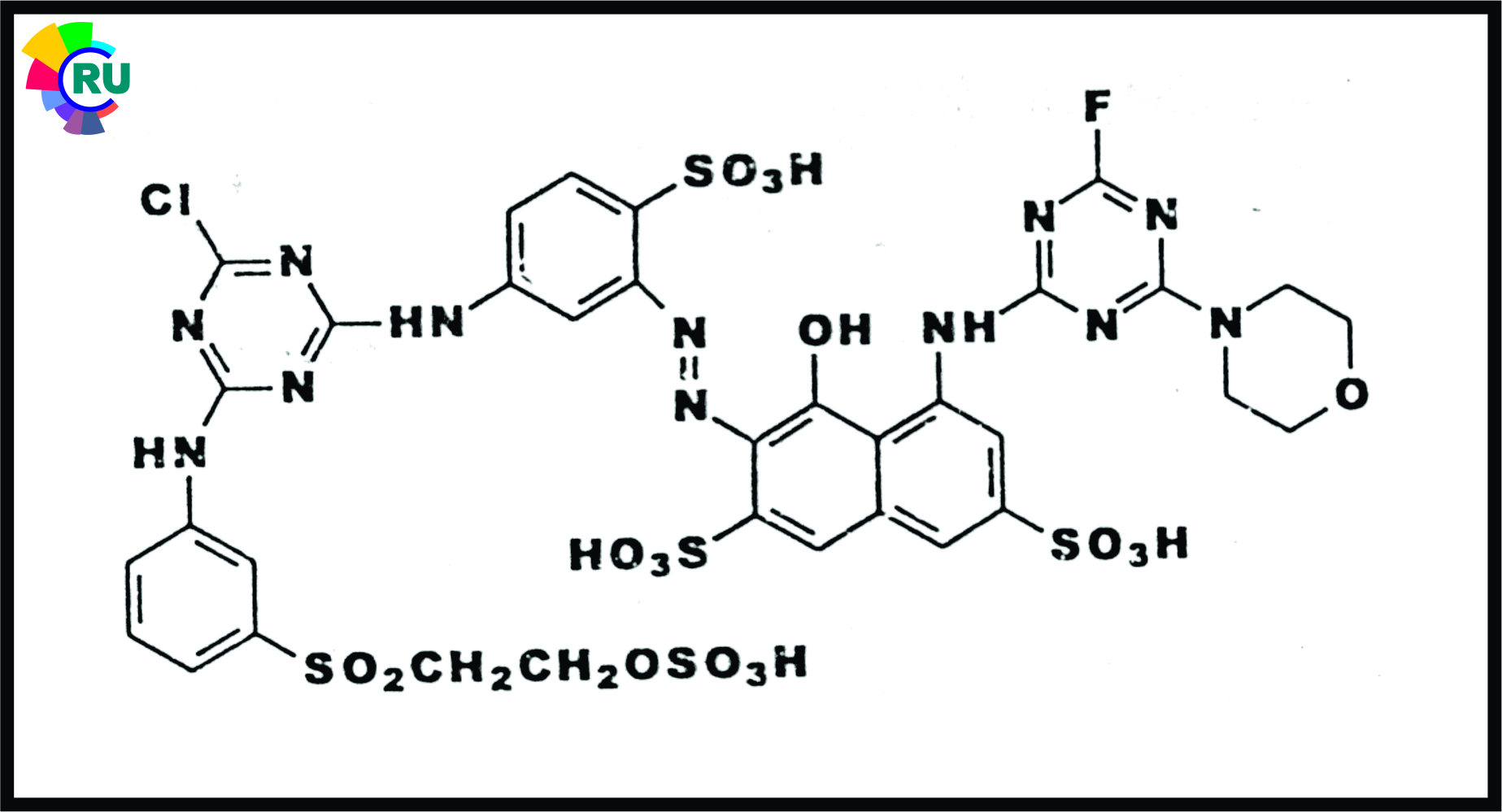
Monofluorotriazine / sulphatoelrylsulphone dyes:-
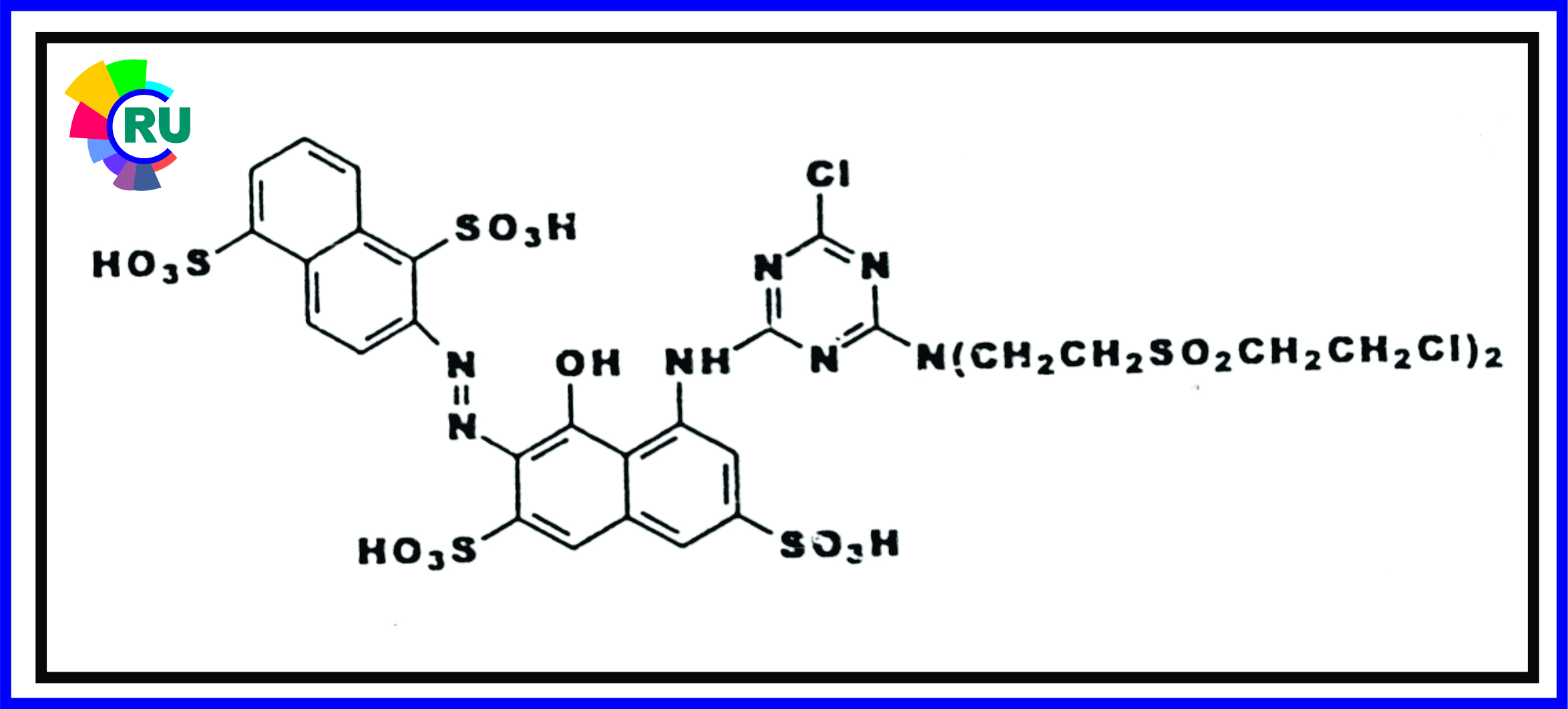
Polyfunctional reactive systems:- (Part 1)
Polyfunctional reactive systems:- (Part 2)
Chromophoroic groups:- Explained in brief
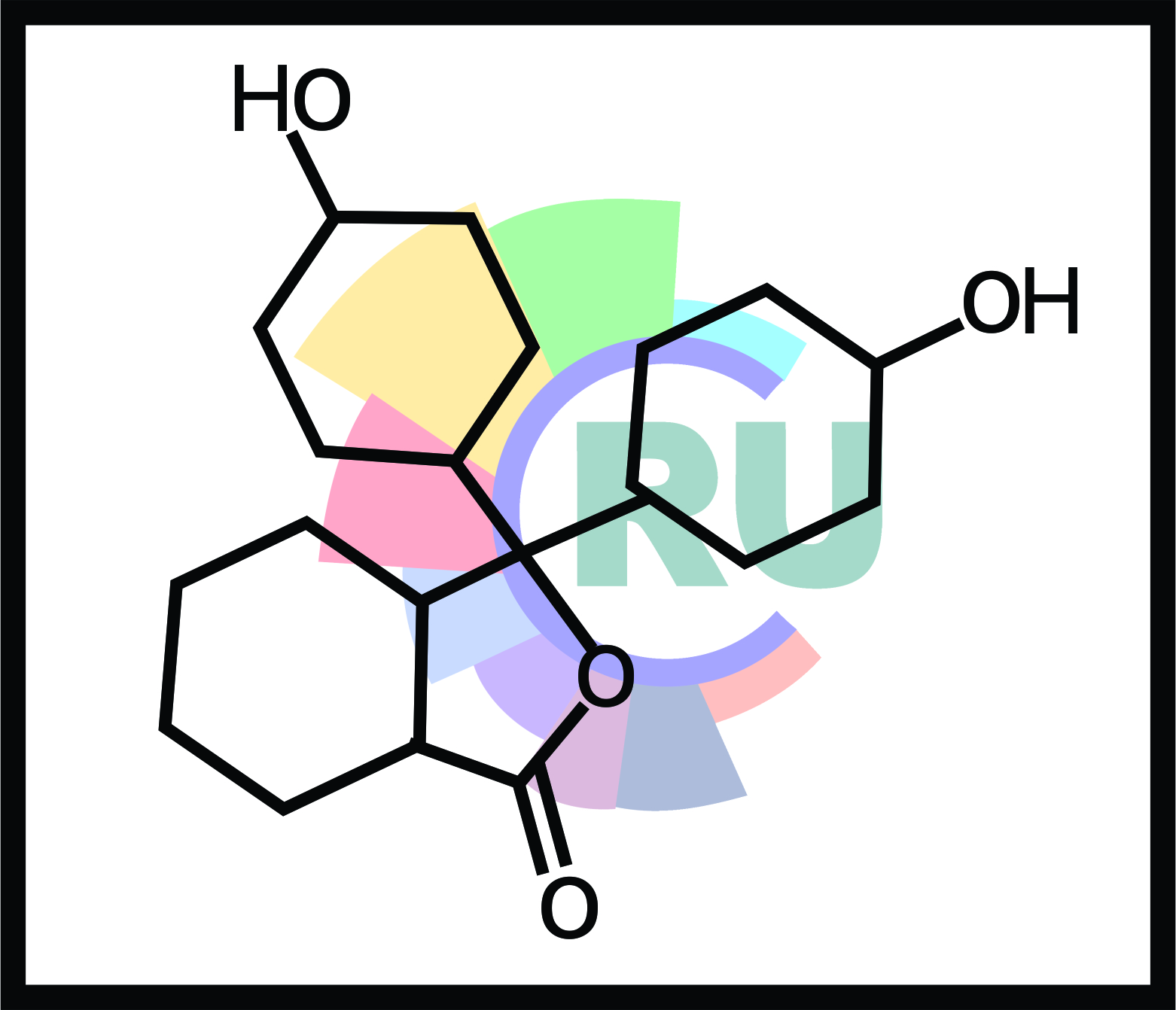
Anthraquinone reactive dyes:- Explained in
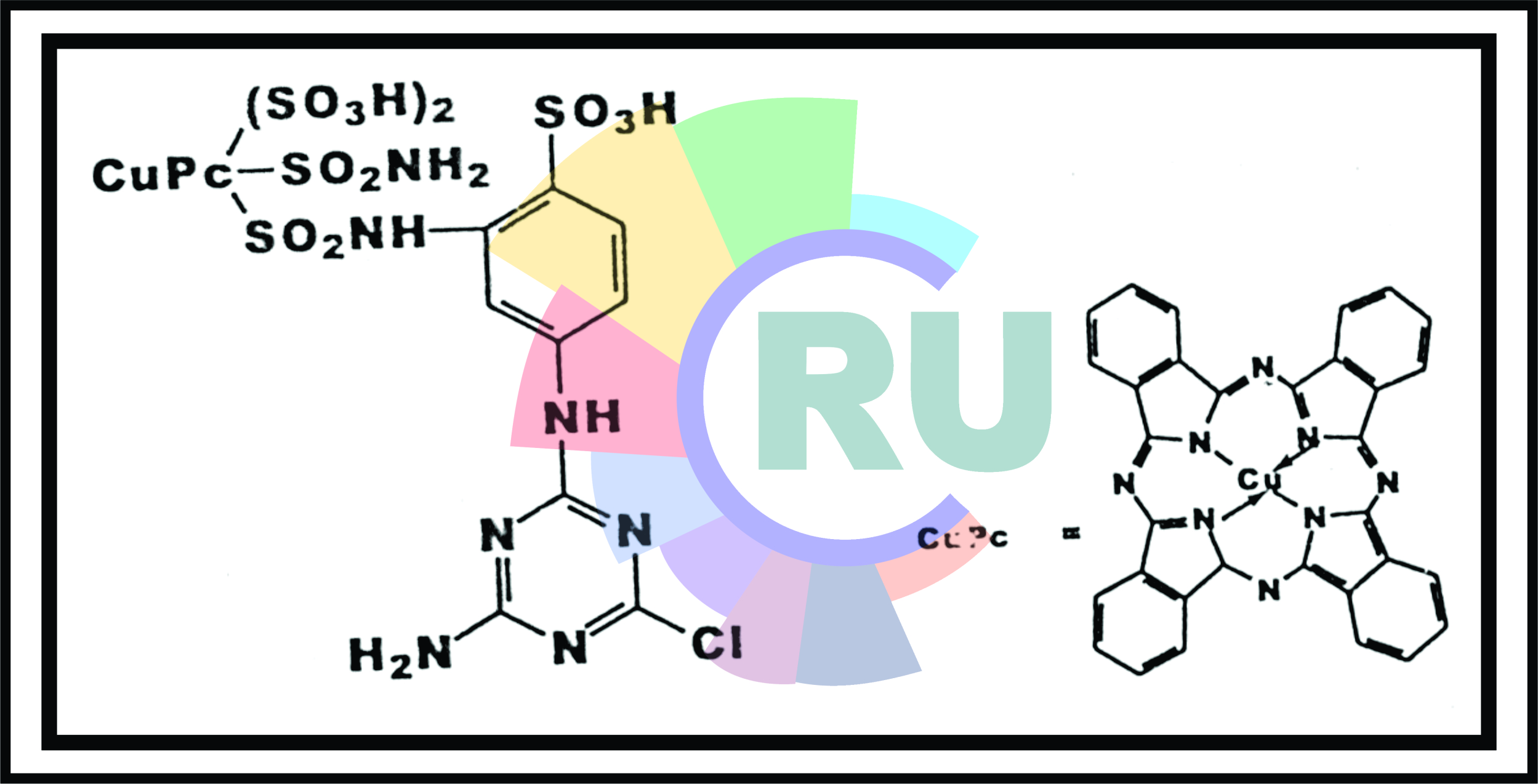
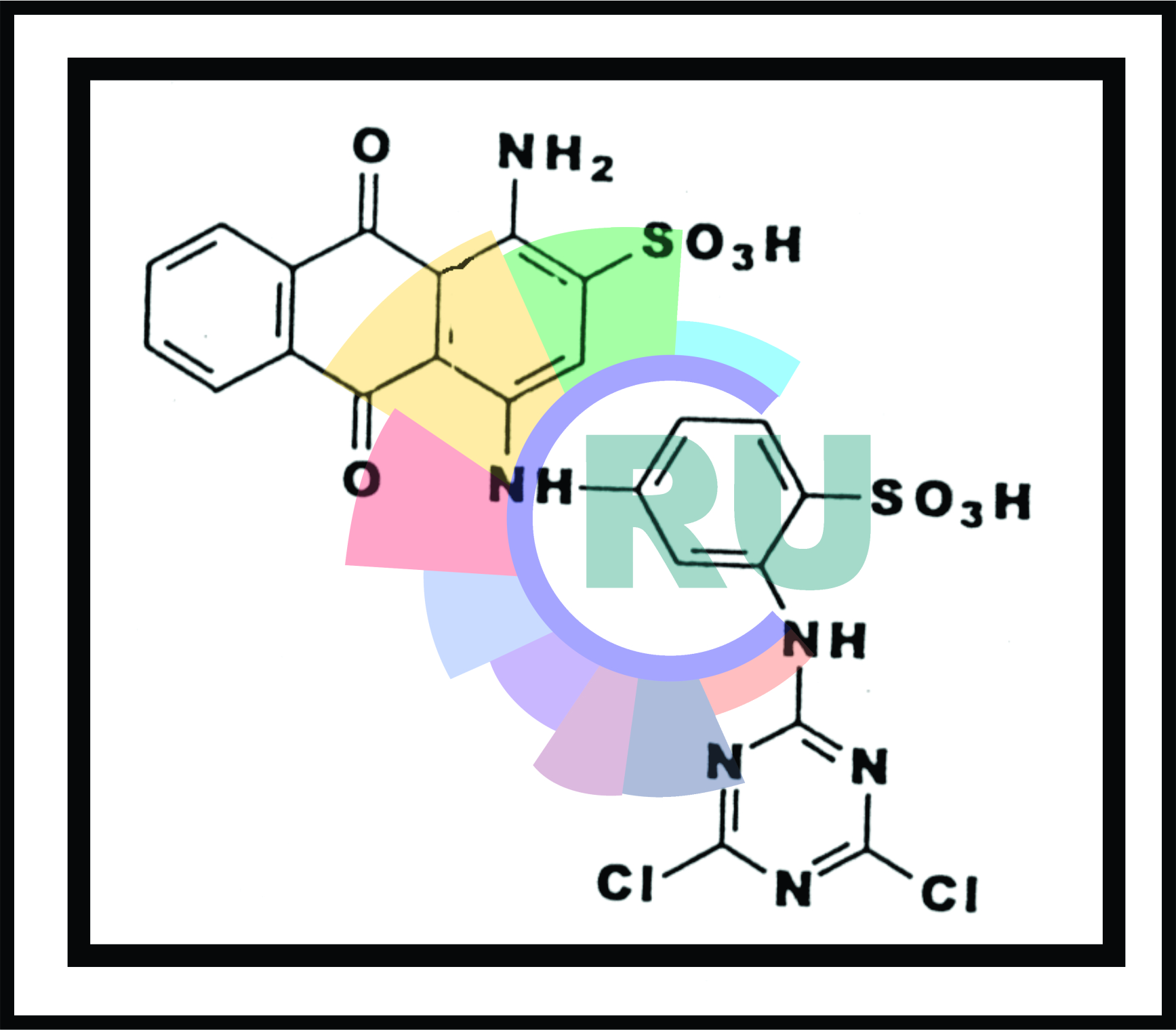
Phthalocyanine reactive dyes:- Explained in brief
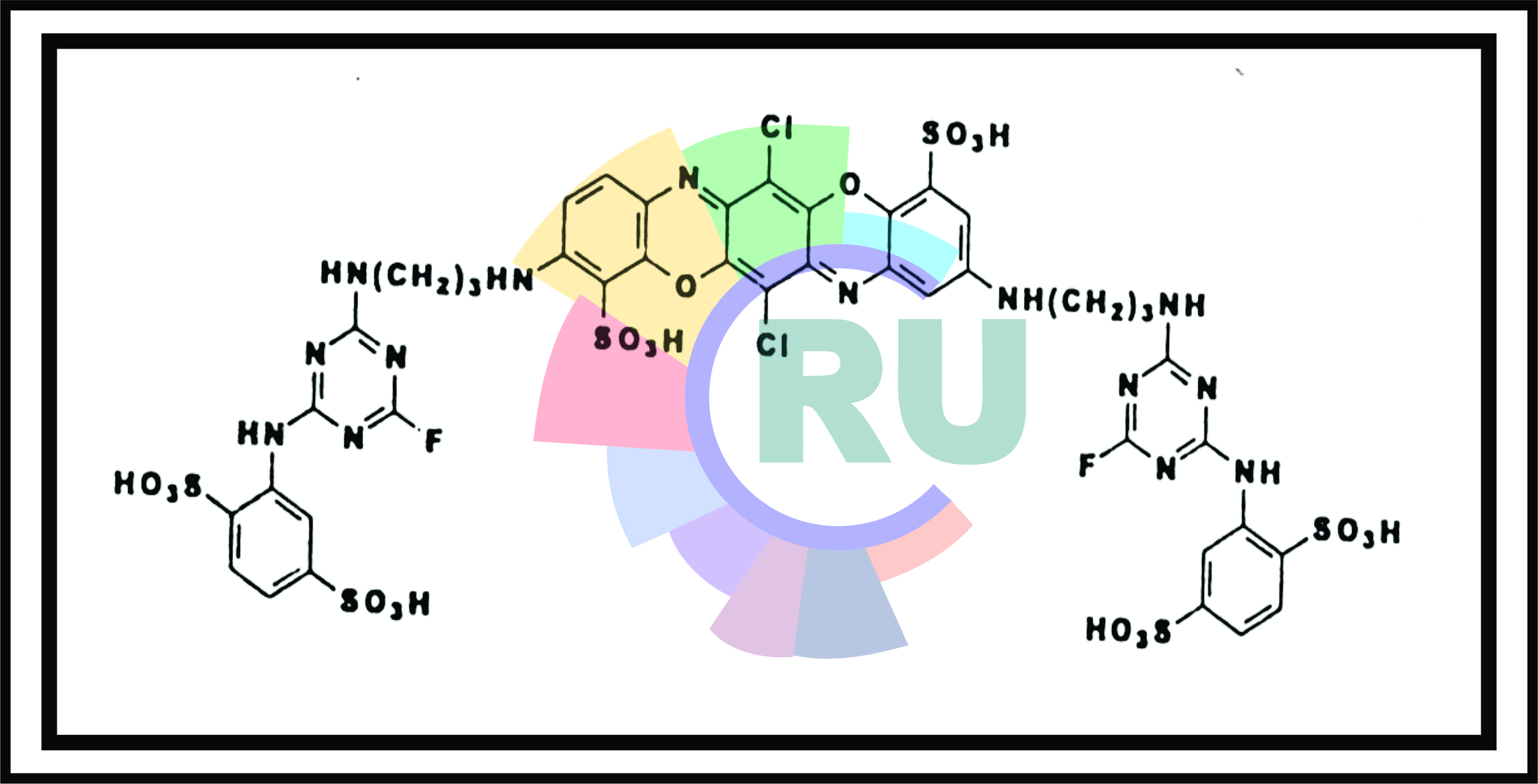
Triphenodioxazine reactive dyes:-

Reactive dye-fiber fixation:- (Part 1)

Reactive dye-fiber fixation:- (Part 2)
Fixation involving a phosphonic acid group
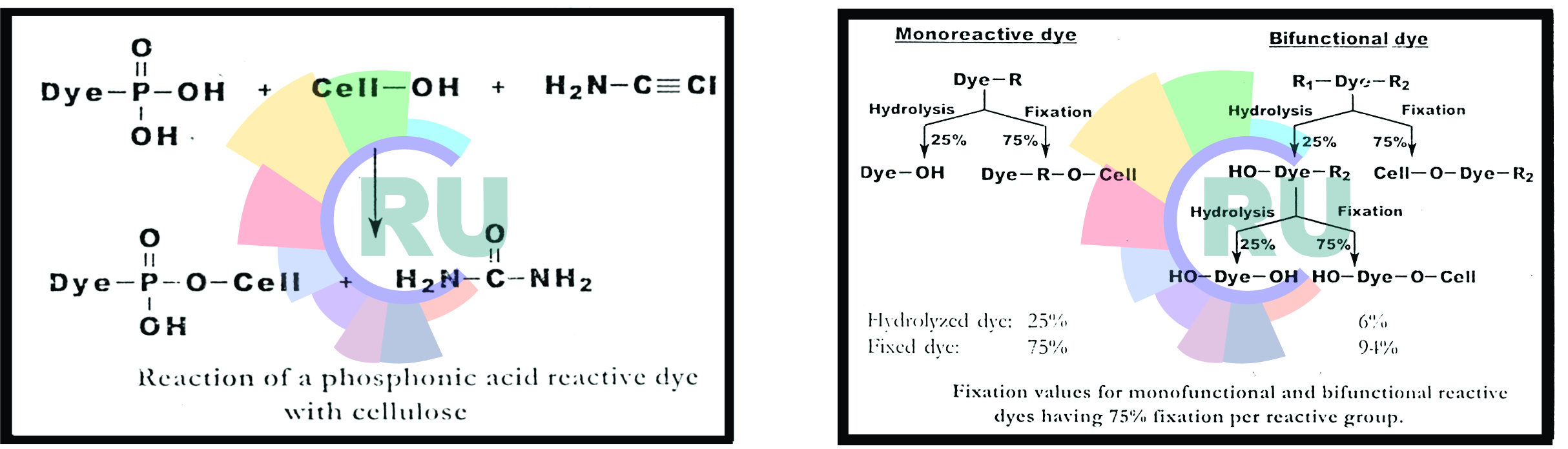
Fixation of bifunhctional reactive dyes

The traditional or conventional method:- Explained

The constant temperature dyeing method:- Explained

The high temperature dyeing method
Semi-continuous or pad-batch dyeing processes (Par

