Q-switch dyes:- Explained in brief
by : ---
Q-switch dyes:-
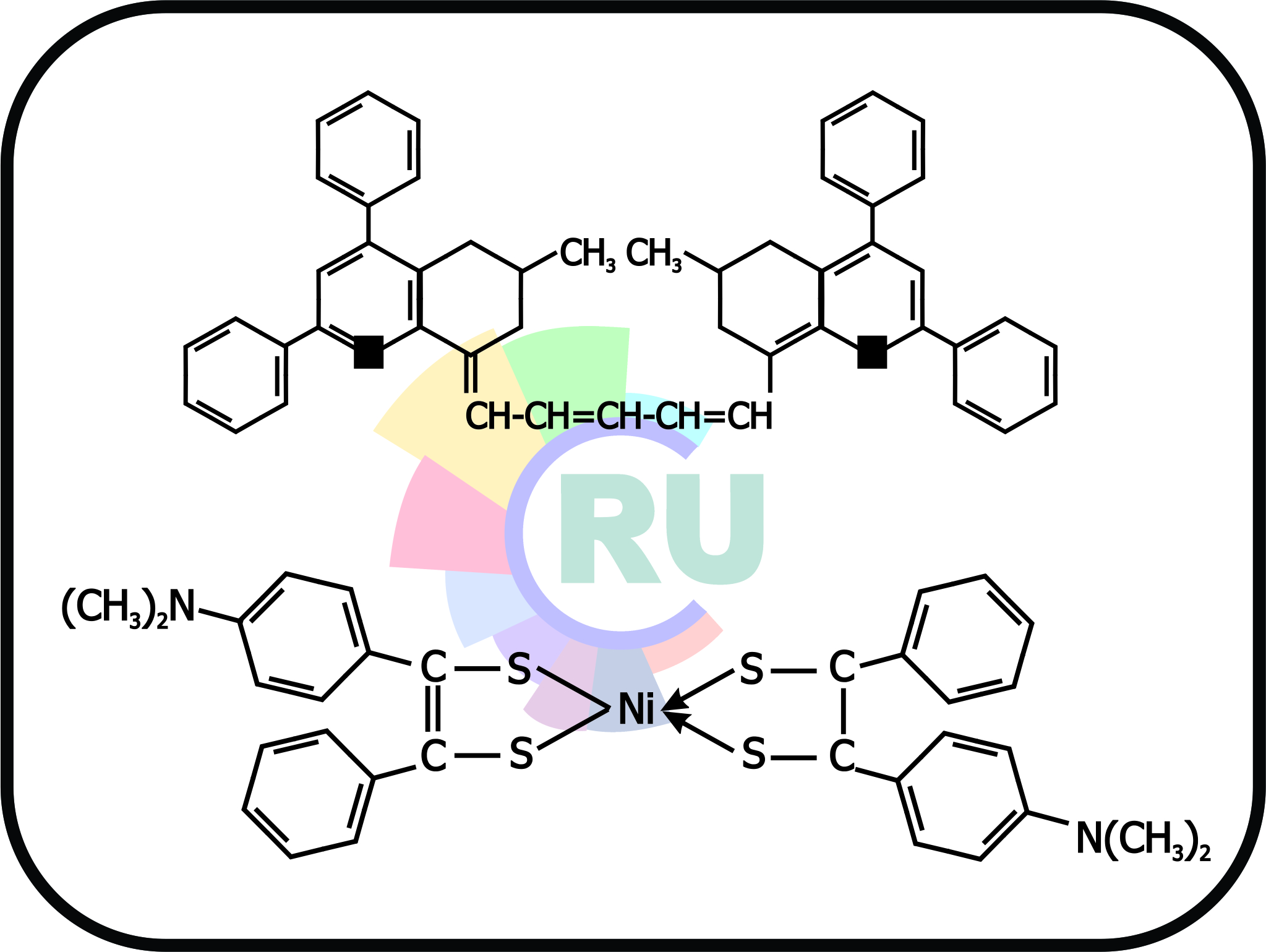
A later development in laser technology is the use of Q-switch dye cells to improve the energy output of mainly solid state lasers. The term Q-refers to the quality factor of a laser cavity. By including in the cavity of a solid-state ruby or Nd:YAG laser [88] a cell containing a solution of a Q-switch dye or saturable absorber, a sudden release of energy as a pulse of laser light can result. The position of such a cell is shown at A Figure 5. At low intensities of light impinging on the cell, the absorbance of the dye solution is constant, but, as the intensity builds up, the absorption coefficient begins to drop sharply and the solution within the cell becomes increasingly transparent. Thus the dye cell acts as a shutter, blocking the light path to the left-hand mirror and opening up the light path when the light reaches a high energy level. Dye Q-switching is mostly limited to pulsed solid-state ruby lasers with stimulated emission at 694 nm, and Nd:YAG with an emission at 1060 nm. Consequently, to act as a Q-switch, the dye must have an absorption peak at approx, one of these wavelengths. Compounds suitable for the Nd:glass laser emitting at 1060 nm are the dye (13) absorbing at 1045 nm and the nickel complex.