Semi-continuous or pad-batch dyeing processes:- (P

Continuous dyeing processes:- Explained in brief

The conventional dyeing process (pad-dry-pad-steam
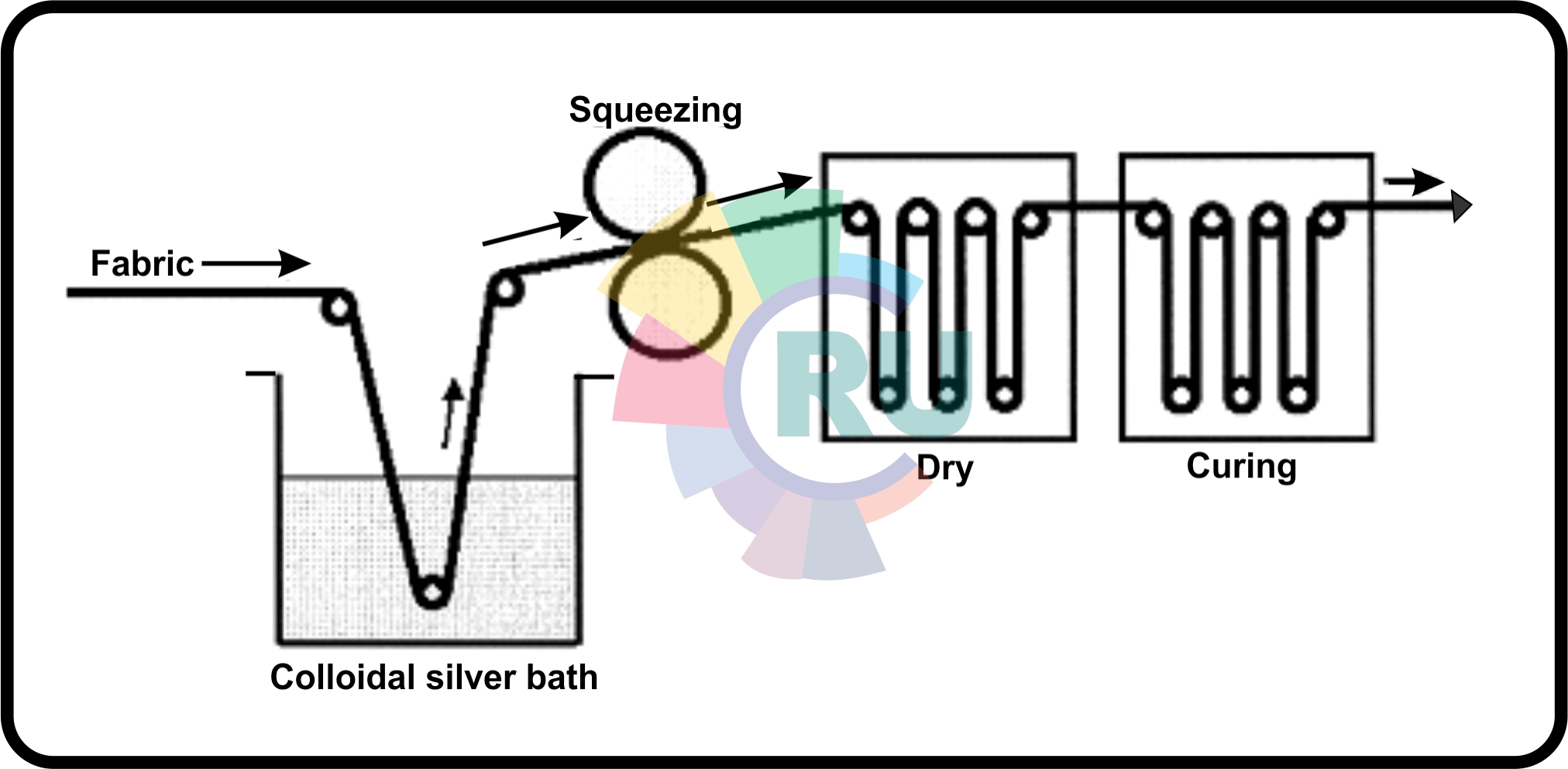
Pad-dry-cure method (Part 1)

Pad-dry-cure method (Part 2)

Printing:- Explained in brief
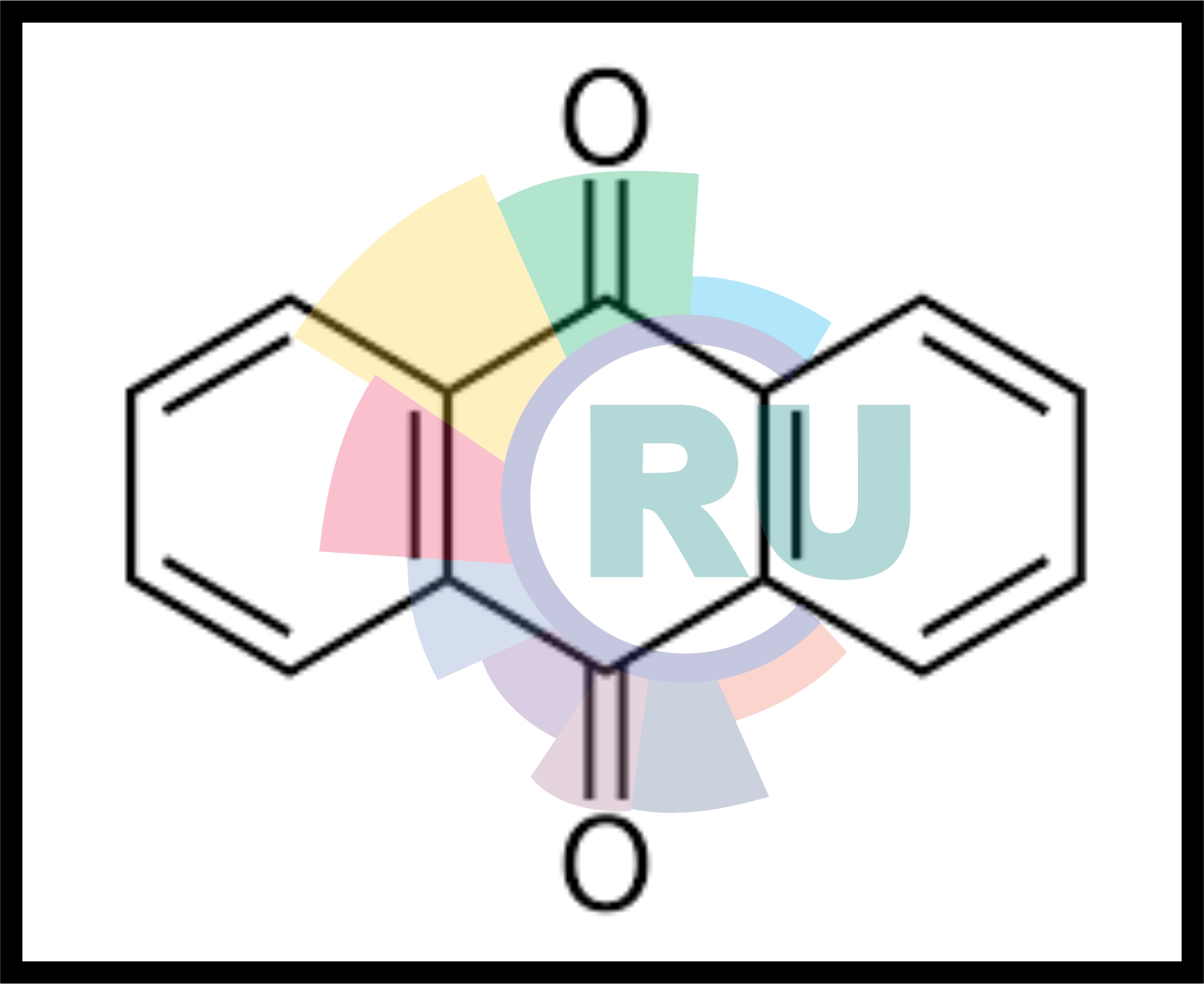
Anthraquinonoid dyes (Part 1)
Anthraquinonoid dyes (Part 2)
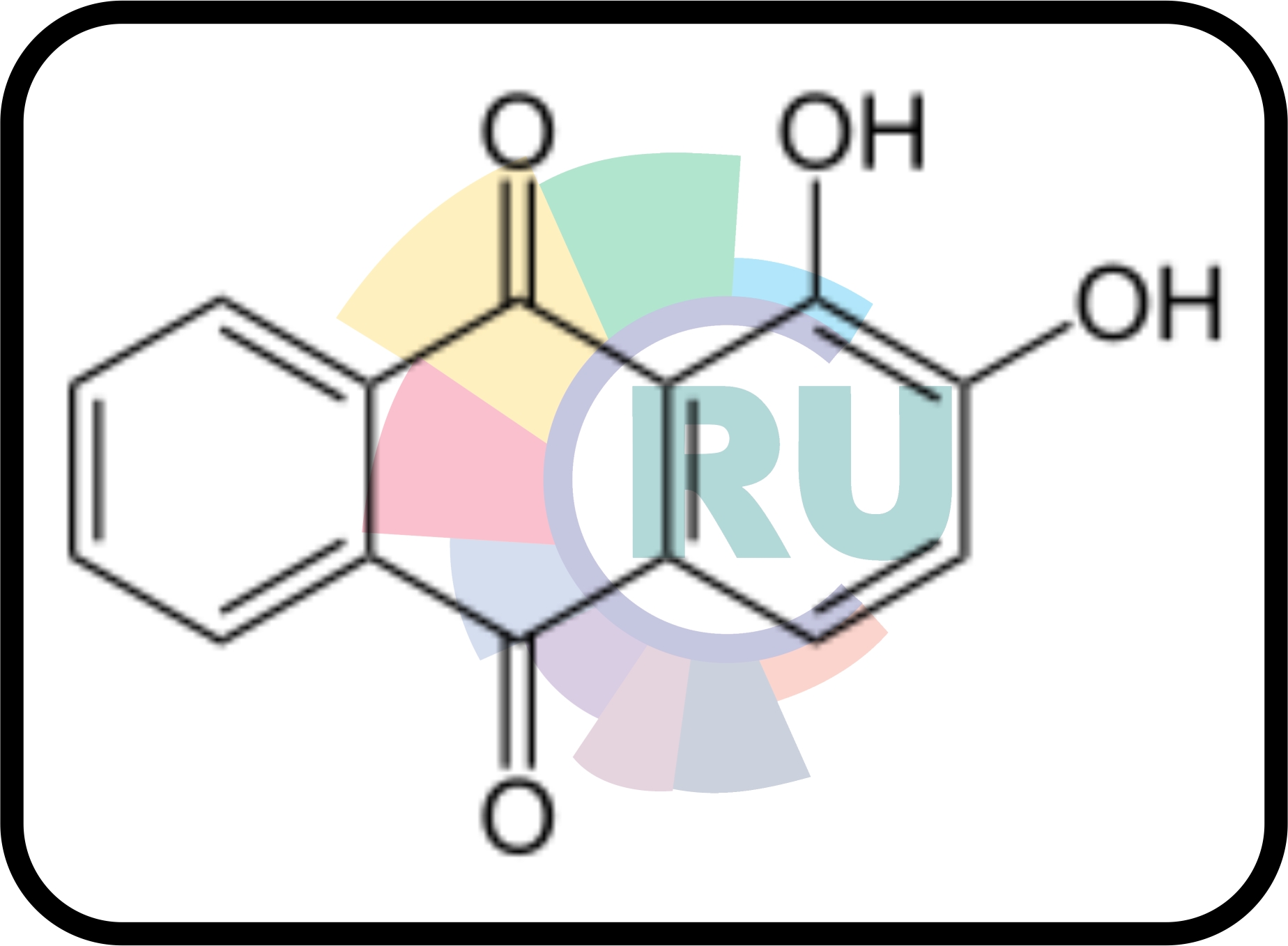
Direct anthraquinone dyes:
Disperse anthraquinone dyes
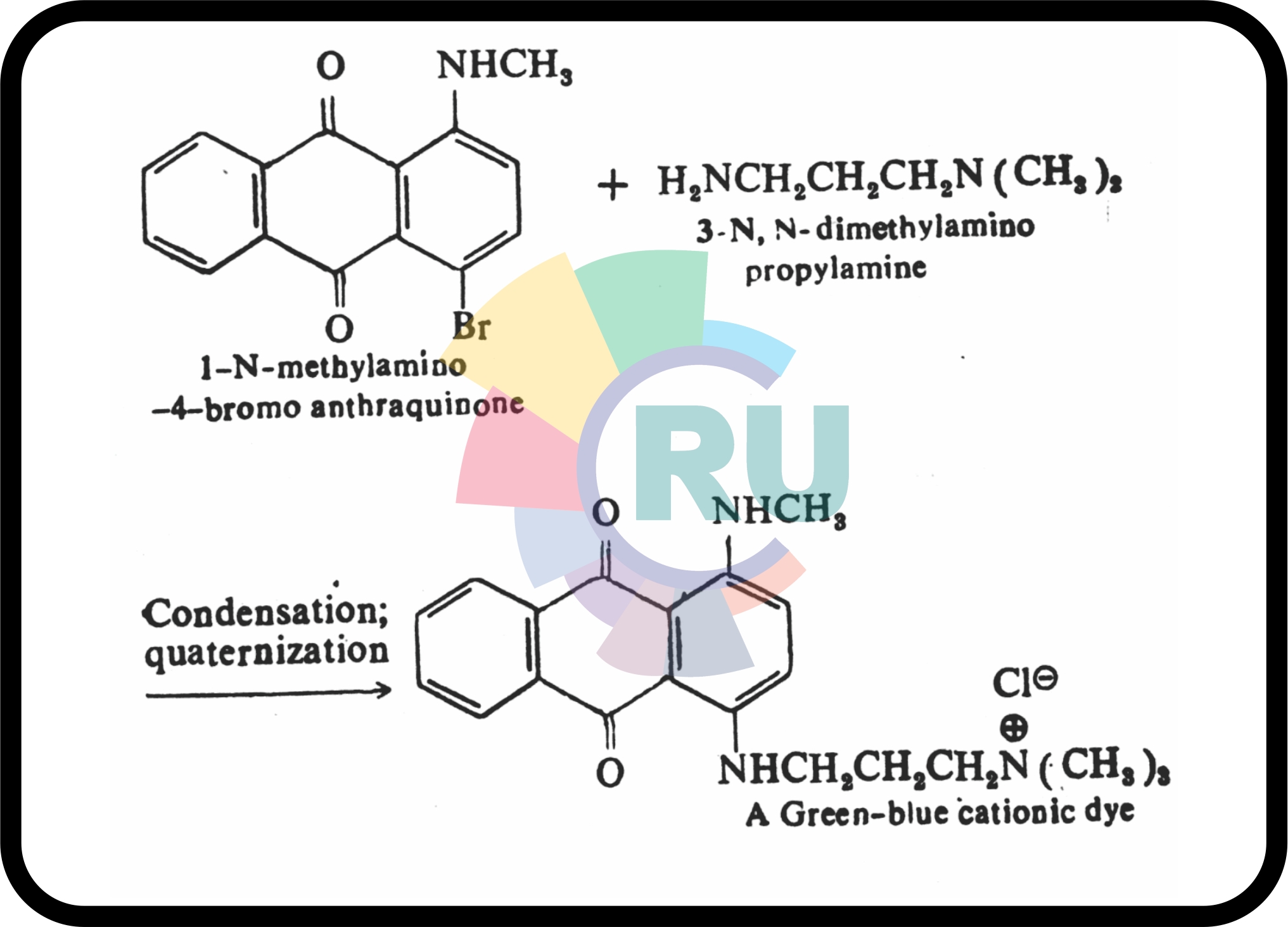
Cationic anthraquinone dyes (Part 1)
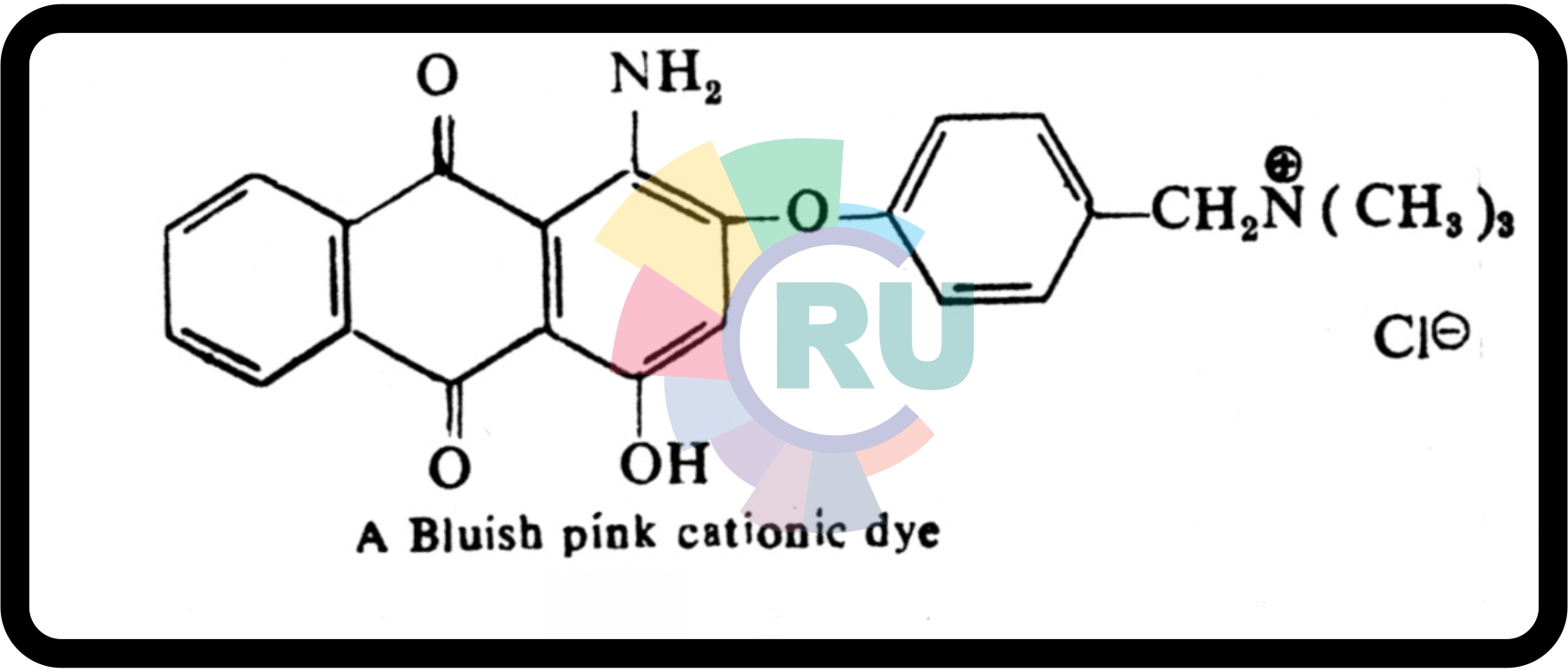
Cationic anthraquinone dyes:- (Part 2)
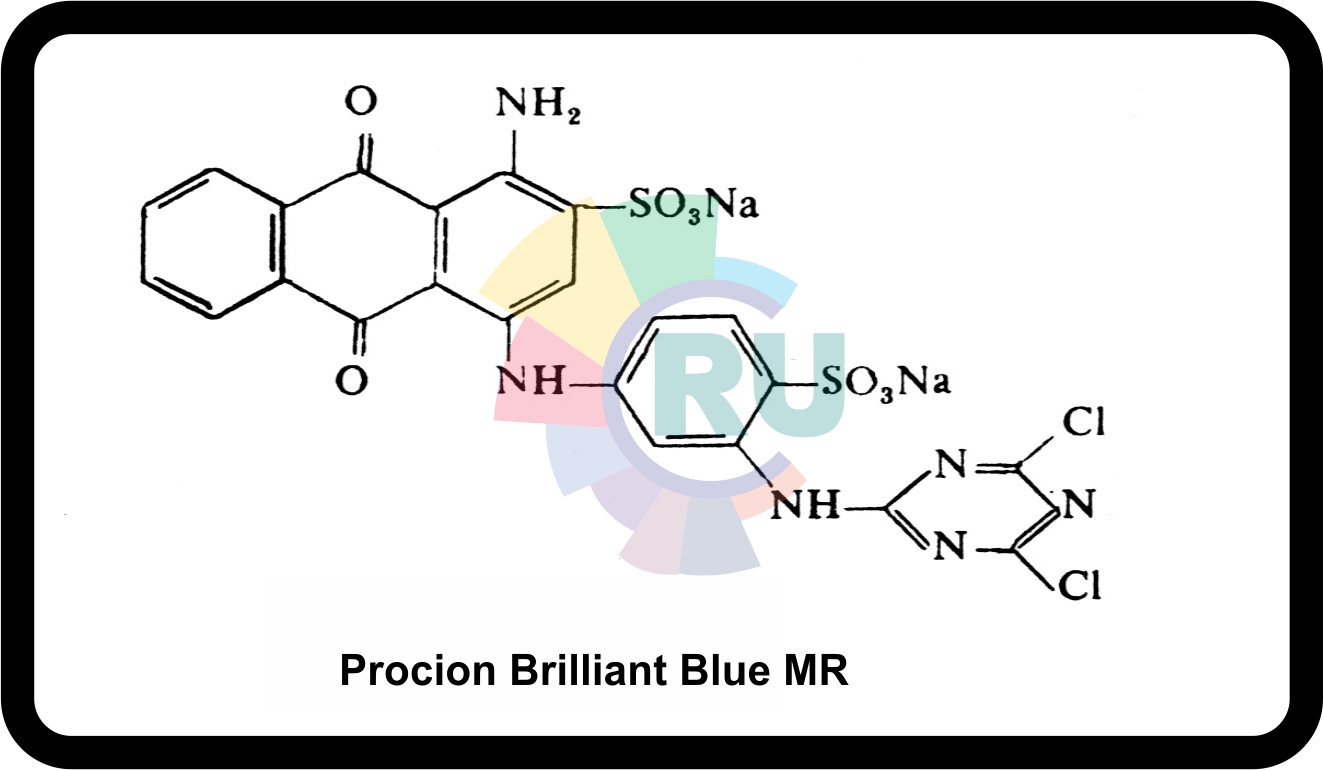
Reactive anthraquinone dyes :

Antraquinonoid Vat dyes:-
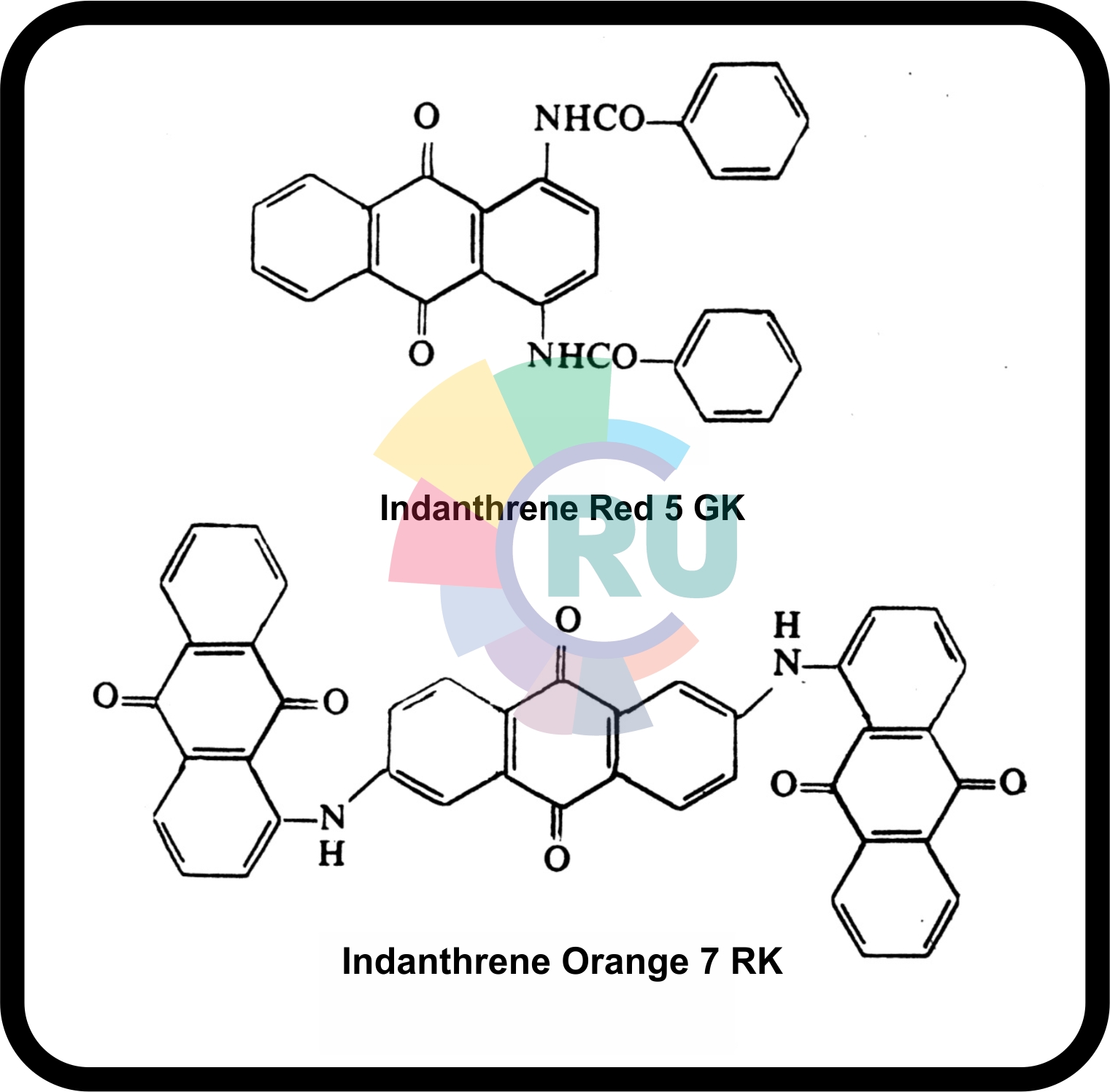
Vat dyes containing simple anthraquinone derivativ
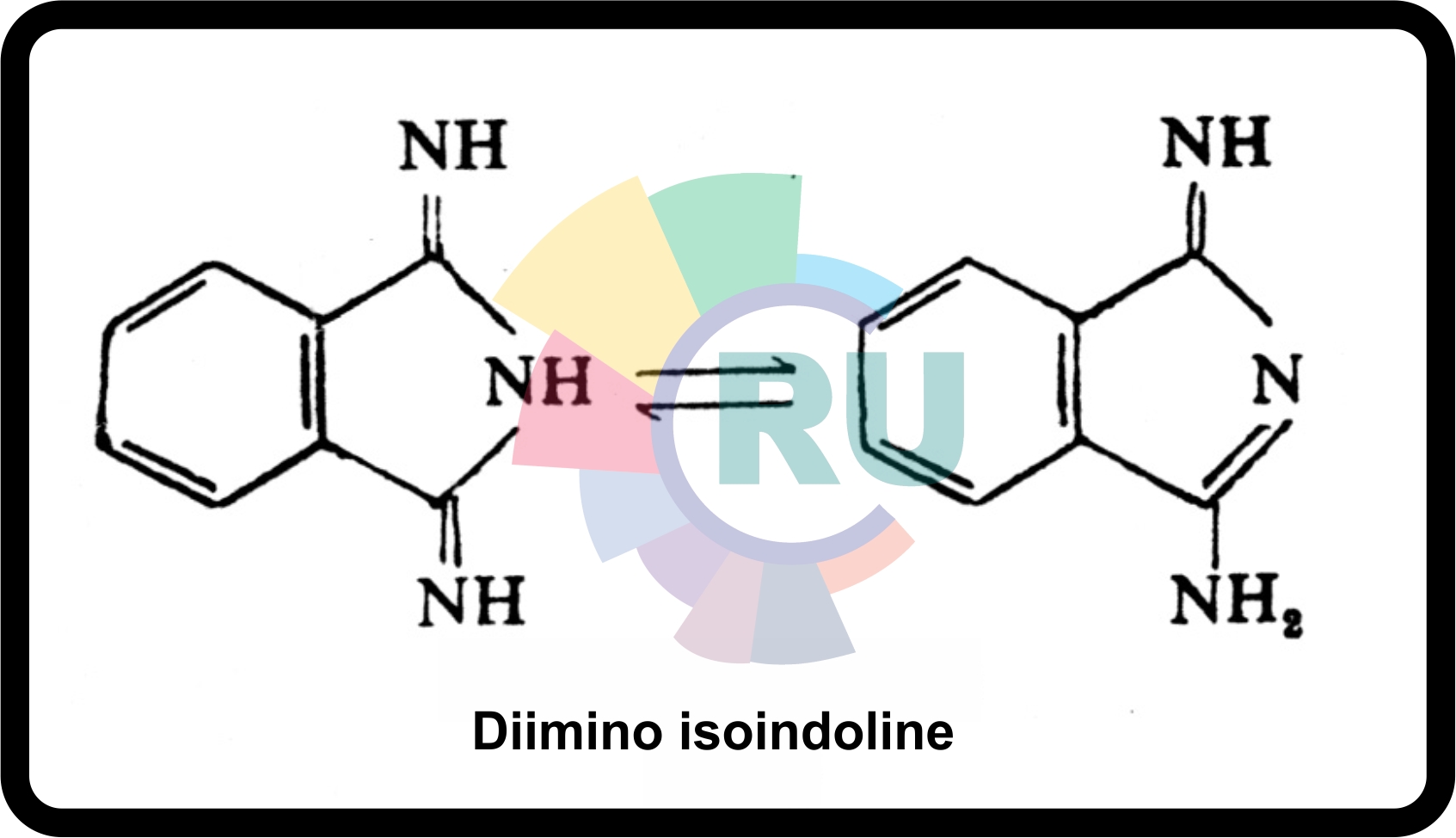
Phthalogens:- Explained in brief
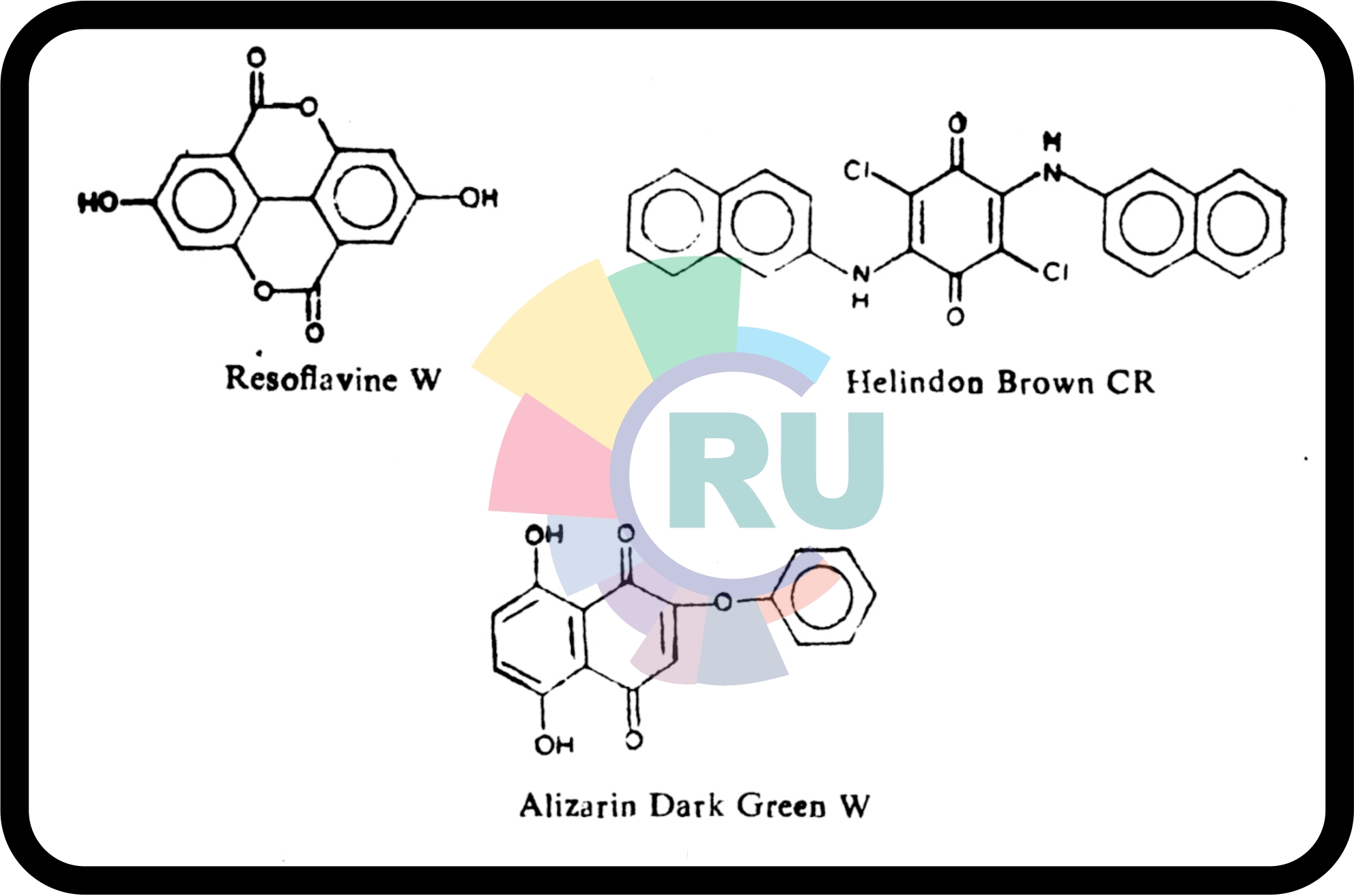
Lactone, Aminoketone and Hydro xyketone dyes:-
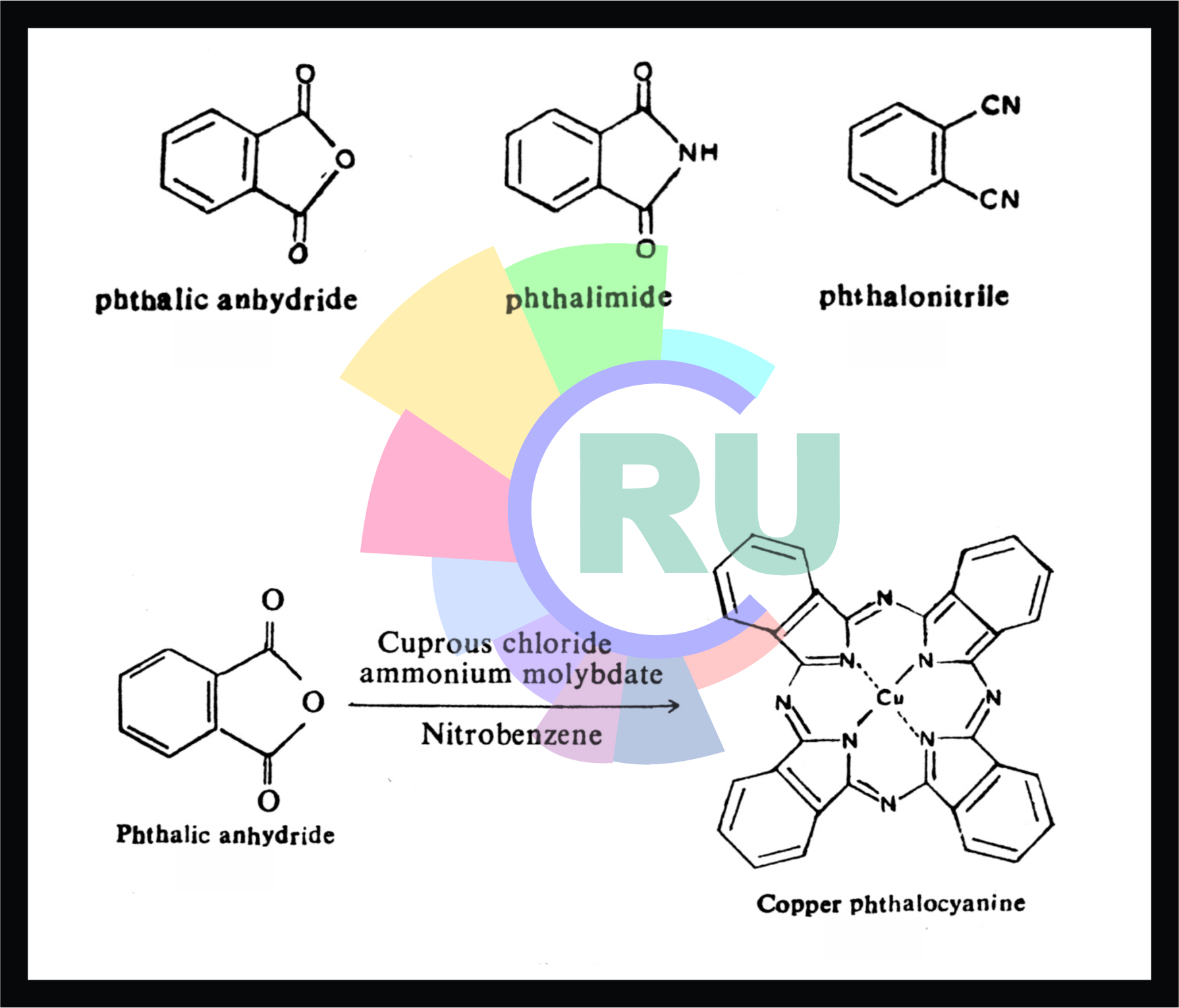
Phthalacyanine dyes:- (Part 1)
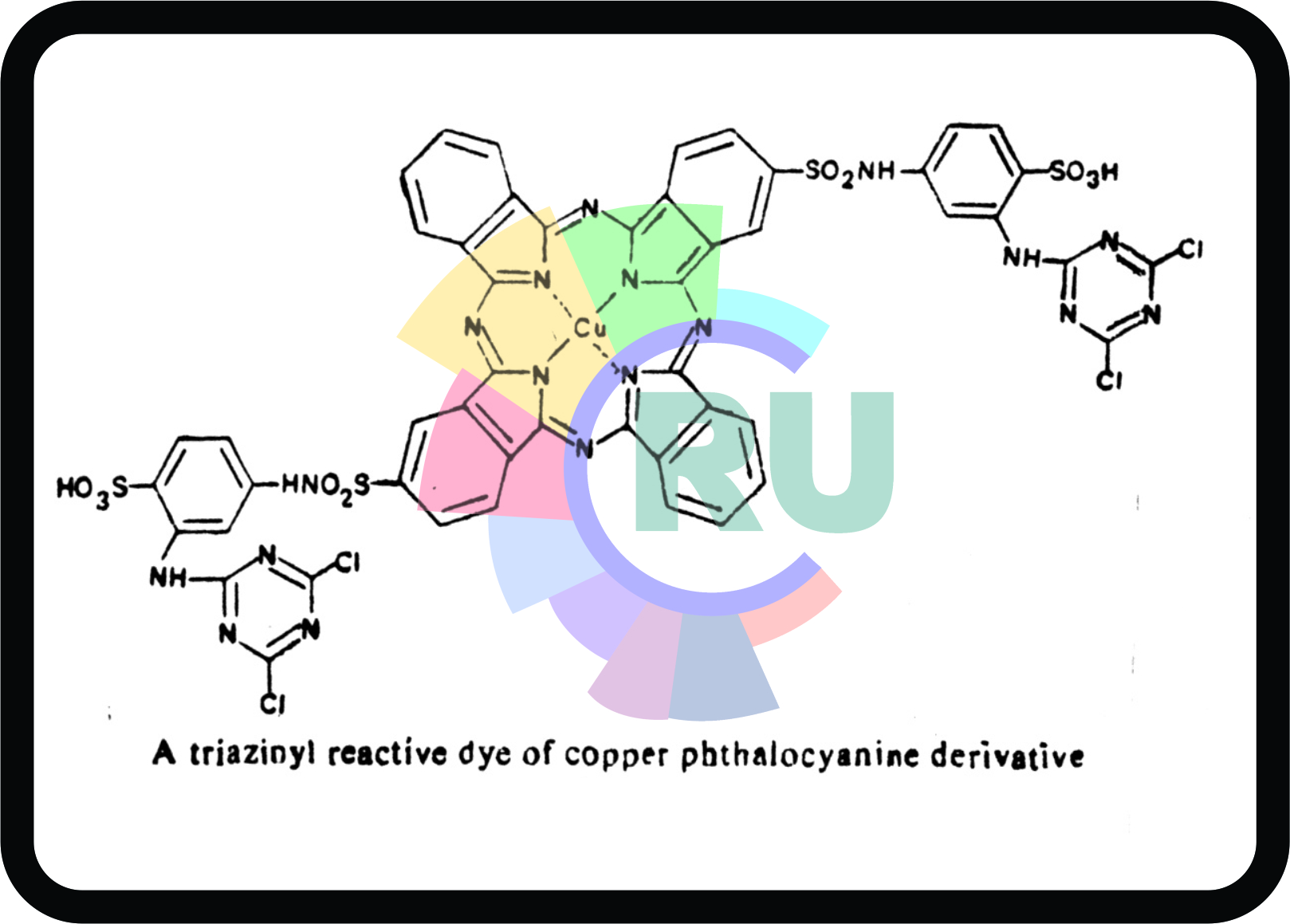
Phthalacyanine dyes:- (Part 2)
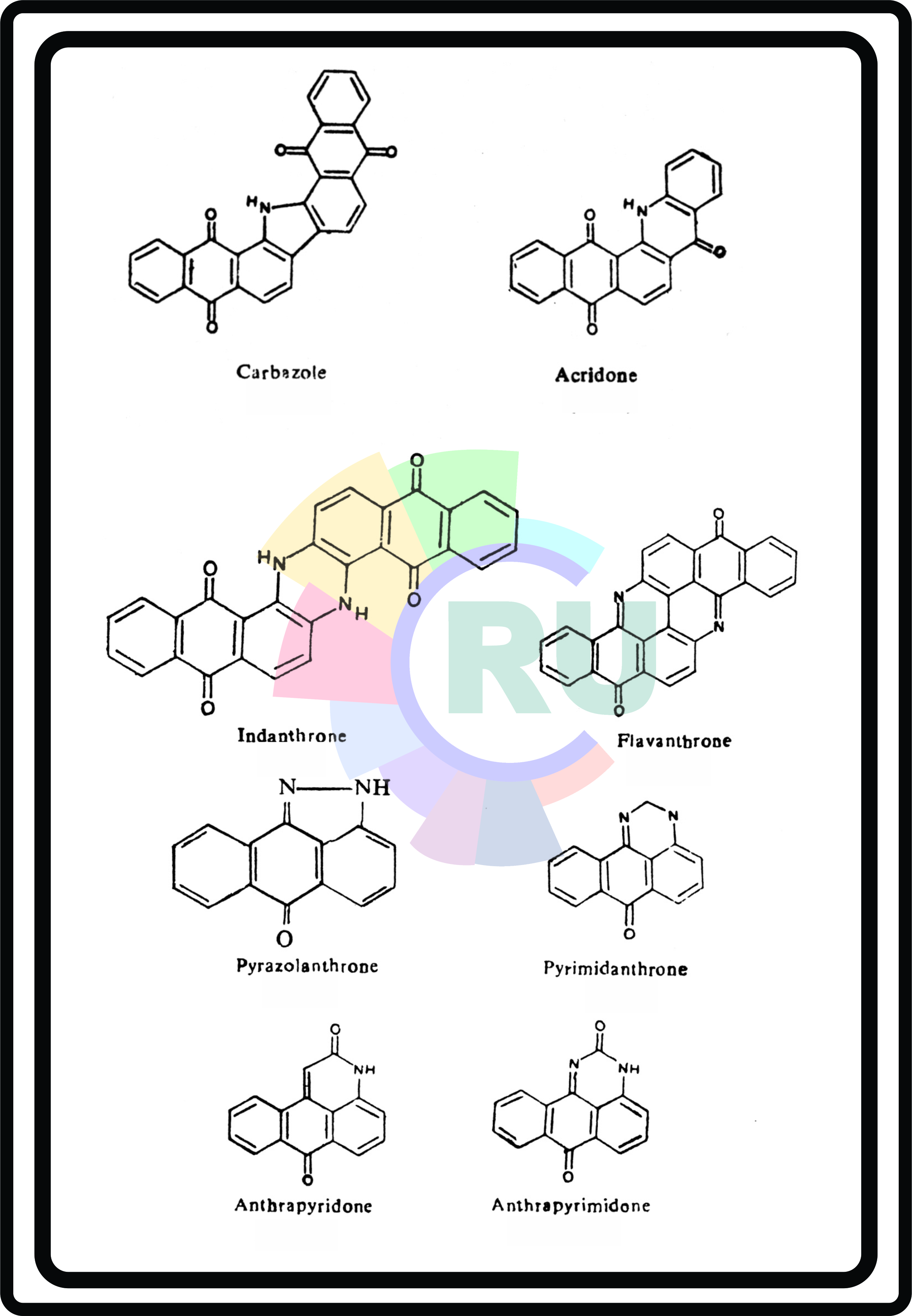
Vat dyes containing anthraquinone with fused hete
Vat dyes containing anthraquinone with fused heter
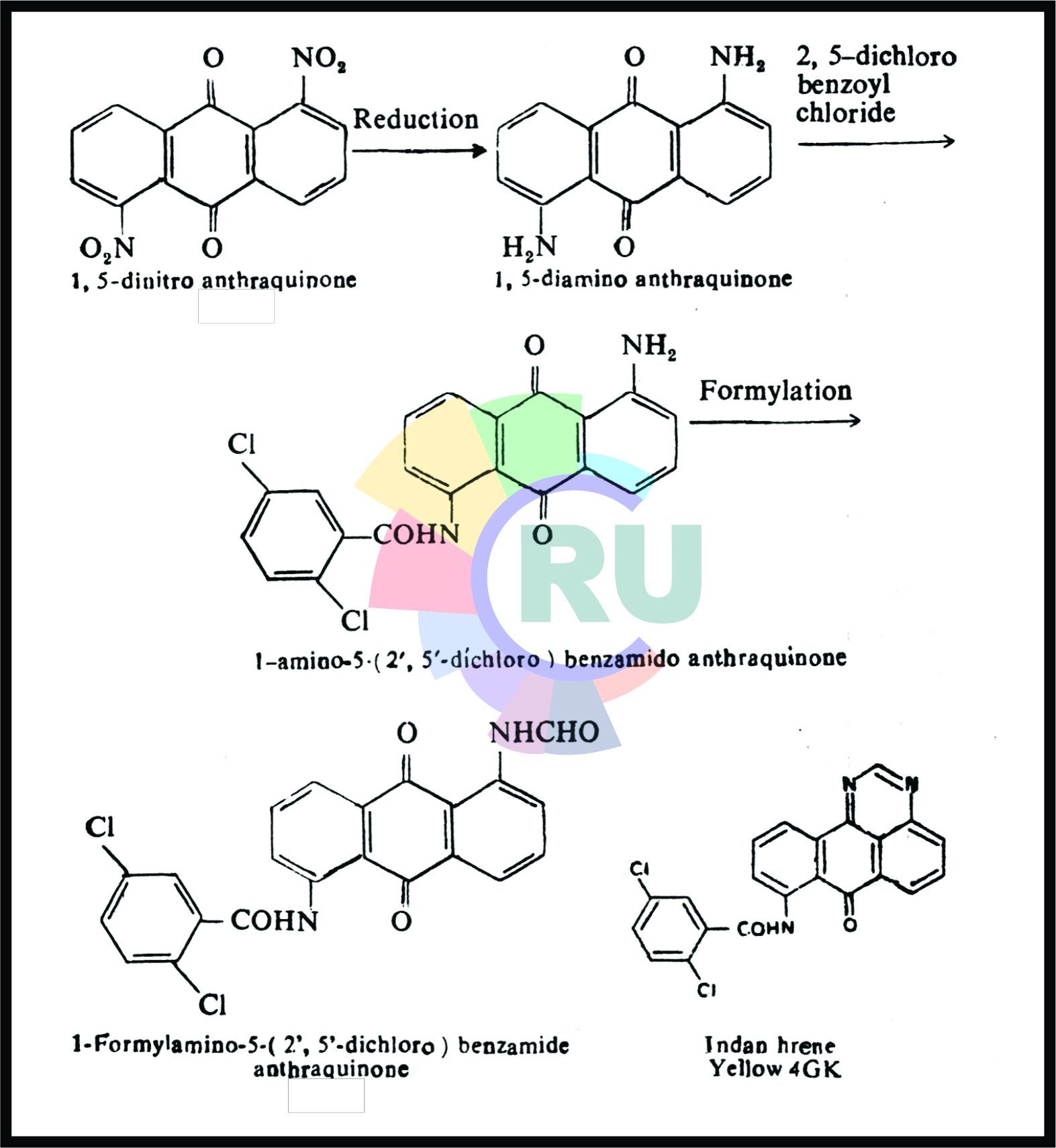
Infra-red absorbing dyes:- Explained in brief
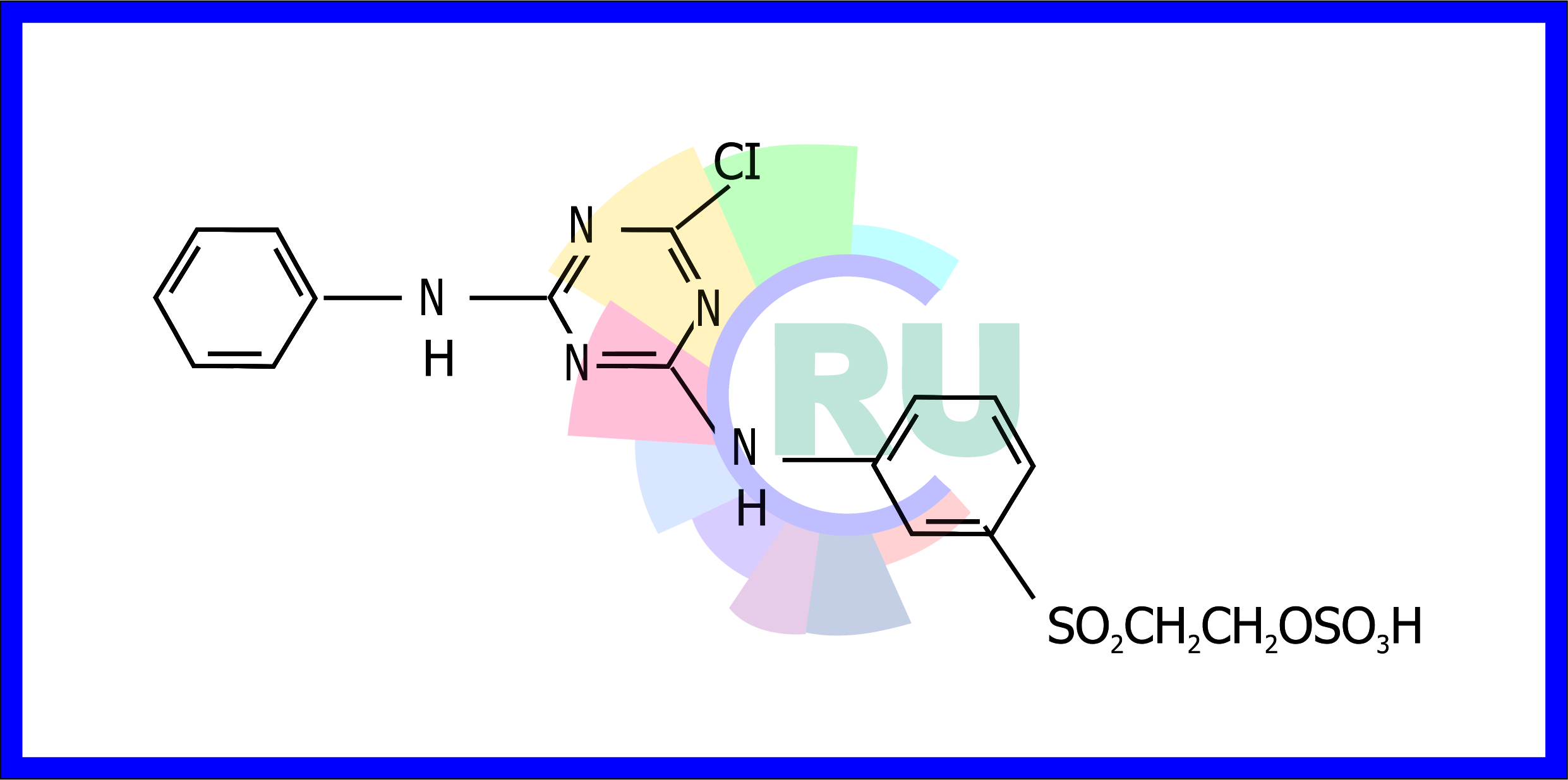
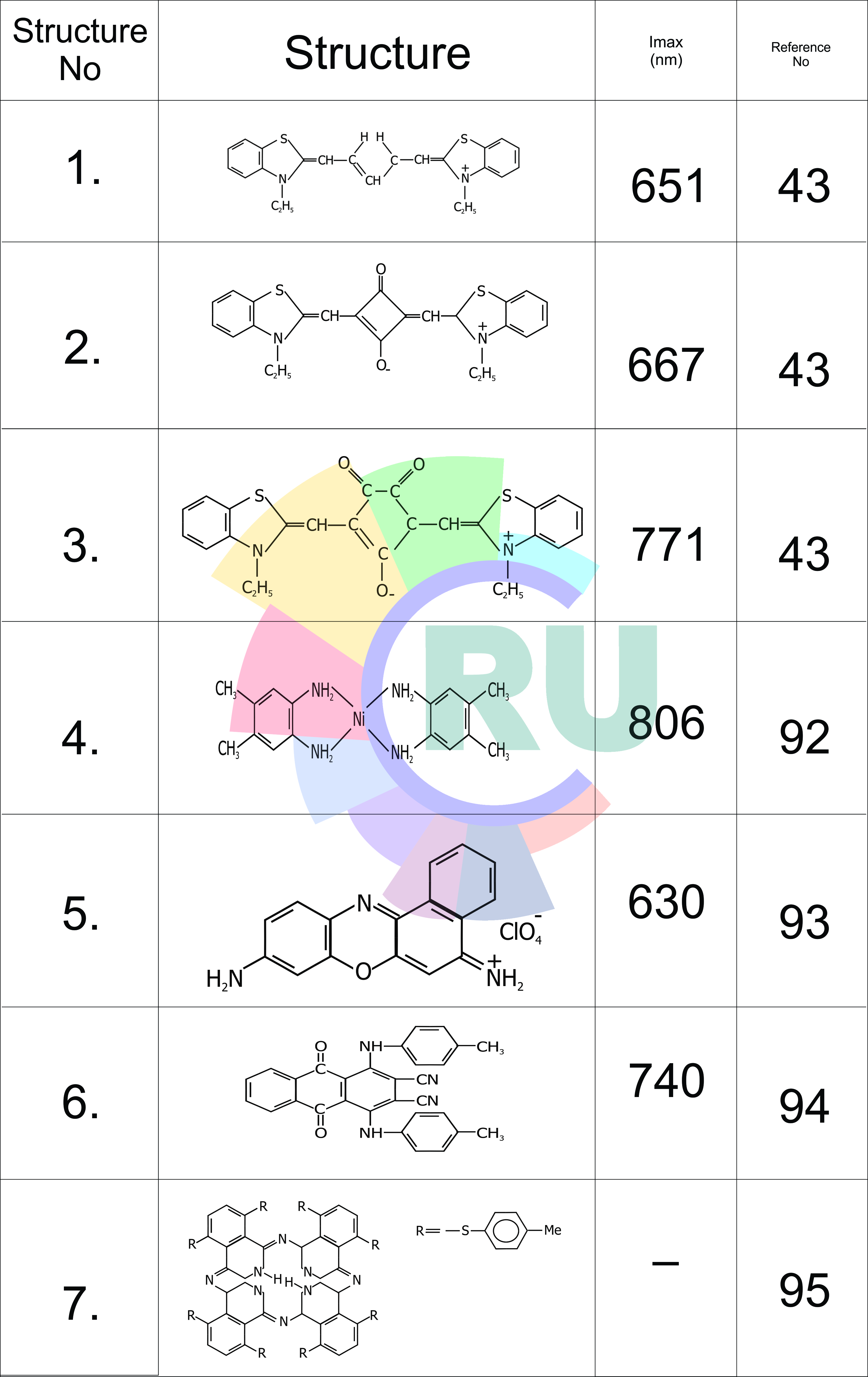
A universal dye for fibres:-
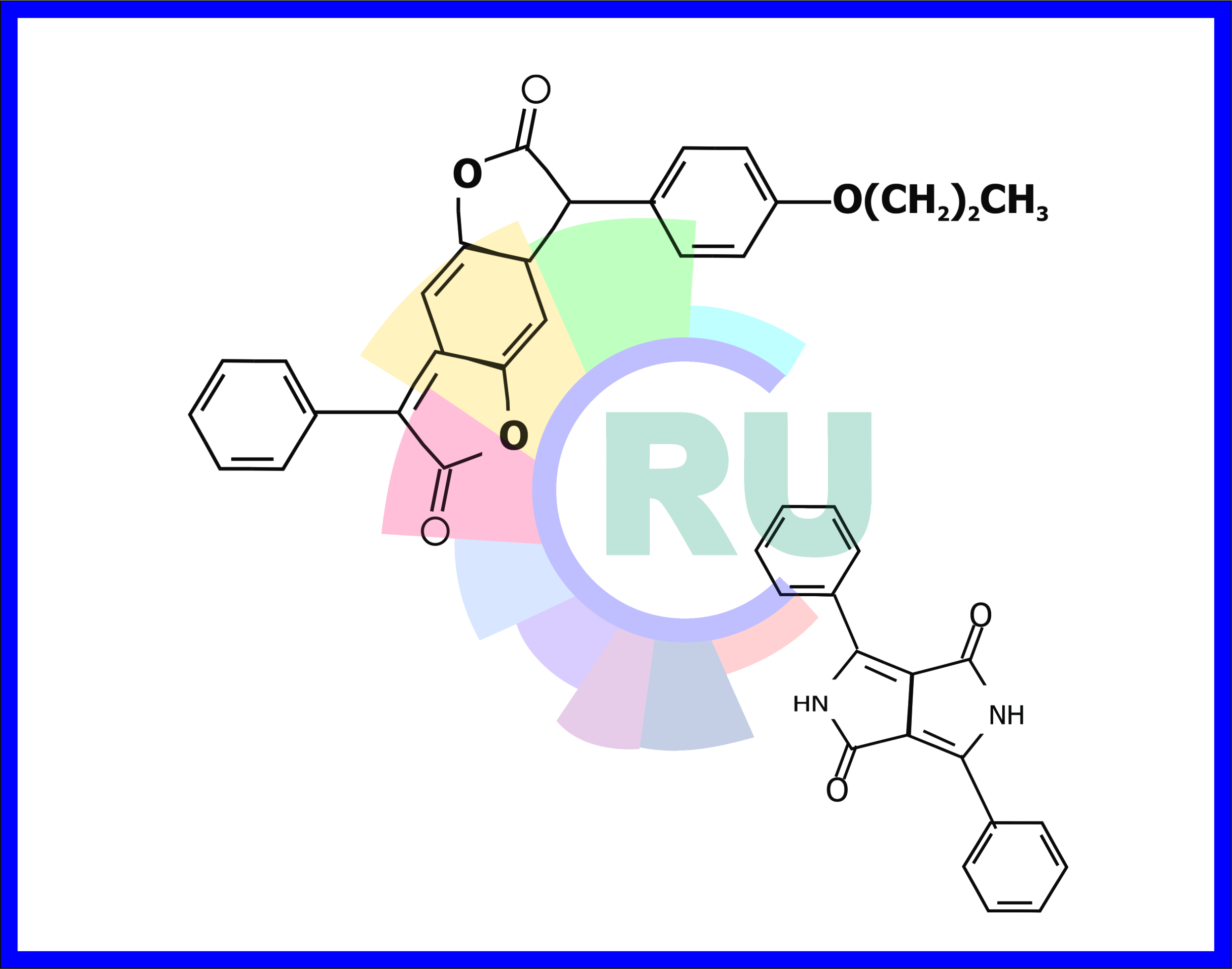
THE POTEBTLAL FOR NEW CHROMOPHORES:-
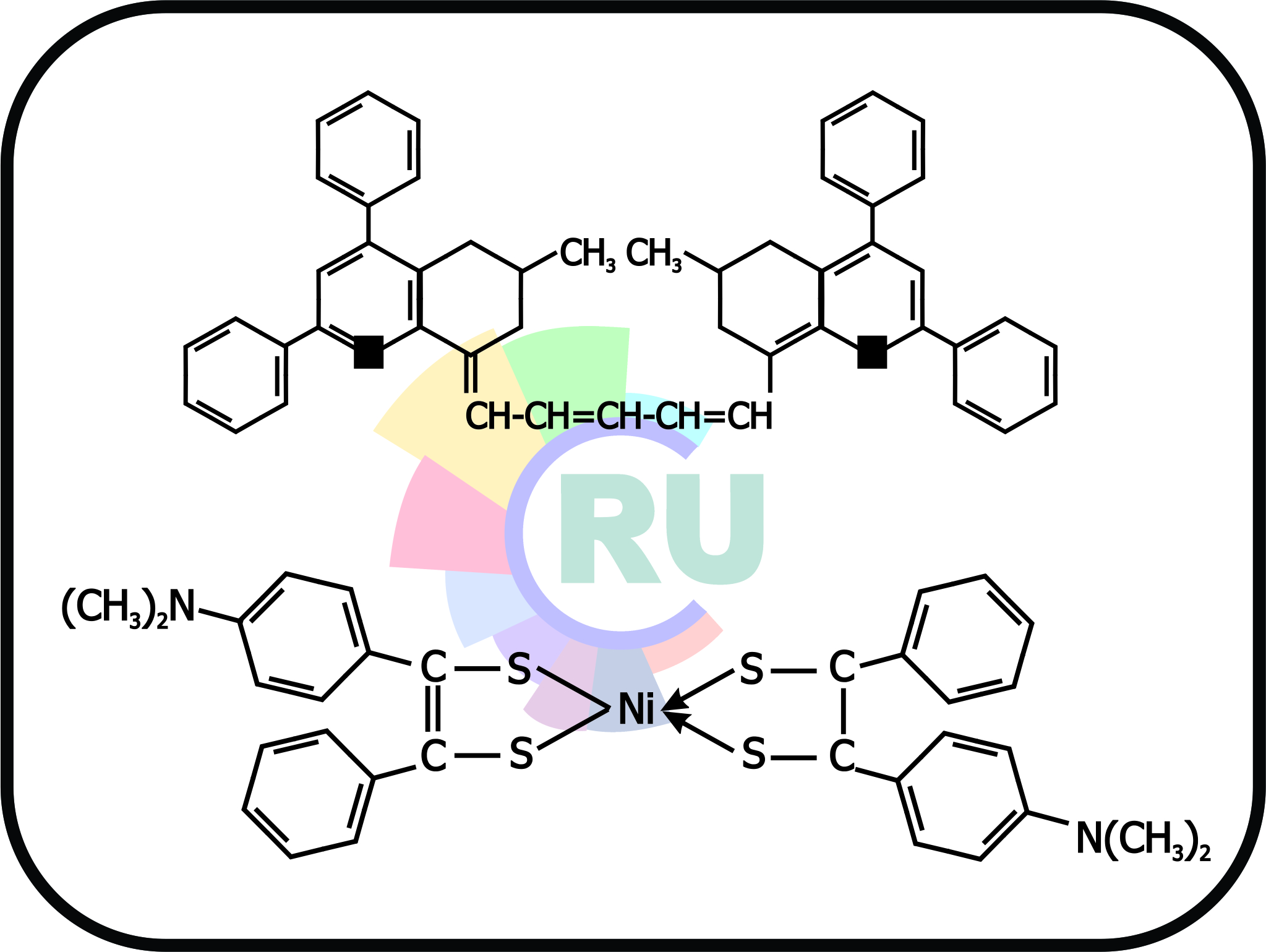
Q-switch dyes:- Explained in brief
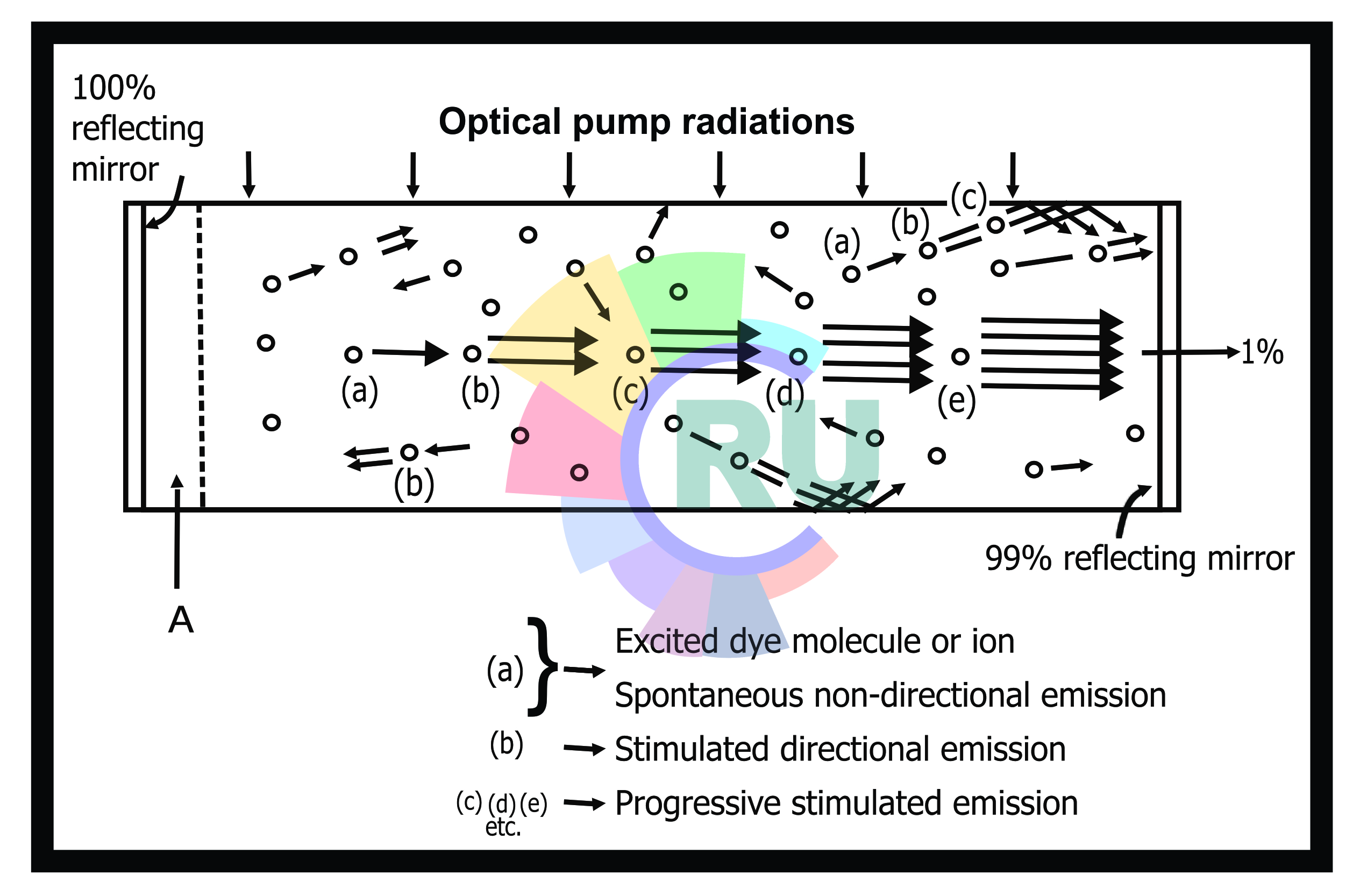
Process of Decolorisation:-
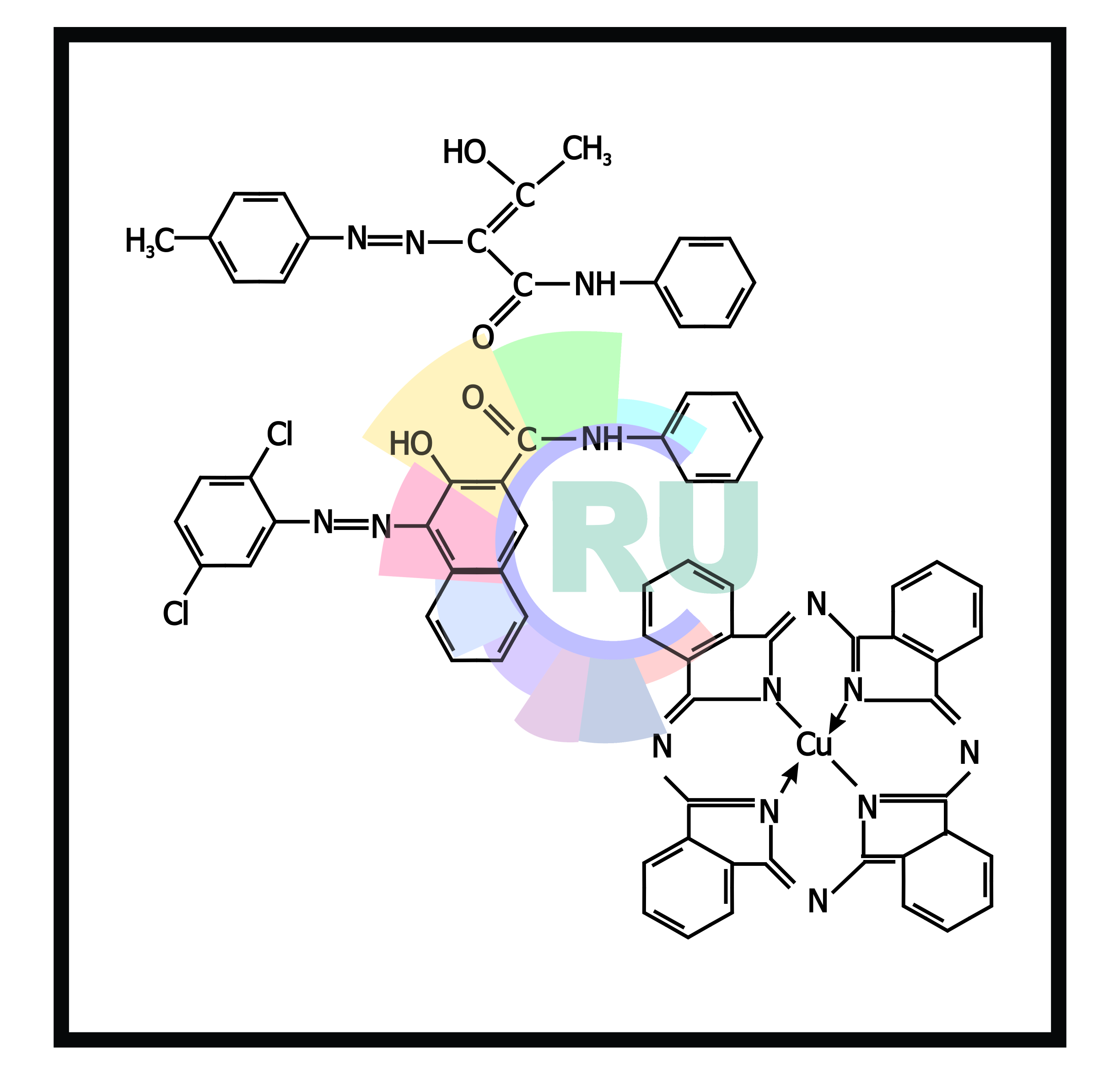
Colour photocopying:- Explained in brief
Mead process:- Explained in brief
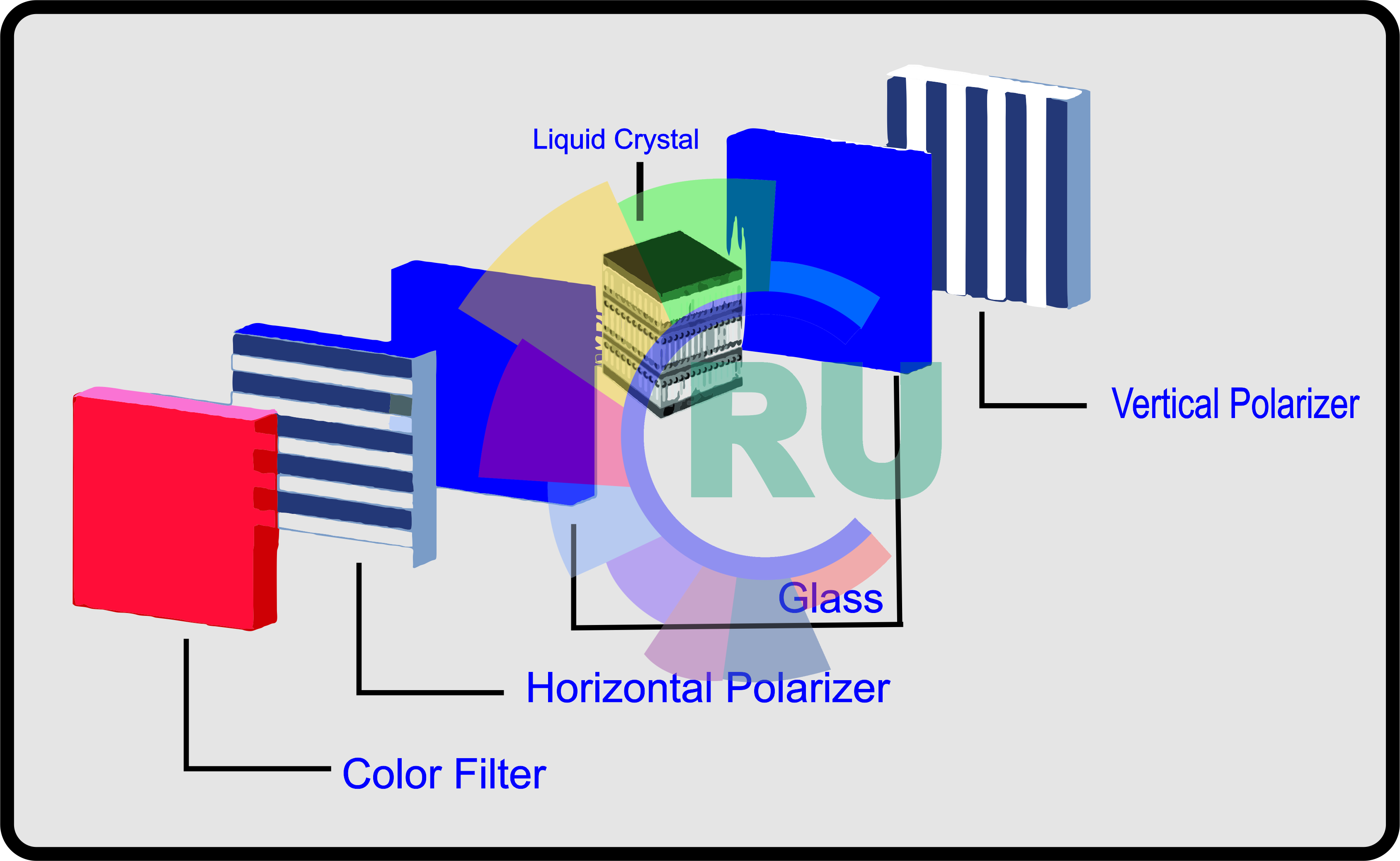
DYES FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAYS (LCD'S) (Part 1)
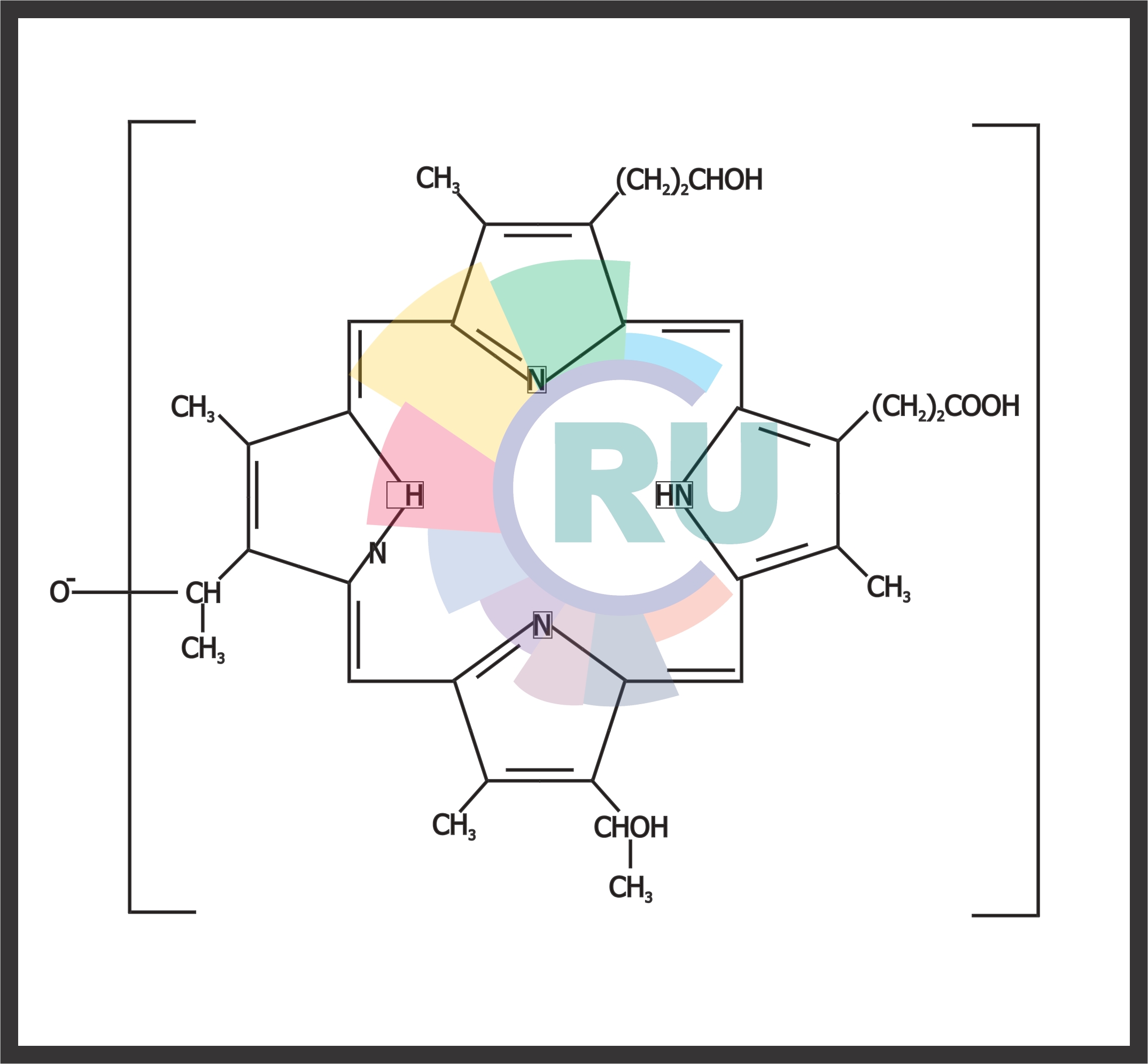
Photosensitisers and dyes for PDT:- (Part 1)
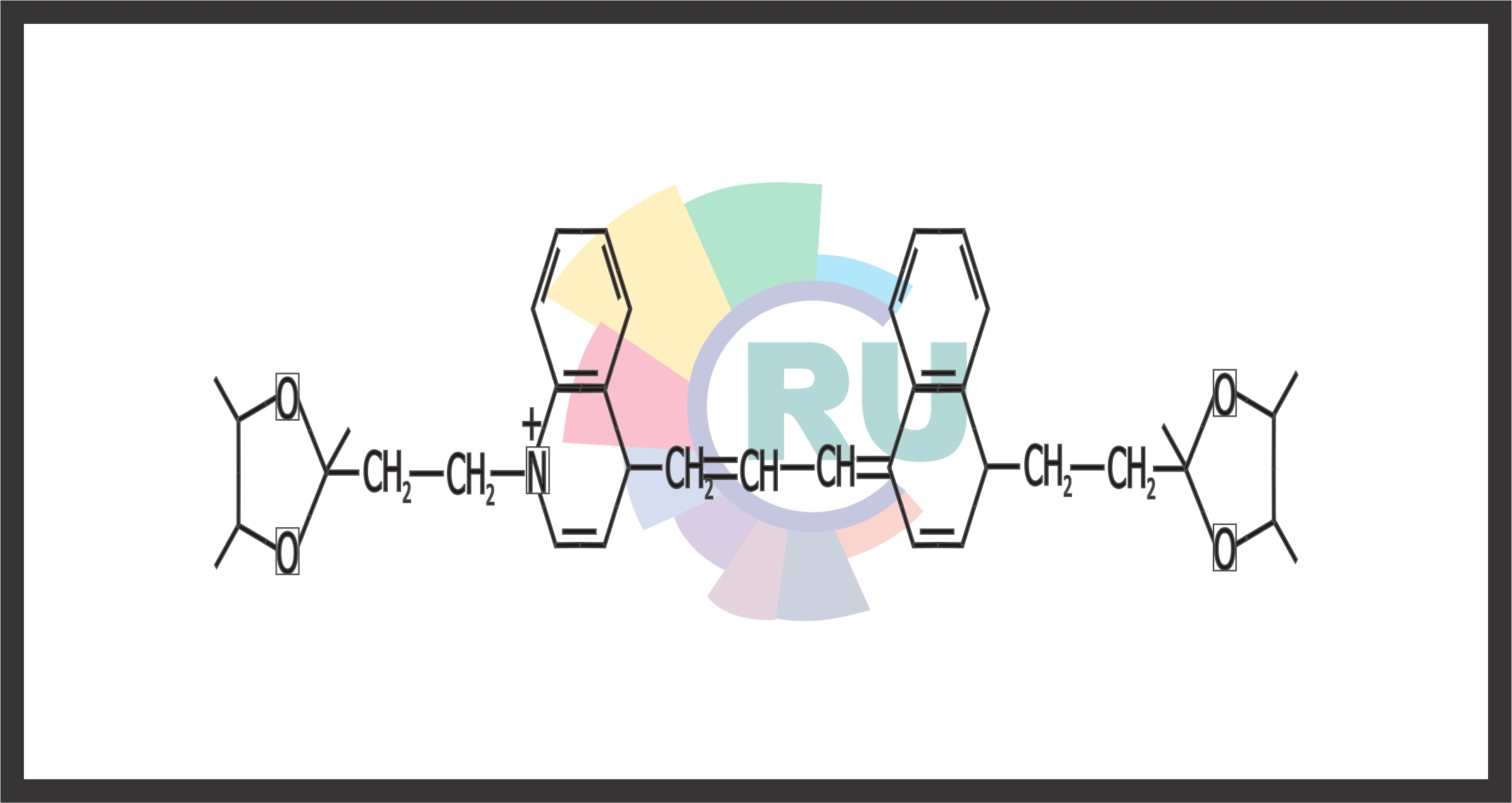
Photosensitisers and dyes for PDT:- (PART 2)

Application of acid dyes to silk (Part 1)

Application of acid dyes to silk :- (Part 2)

Premetalized (1:1 Metal Complex) Dyes on Wool : (P
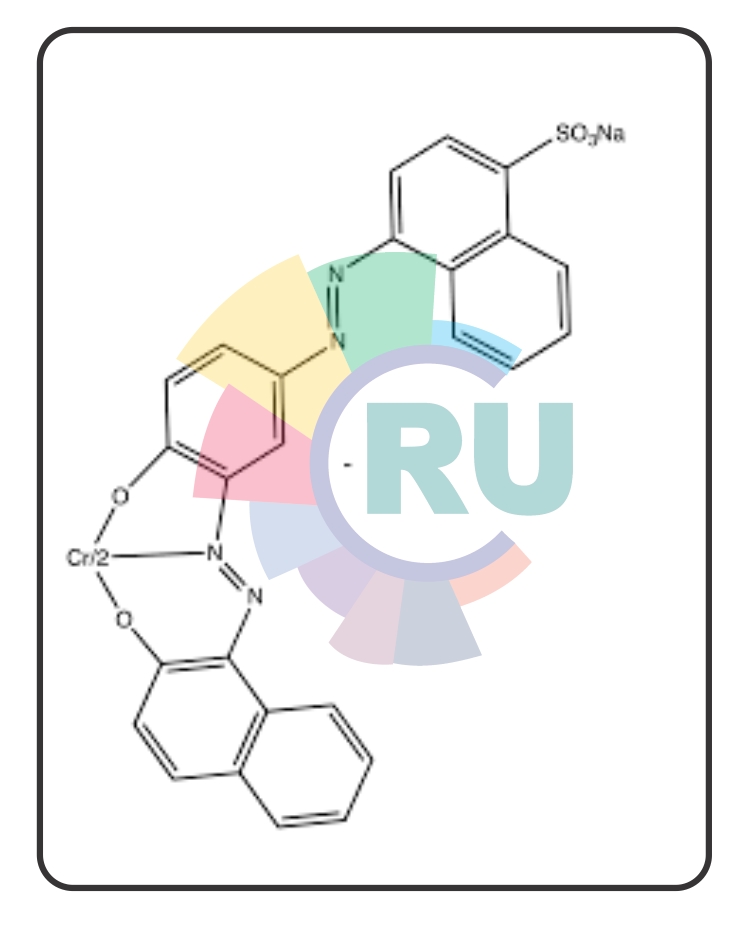
Premetalized (1:1 Metal Complex) Dyes on Wool : (P

Organic Fixing Agents : (Part 1)

Organic Fixing Agents : (Part 2)

High-temperature aqueous dyeing:- (Part 1)

High-temperature aqueous dyeing : (Part 2)
Treatment of liquid effluent at the plant before d

BIOLOGICAL AND MEDICAL USES OF DYES:-

Dyeing of cotton, Linen, Rayon, Wool, Silk and Mis

Dyeing of cotton, Linen, Rayon, Wool, Silk and Mis

Aftertreatment of Direct Dyes:-

Acetic acid:- Explained in brief
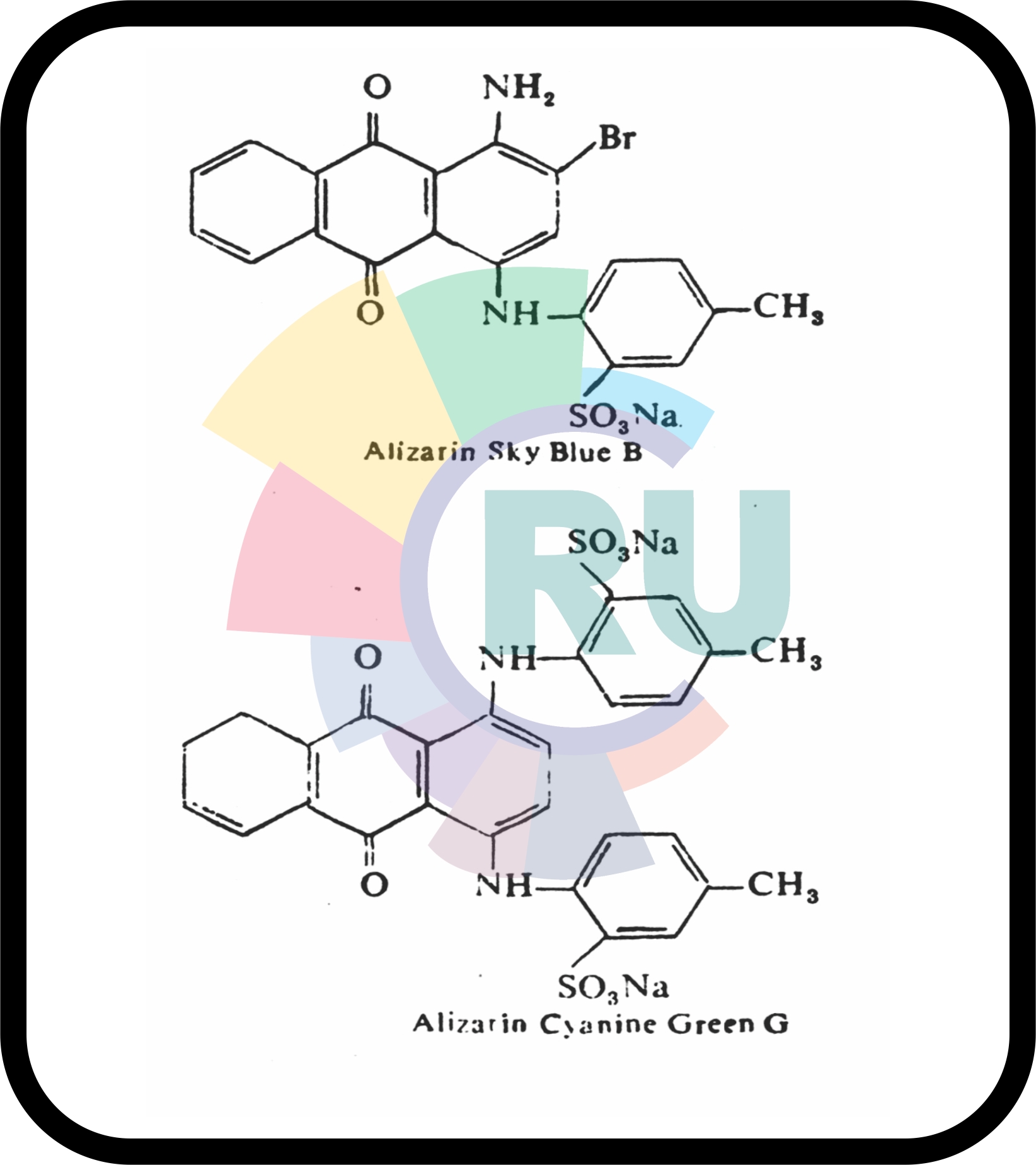
Acid anthraquinone dyes:-

The general rules of Actual Dyeing Process:-

Semi-continuous methods fall into two broad catego
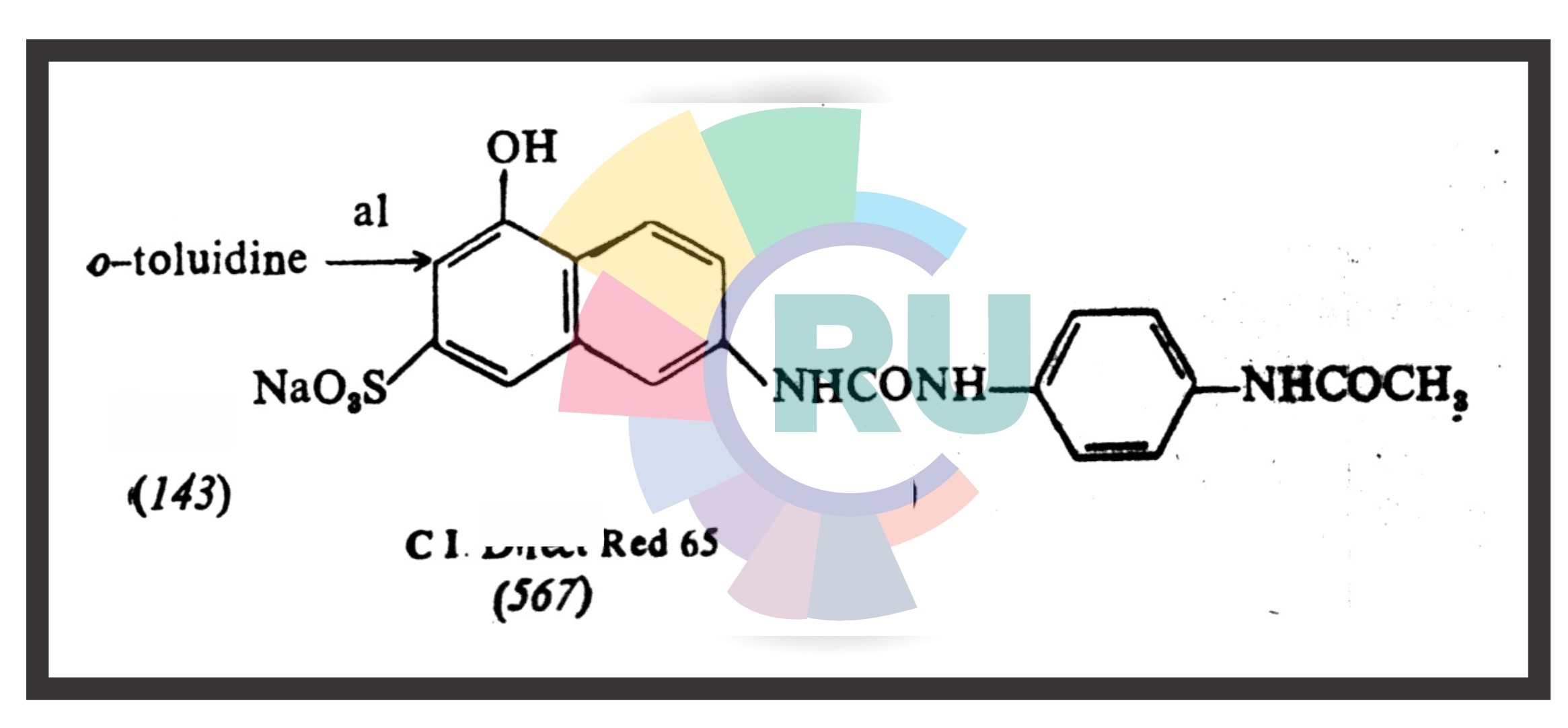
Monoazo direct dyes:- Explained in brief
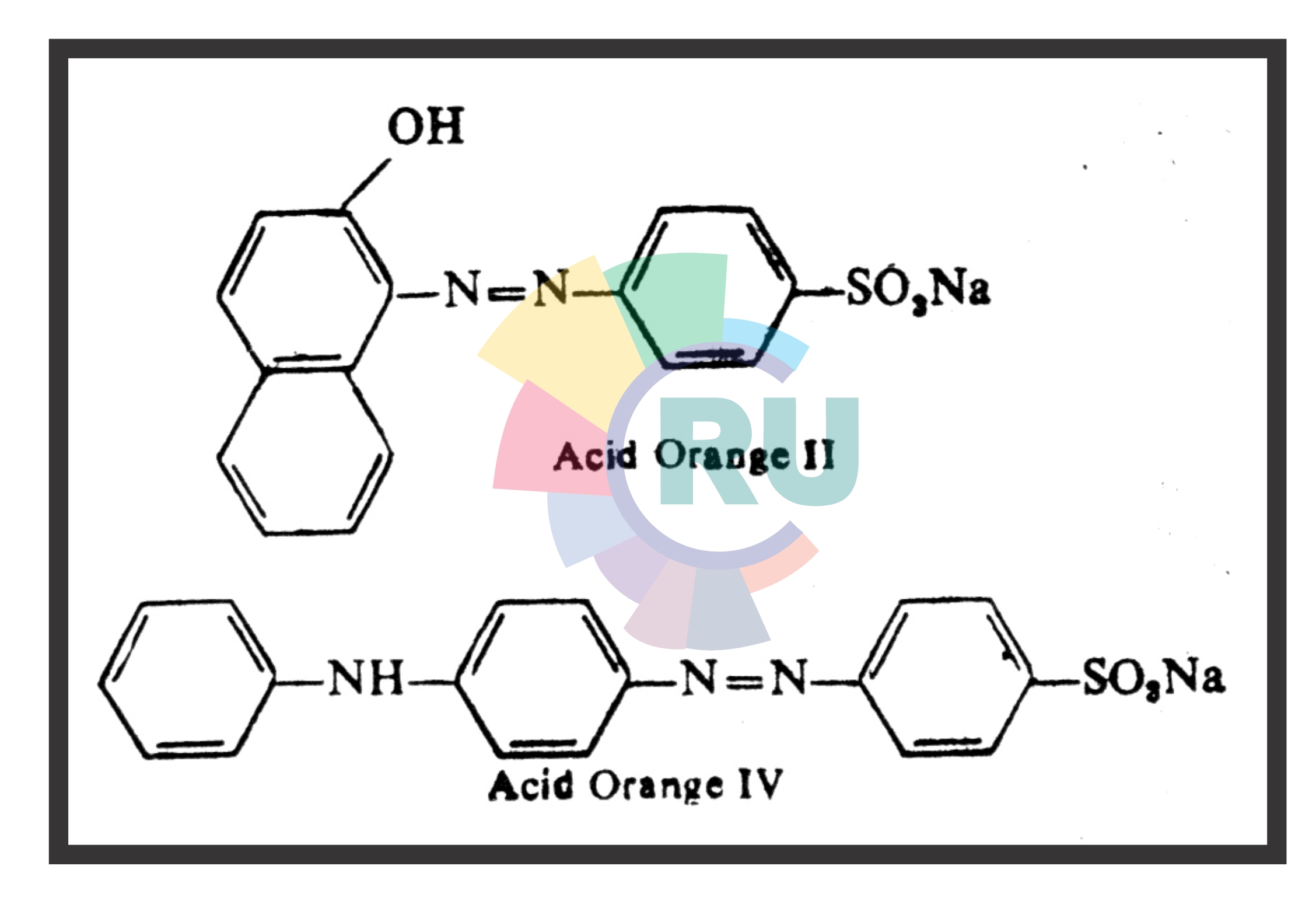
Monoazo Acid dyes:- (Part 1)
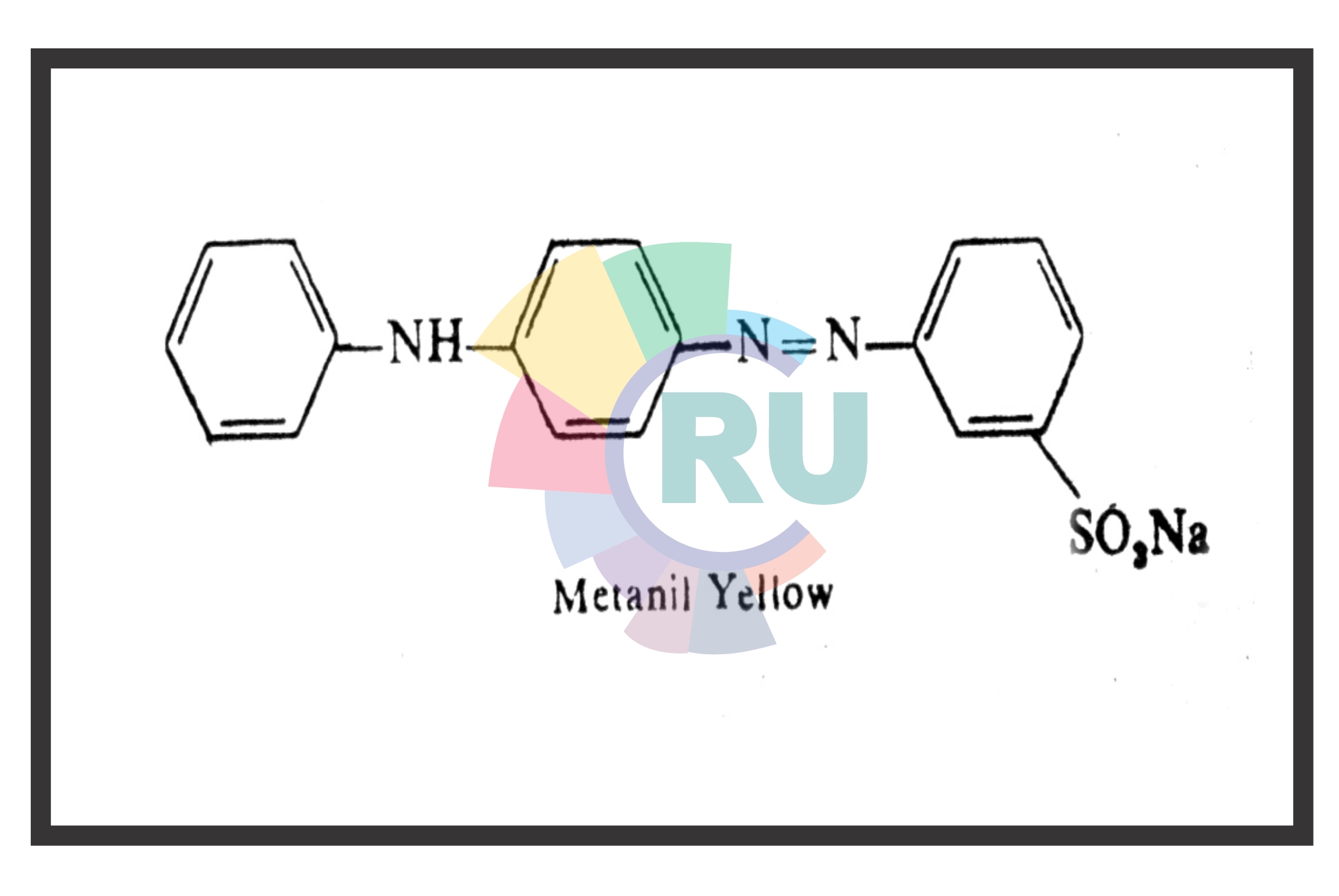
Monoazo Acid dyes:- (Part 2)
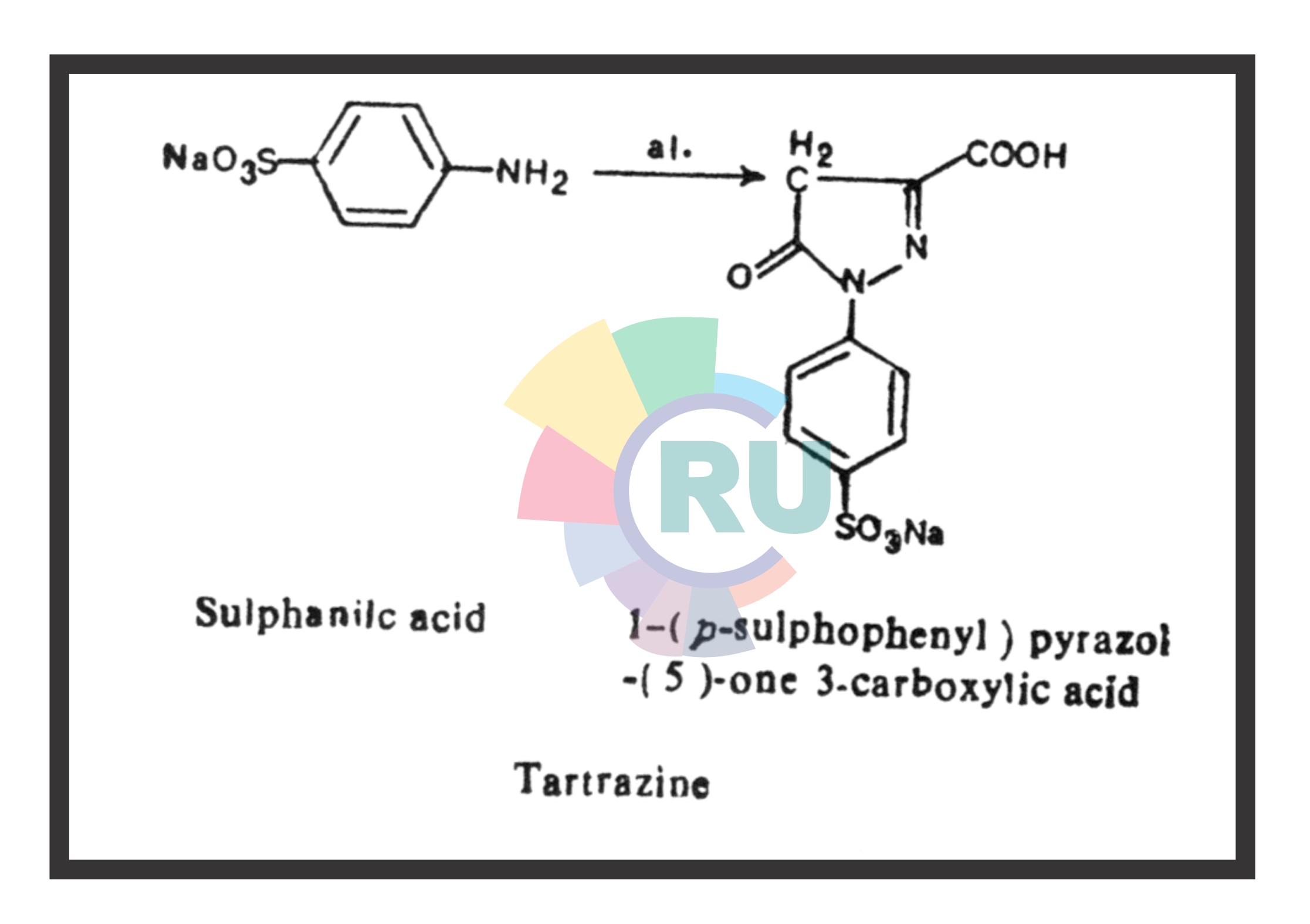
Monoazo food colours:- (Part 1)
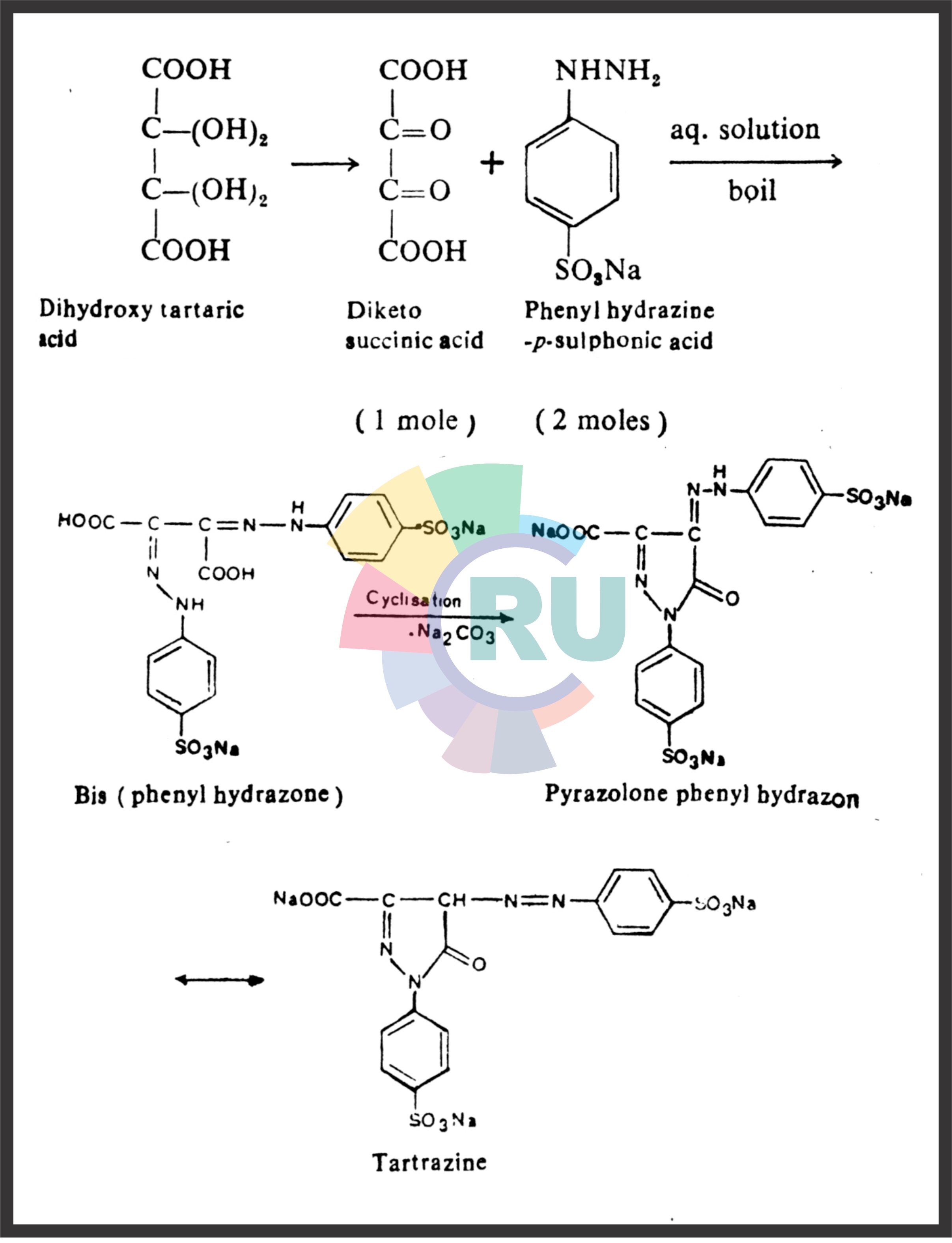
Monoazo food colours :- (Part 2)
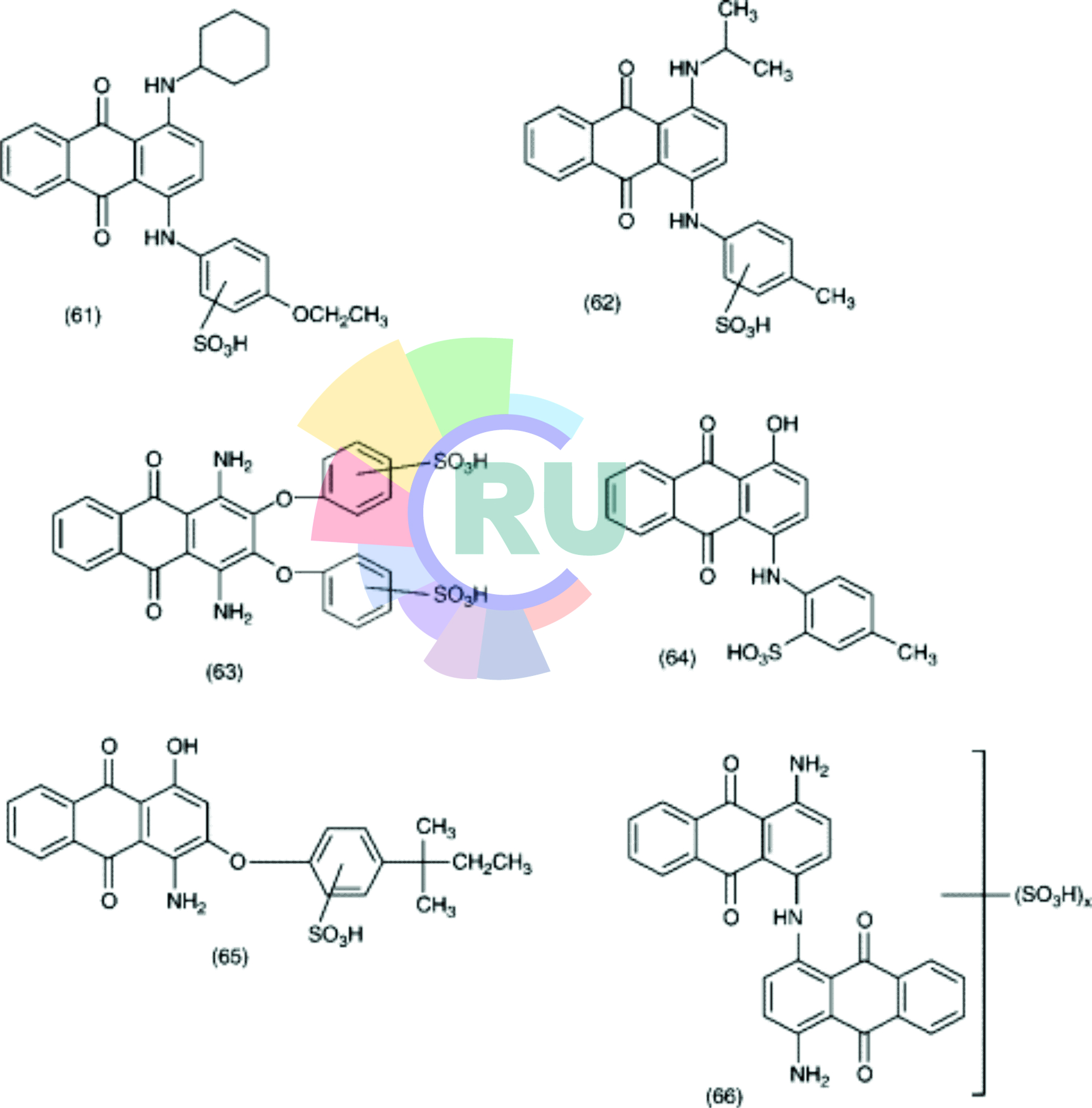
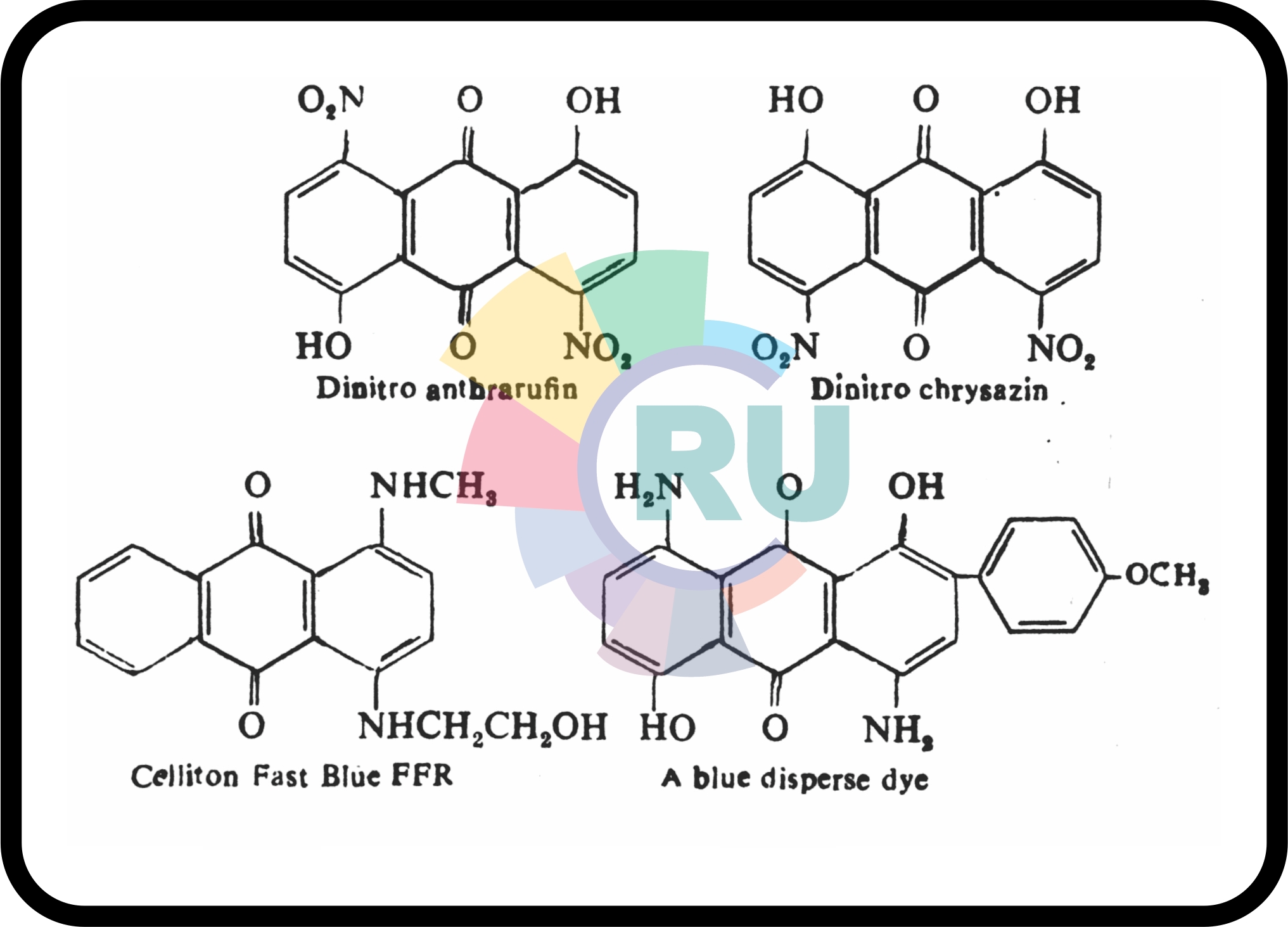
Disperse Anthraquinone Dyes - 2
Vat Dyes Containing Polycyclic Systems
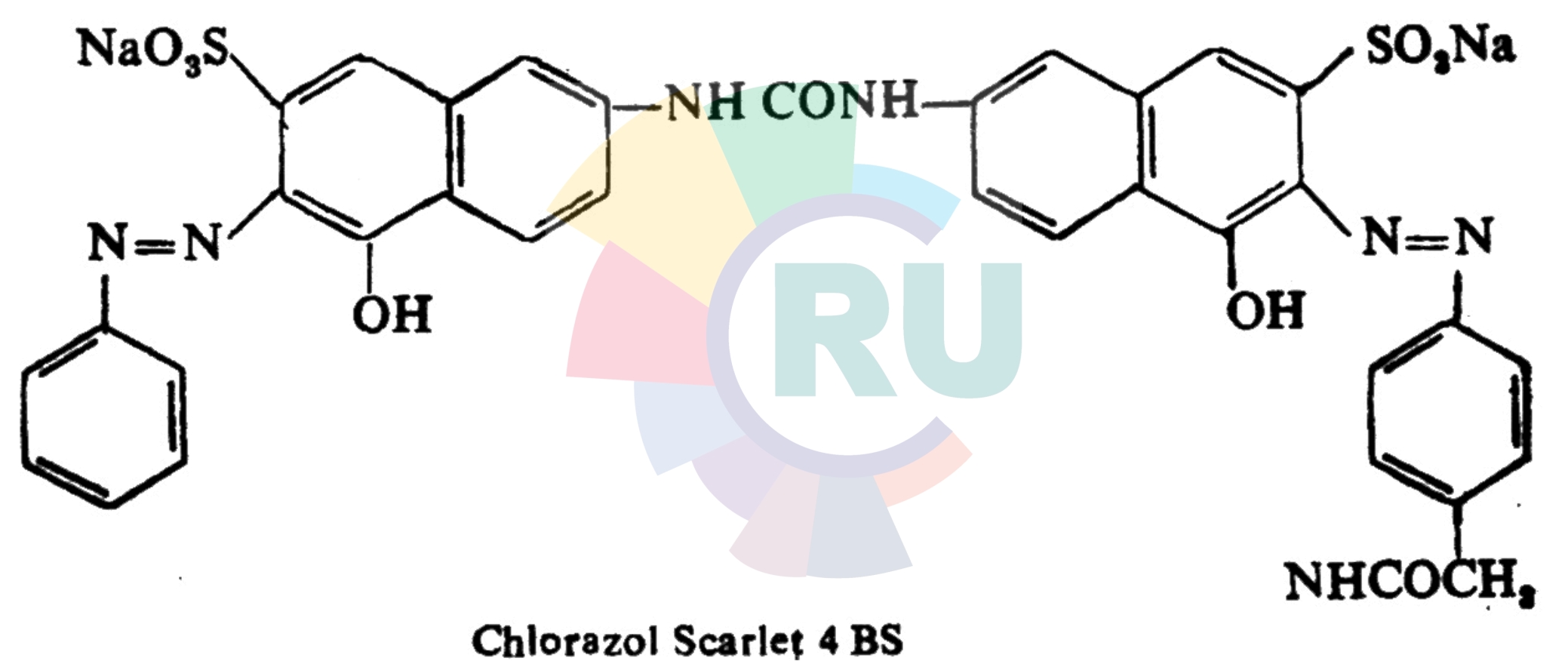
Disazo Dyes of the Type -2

What is Fiber Reactive Dye?
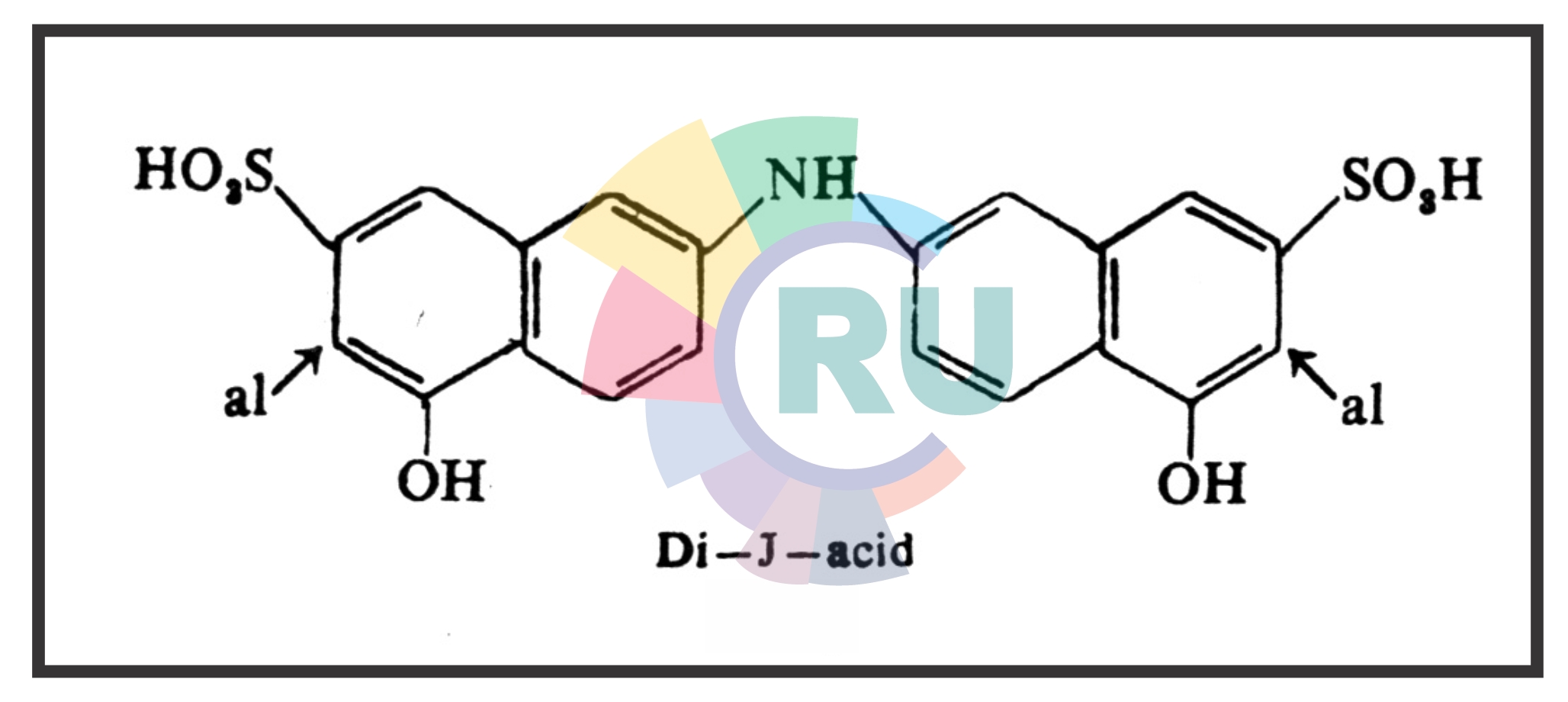
Disazo Or Bisazo Dyes:- (Part 2)
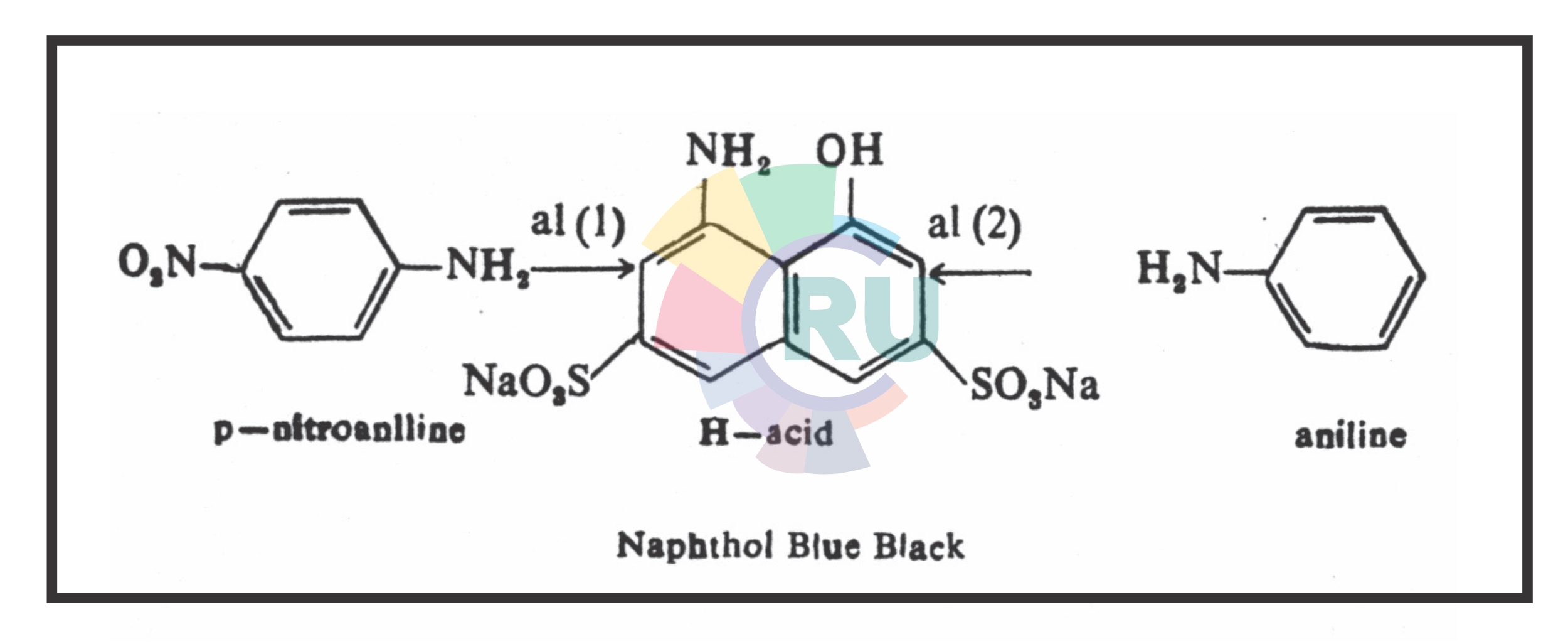
Diazo dyes of the type : A ——> Z ——> A1
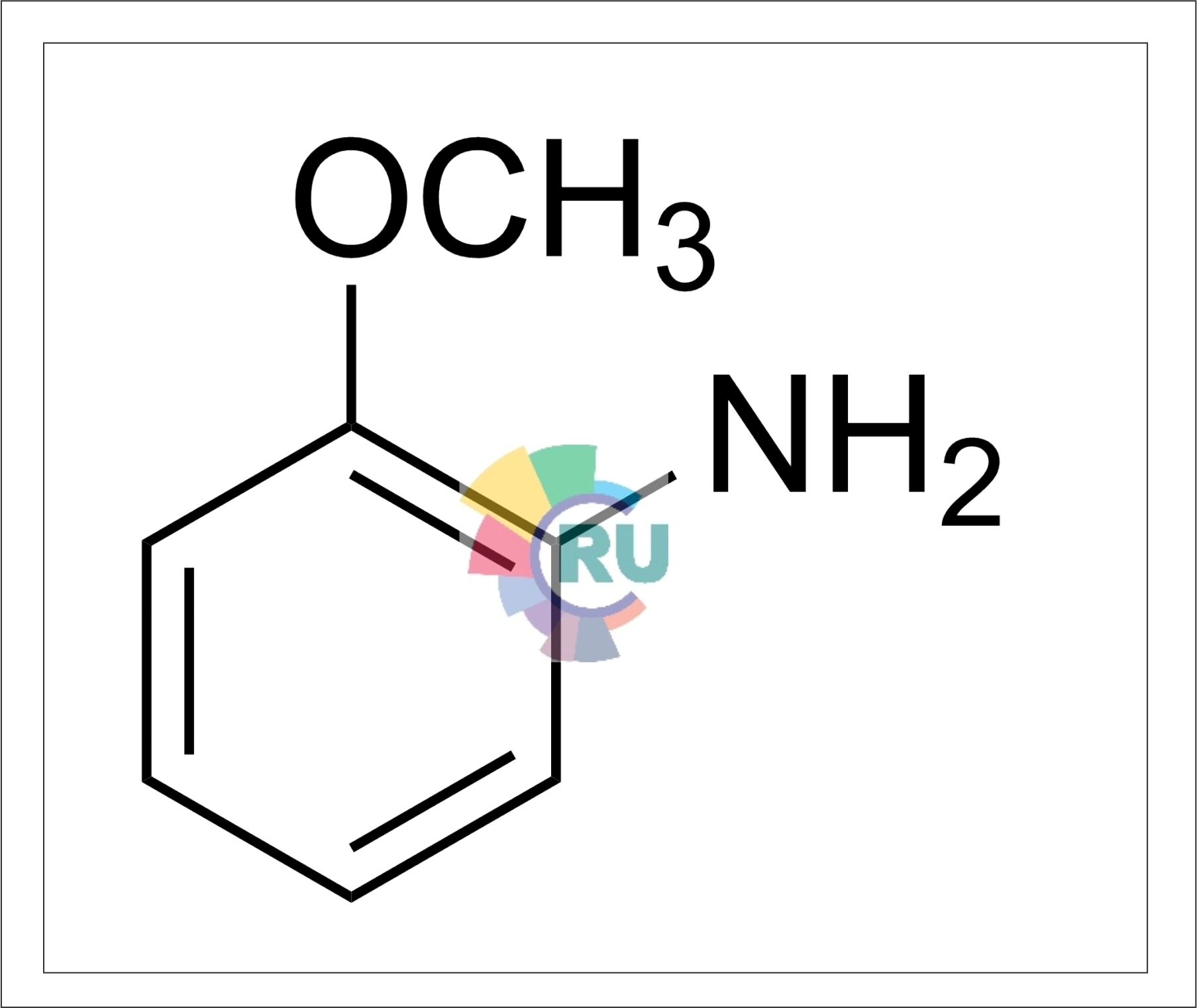
Aminoazotoluene preparation
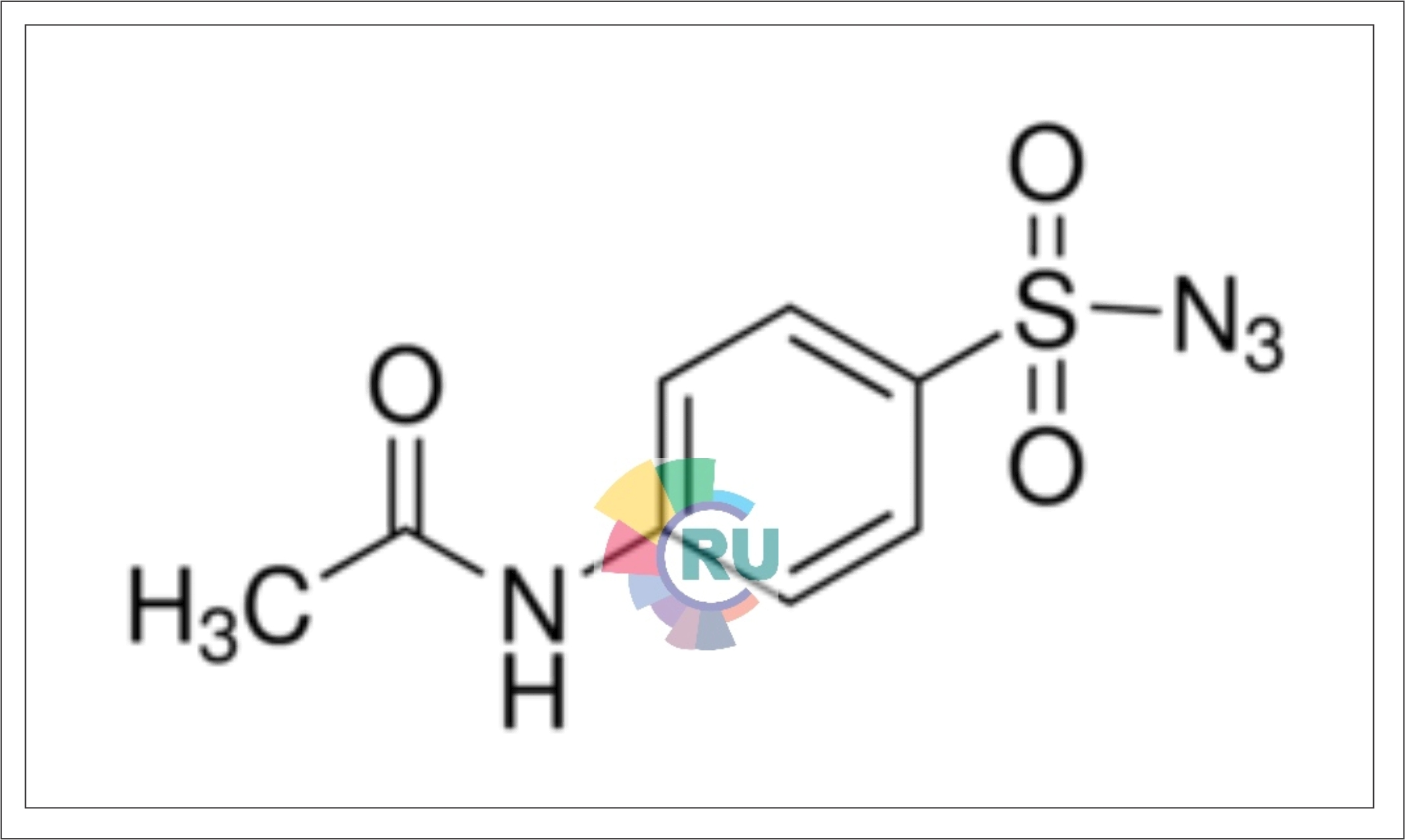
4-Acetamidobenzenesulphonylazide
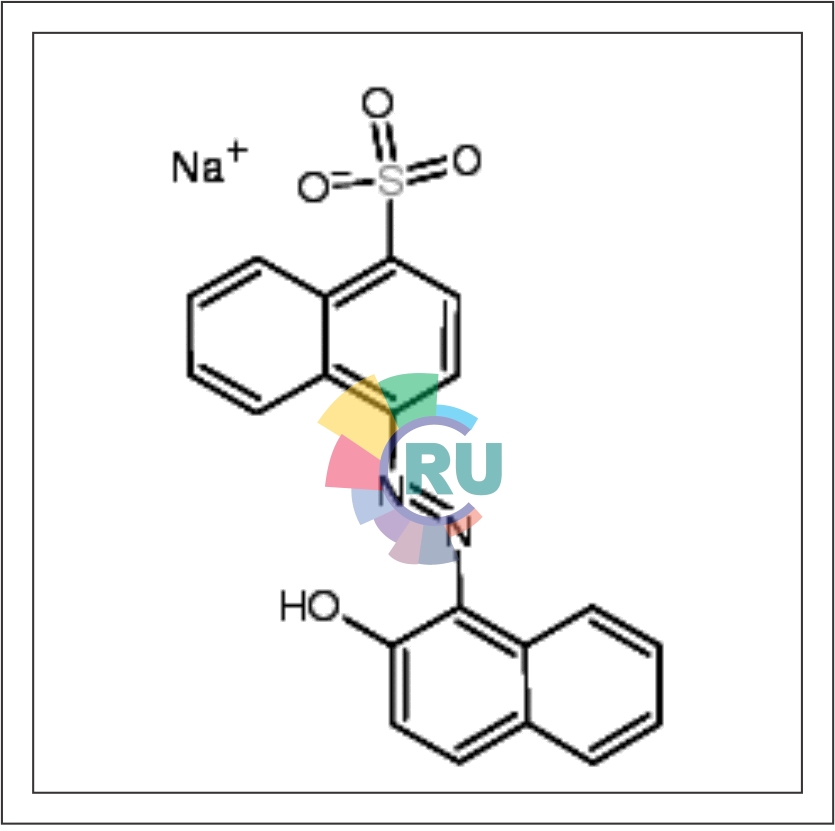
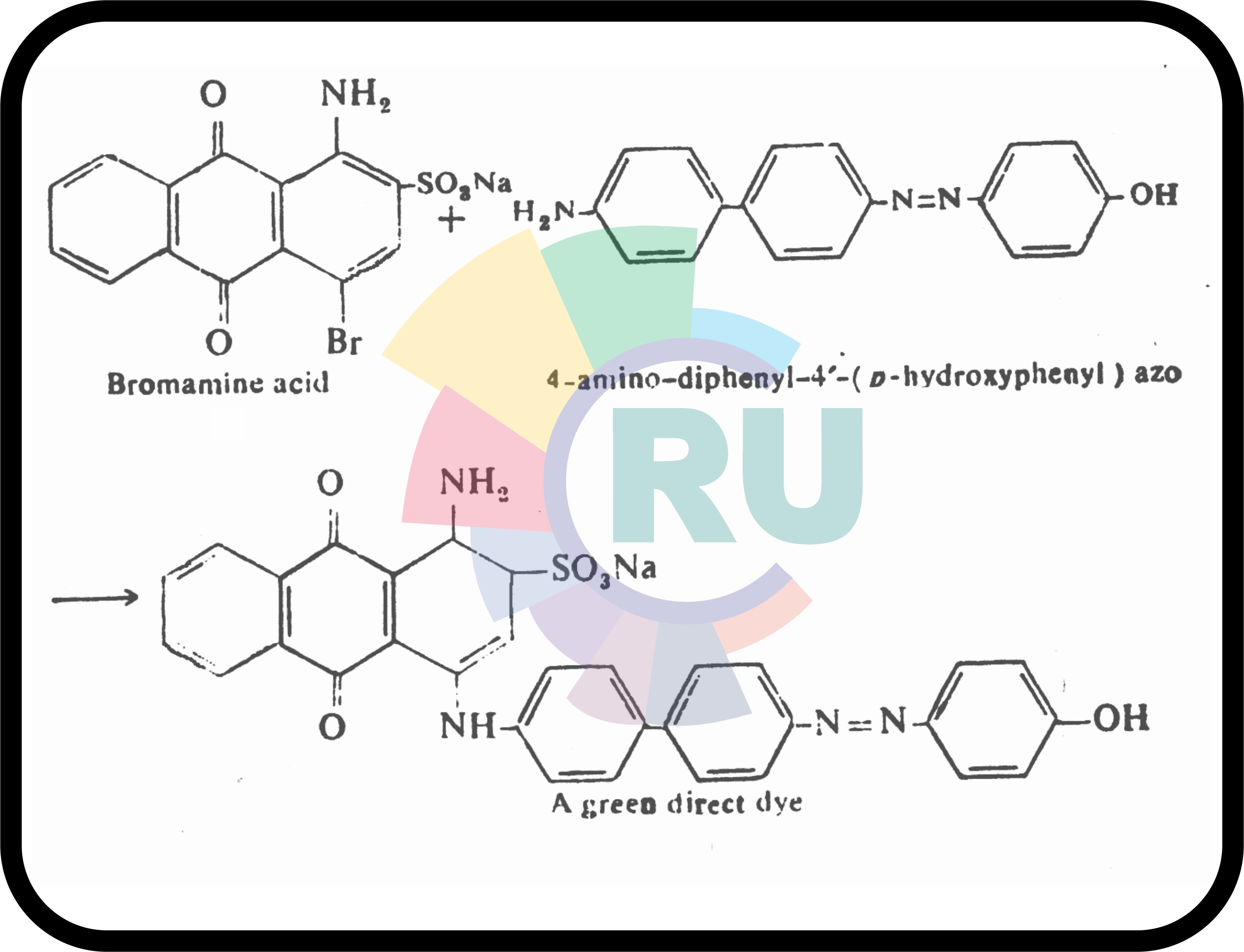
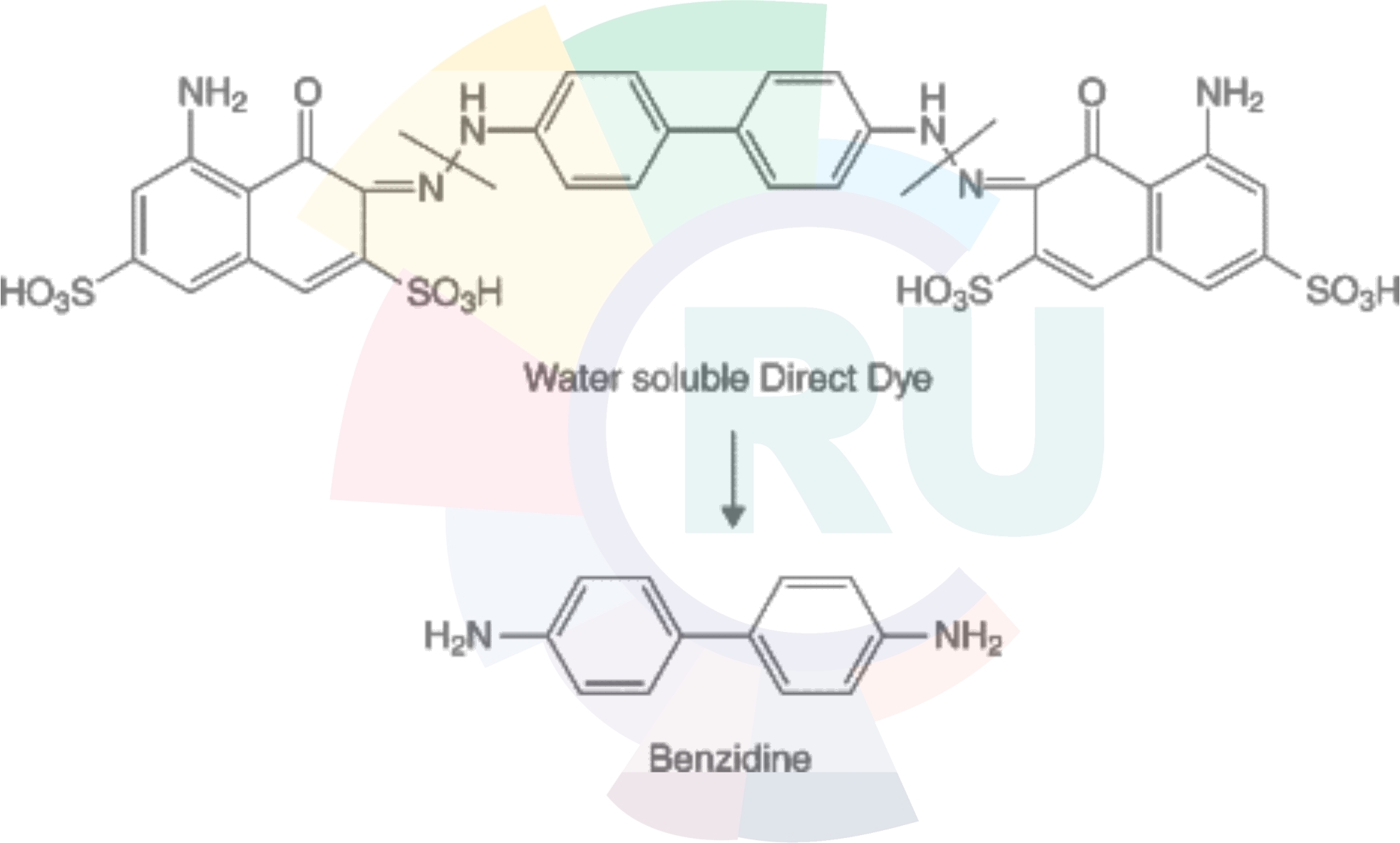
Direct dyes from benzidine congeners

What is Fiber Reactive Dye? - 1

Rainbow of No-Wrinkle Cotton
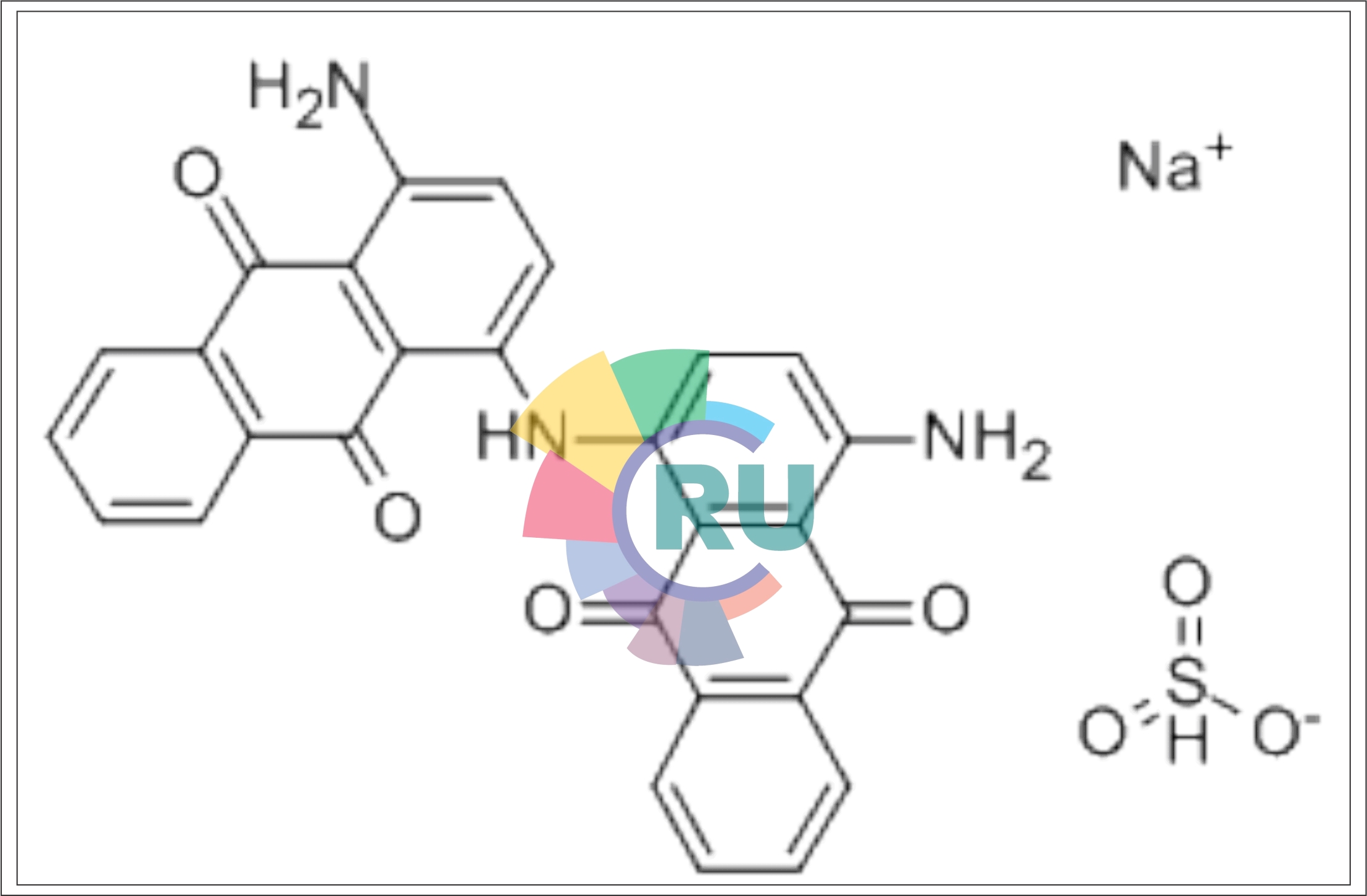
Direct dyes from benzidine congeners --1
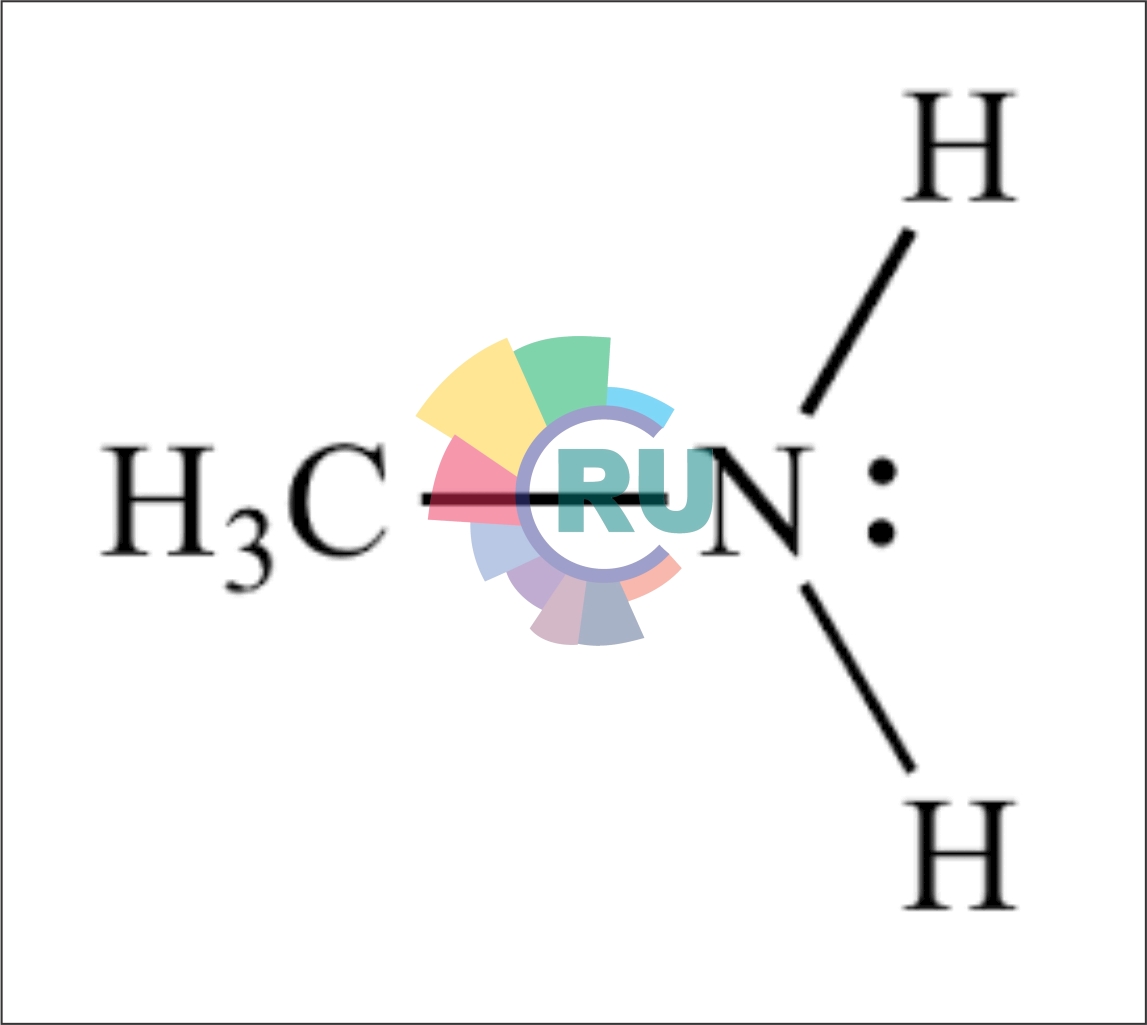
High affinity direct dyes containing cyclic amide

Chocie of Colours according to Fastness Requiremen
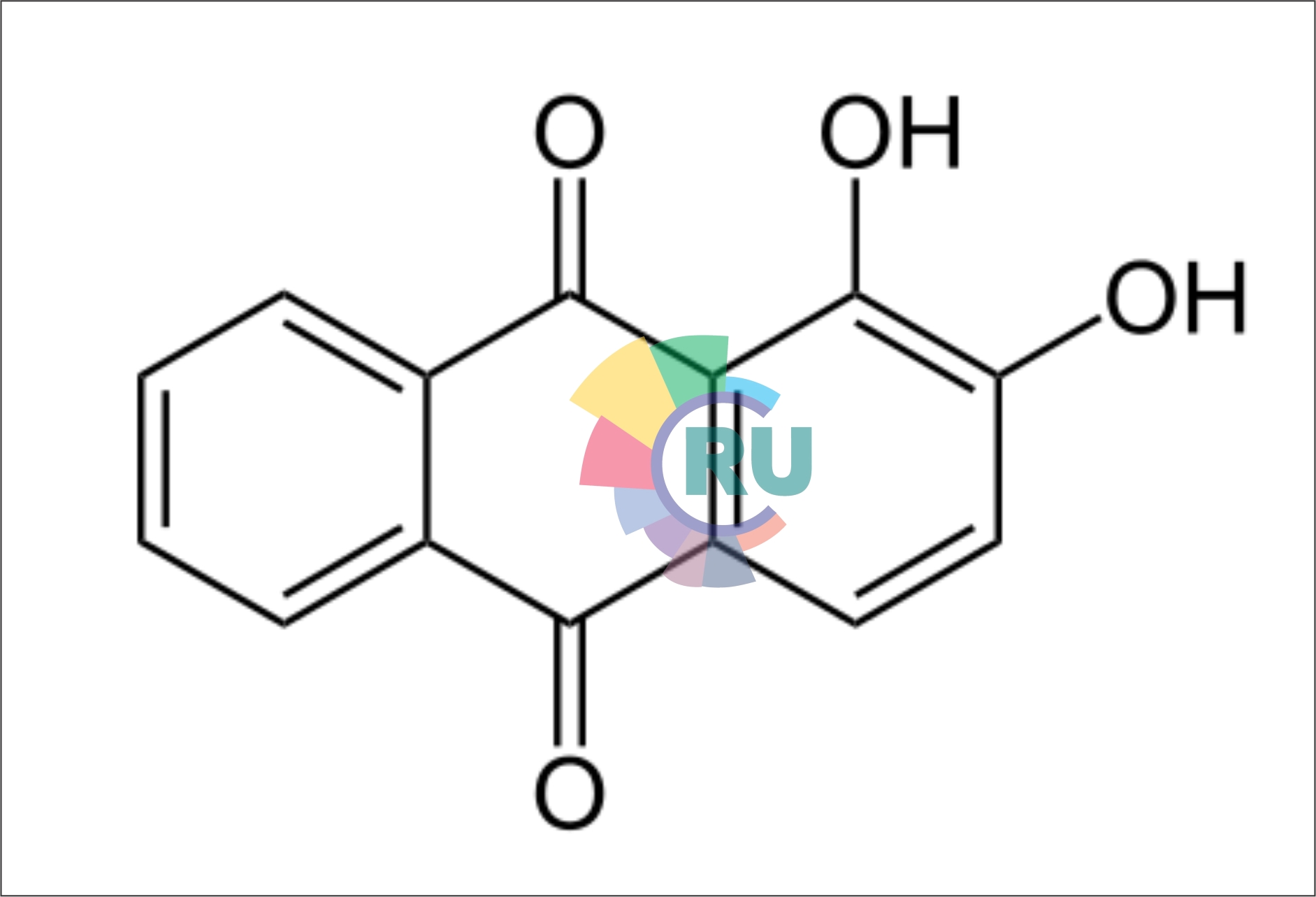
Acid anthraquinone dyes-1

NOVEL AND IMPROVED PROCESSES - Electron beam (EB)
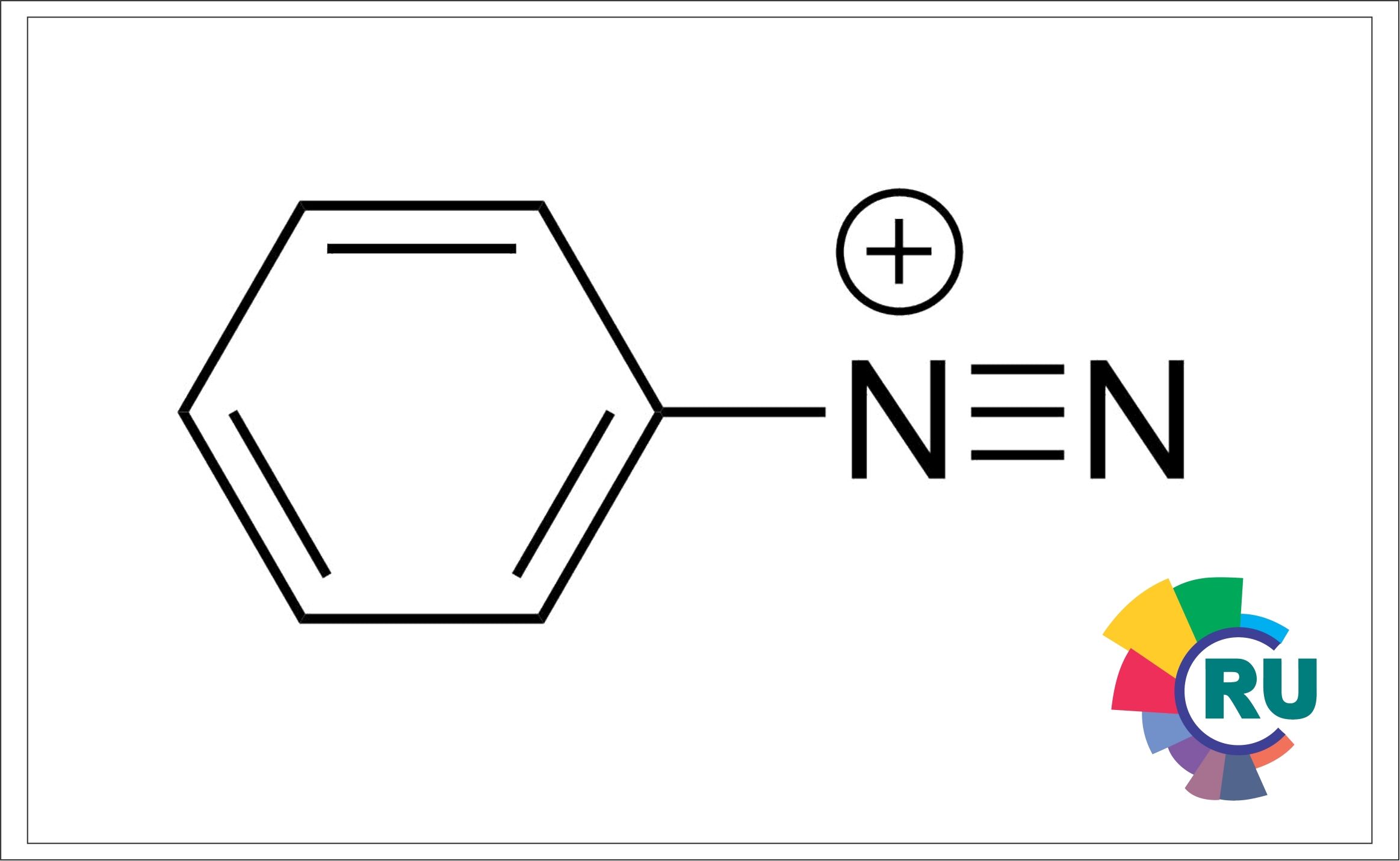
Diazinium colour formers - 1
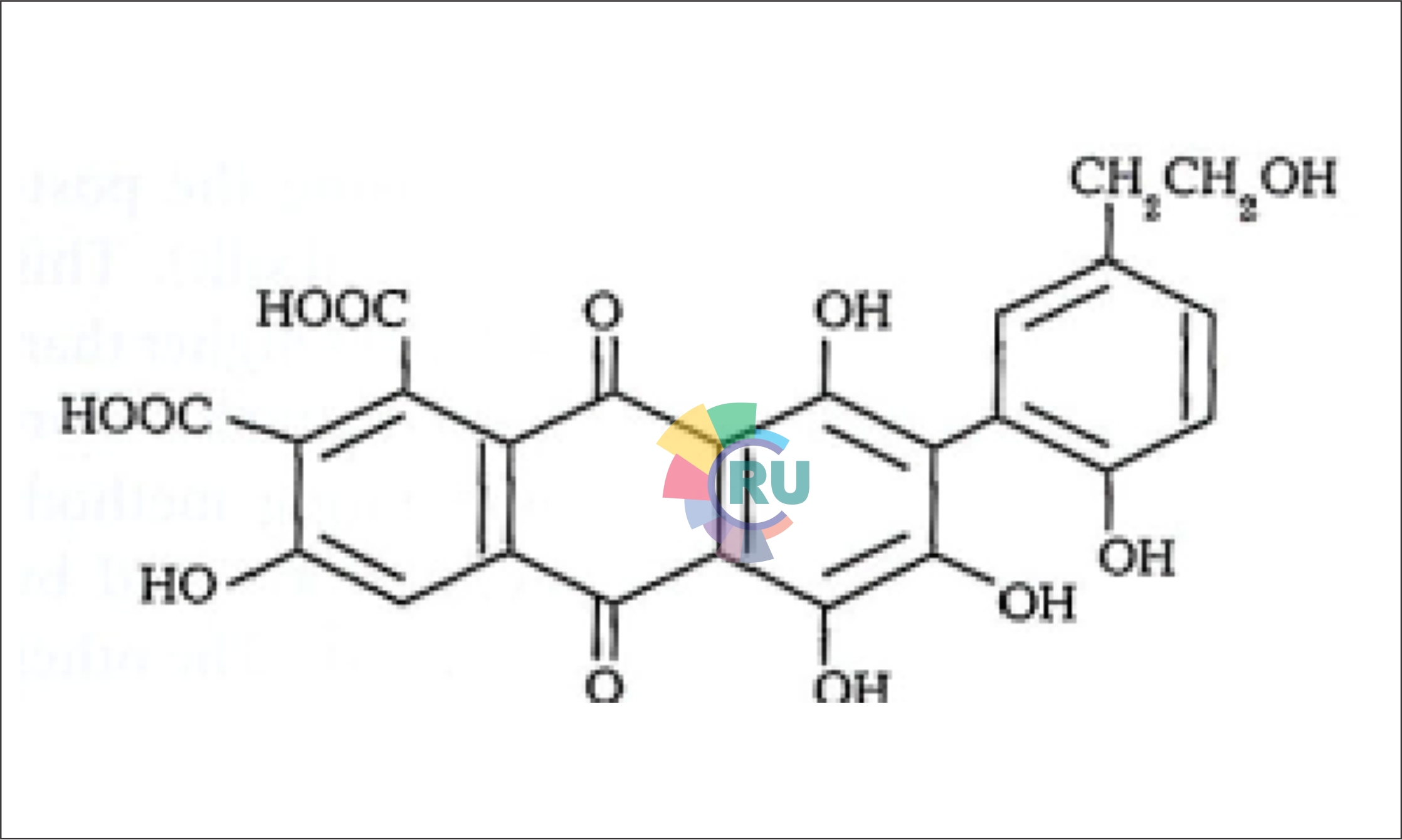
Appropriate dyeing conditions
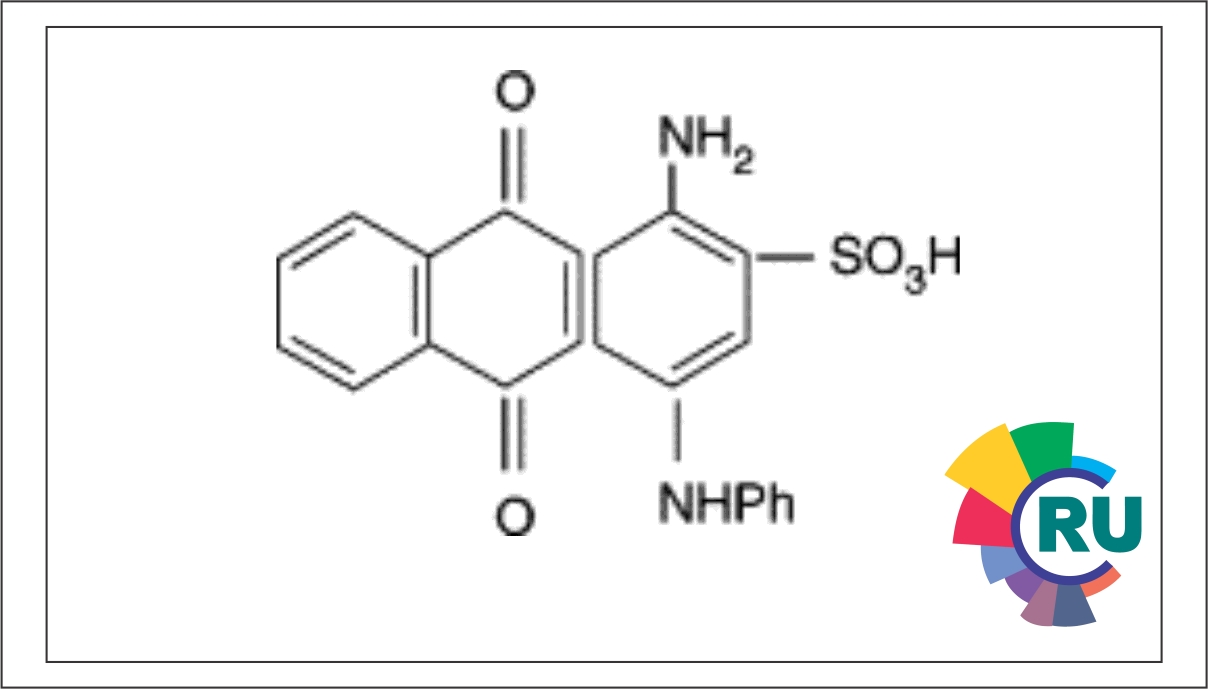
The Ciba reactive dye ranges
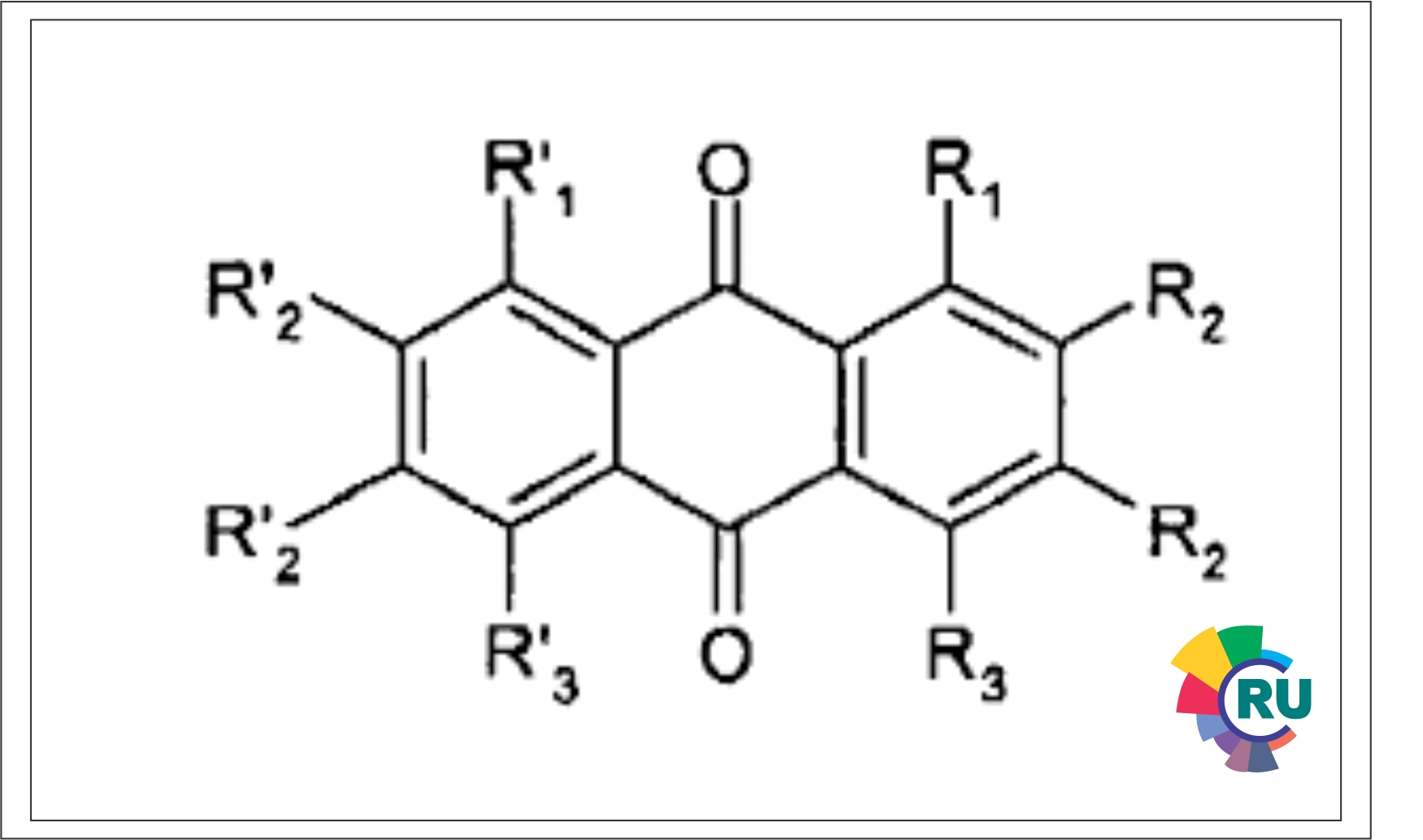
Direct anthraquinone dyes
Semi-continuous methods fall into two broad catego
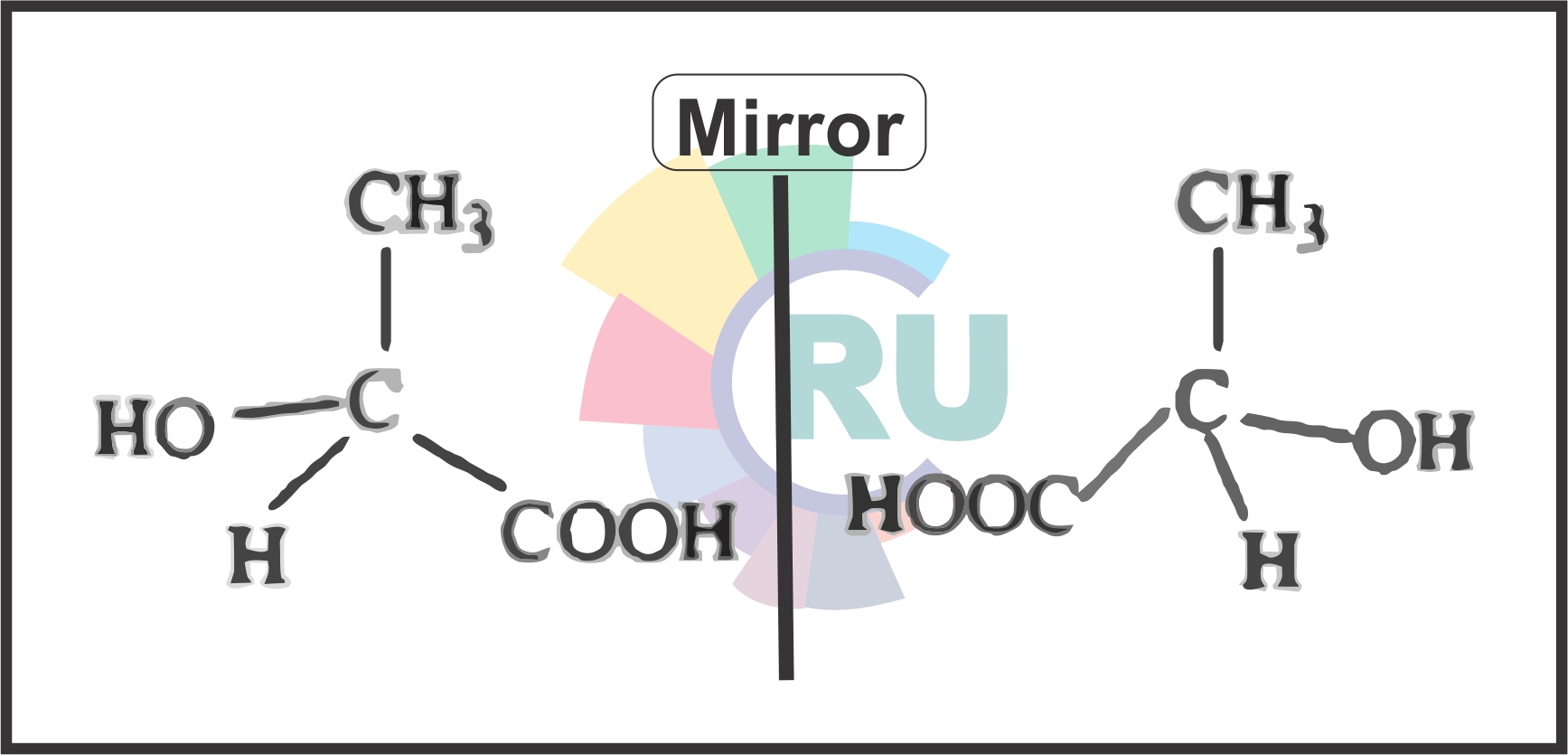
Lactic acid CH3-CH-COOH ½ OH
Adipatic acid (HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH)
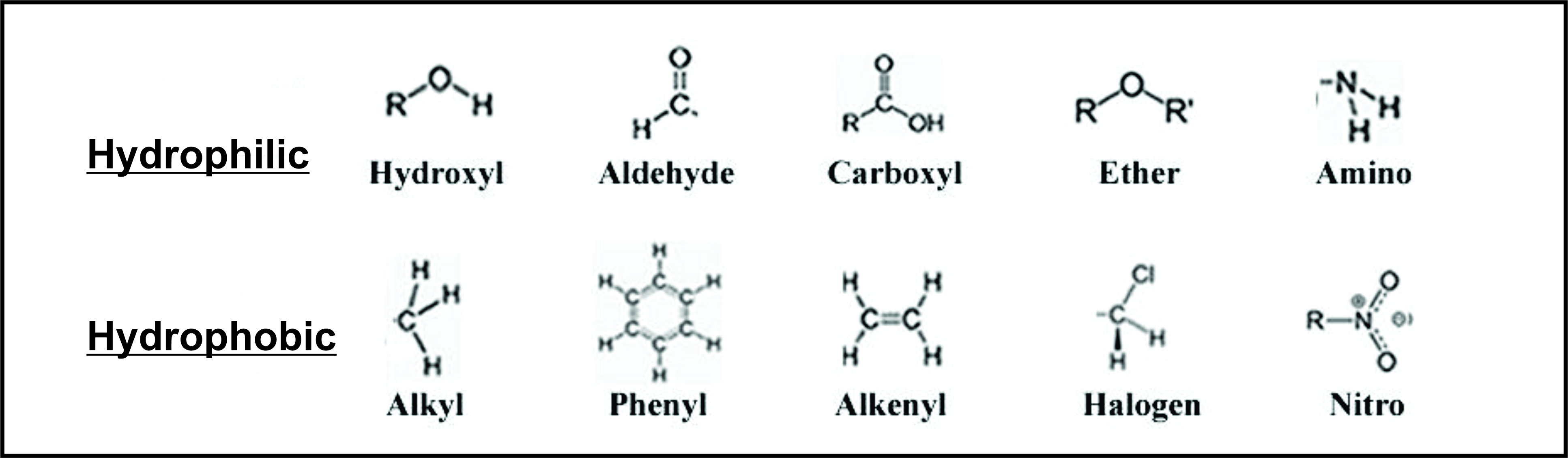
Hydrophobic Rest Hydrophilic Group:-

The Versatility of Polyester
Bicarboxylic Acids:- Explained in brief
Bicarboxylic and Hydroxycarboxylic Acids
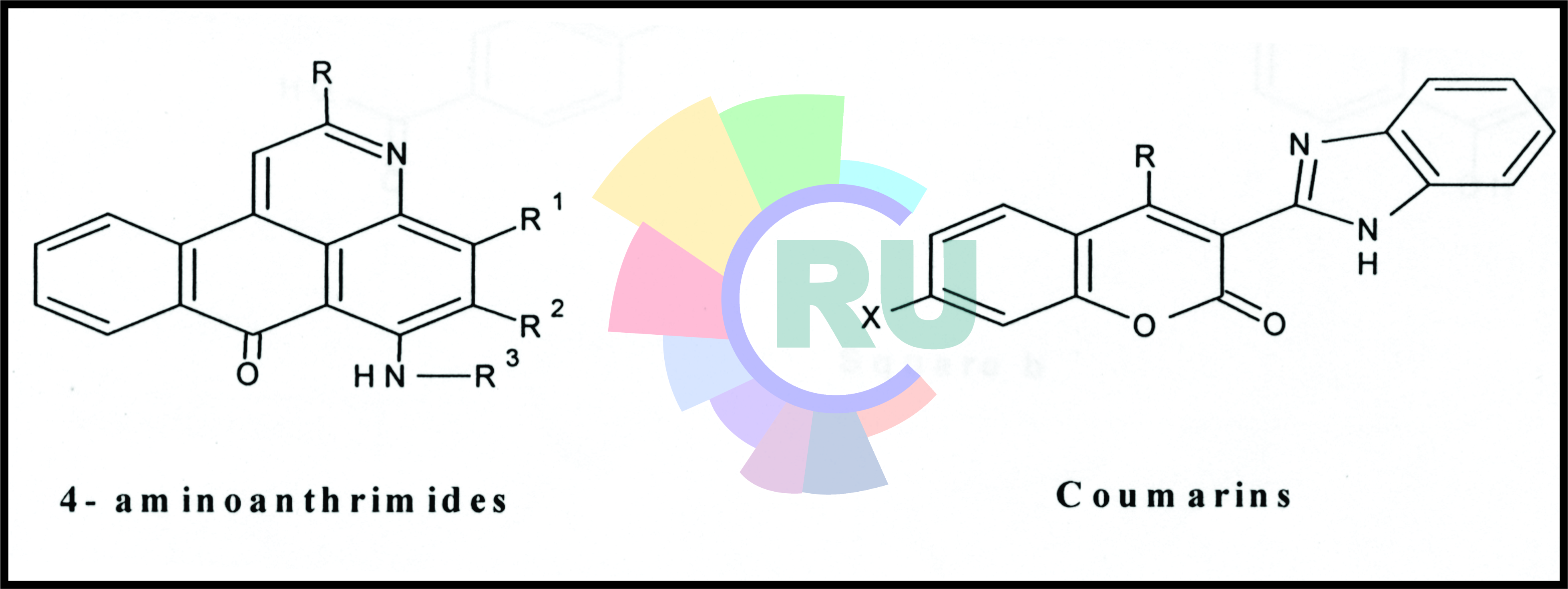
Coumarin and Antrimides Dyes
The Versatility of Polyester:-
Automotives:- Explained in brief
Structure of the Molecule and its Reactions:-
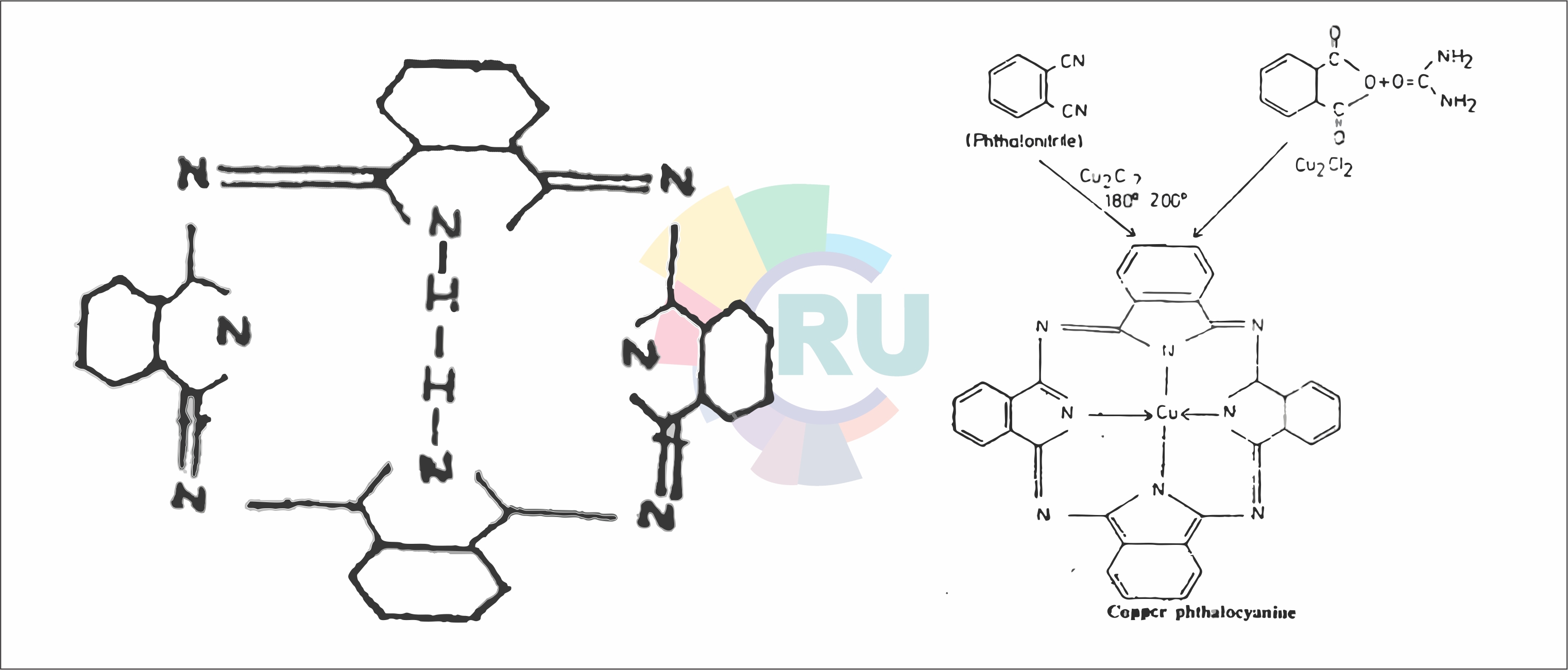
Phthalocyanine dyes and pigments:-